Audience
Cable
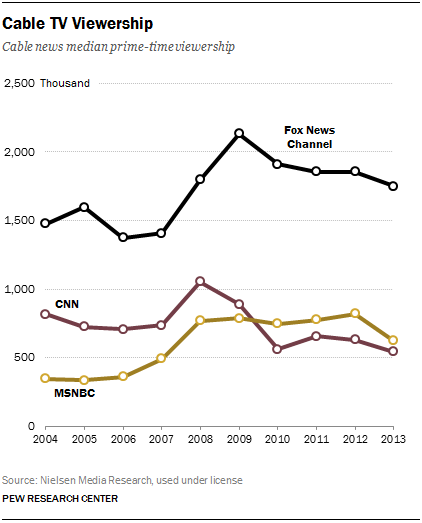
In 2013, the cable news audience, by nearly all measures, declined. The combined median prime-time viewership of the three major news channels—CNN, Fox News and MSNBC—dropped 11% to about 3 million, the smallest it has been since 2007. The Nielsen Media Research data show that the biggest decline came at MSNBC, which lost nearly a quarter (24%) of its prime-time audience. CNN, under new management, ended its fourth year in third place, with a 13% decline in prime time. Fox, while down 6%, still drew more viewers (1.75 million) than its two competitors combined (619,500 at MSNBC and 543,000 at CNN).
The daytime audience for cable news was more stable, holding flat at about 2 million viewers across the three news channels. CNN (up 12%) and Fox (up 2%) actually experienced growth here. That was counterbalanced by more deep loses at MSNBC (down 15.5%).
Local TV
After years in decline, local television news showed new signs of life in 2013. Viewership increased in every key time slot. Local morning news (5 to 7 a.m. Eastern Time or equivalent) gained 6.3%, early evening newscasts followed with a 3.3% increase and late night news programs were flat (up 0.1%). This follows declines every year across all time slots from 2008 to 2012, with the exception of a small uptick in 2011. The jump in viewership in the key timeslots was due largely to significant increases in the November sweeps period when morning news was up 12%, early evening grew by 8% and late night increased by 6%.
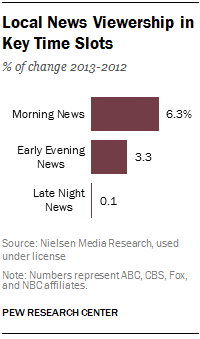
The 2013 picture was more mixed for Fox broadcast affiliates. Morning newscasts gained 9% more audience on average, continuing the steady growth of previous years. However, late-night viewership continued to decline, although the loss in 2013 was small, just 1.2%. Over the past six years, these programs have lost more than 25% of their viewers, while one of the worst performing traditional time slots, the 11 p.m. newscasts, have lost 17.3% since 2007.
Local news in nontraditional time slots are expanding their audience. The nontraditional early-morning news slots continued to grow. At 4:30 a.m., viewership increased 13% to 2.9 million. Viewership at 4 a.m. increased by 21% on average, to 257,000, following a 19% increase in 2012. Newscasts at midday and following the network news at 7 p.m. added viewers after having lost audience the year before. Midday newscasts saw a 5% increase of their audience and viewership also grew 2% for 7 p.m. newscasts. Though audiences in these time slots are growing, the programs attract far fewer viewers than some of the most popular hours for local TV. Late-night news programs, for instance, averaged 24.3 million viewers in 2013.
Network
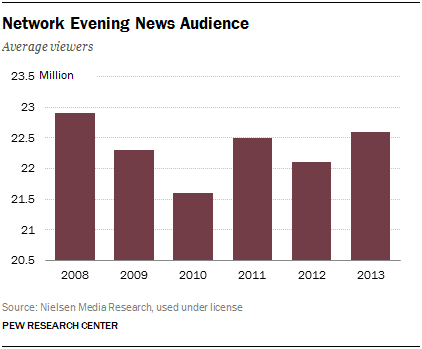
In the evening, an average of 22.6 million viewers tuned into one of the three commercial broadcast news programs on ABC, CBS or NBC, a 2.3% increase over the average viewership for 2012, according to Pew Research analysis of Nielsen Media Research data. The ABC World News increased 2.2% to 7.7 million viewers on average and CBS Evening News increased 6.5% to 6.5 million viewers. NBC Nightly News, the ratings leader, was the only evening news program to decrease, dipping 0.7% to 8.4 million viewers on average.
Morning news saw a 6.7% increase in average viewership compared with 2012, to 13.4 million. For years, NBC’s Today show led in viewership and ratings, but ABC’s Good Morning America took the throne in 2012 and grew its margin of victory in 2013. ABC’s Good Morning America increased 11% to 5.5 million viewers on average, CBS This Morning increased 17.9% to 3.2 million viewers and NBC’s Today show decreased 3.7% to 4.7 million.
Newspapers
Newspapers increased their total circulation by 3% daily and 1.6% Sunday, according to an analysis by the Newspaper Association of America’s John Murray. But that result is influenced by liberalized reporting rules by the Association for Audited Media and includes both paying visitors to digital platforms and distribution of Sunday insert packages to nonsubscribers.
Print now accounts for only 71.2% of daily circulation and 74.9% of Sunday, according to Murray. And Murray’s analysis of 15 of the largest newspapers shows that those papers now have just 54.9% of their total circulation in print.
News Magazines
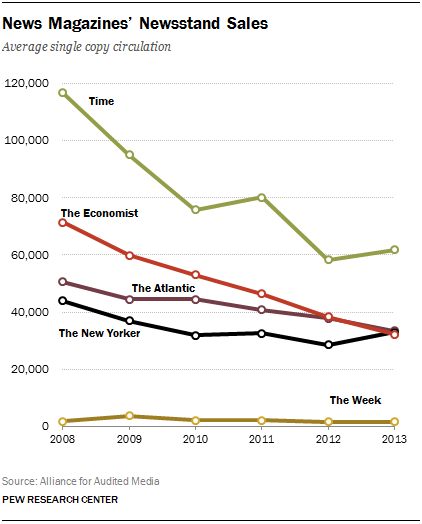
According to the Alliance for Audited Media, sales of newsstand copies for news magazines, the measure most accepted by the industry, fell 2% on average, following years of declining numbers. In 2013, though, the decrease was smaller than the total industry decline in newsstand sales (11%). The Economist was the hardest hit, losing 16% of its newsstand sales, after a 17% decline in 2012. The Atlantic and The Week were also hit (down 12% and 7% respectively). The New Yorker enjoyed a 16% increase, one of the highest reported in past years. Time posted some significant gains too, up 6% from the year before. Since 2008, when Pew Research started tracking these figures, the news magazines have lost 43% of their single-copy sales on average.
Subscriptions were flat, as they have been in years past. But these are normally kept from declining through discounts or special offers.
Audio
Traditional radio continues to reach the vast majority of Americans 12 and older, 91% in 2013 (roughly unchanged from 2012), but online listening is where the growth is. According to Edison Media research, fully 33% of Americans reported listening to online radio “in the last week” in 2013, up from 29% in 2013. In addition, online radio listening in cars (long a stronghold of AM/FM radio) rose to 21%, from 17% in 2012.
Another form of nontraditional radio, podcasting, has largely leveled off. The number of Americans who have “ever” listened to an audio podcast was down slightly from 29% in 2012 to 27% in 2013.
The other main non-AM/FM audio platform, satellite radio, saw moderate growth in subscribers in 2013. By the end of 2013, Sirius XM had 25.6 million subscribers in the U.S., up from 23.9 million at year end 2012.
Alternative Weeklies
Circulation for the top 20 alternative weekly newspapers declined again in 2013, but at a slower pace than in previous years: 6% in 2013, compared to 8% in 2012.
Digital
The vast majority of Americans now get news in some digital format. In 2013, 82% of Americans said they got news on a desktop or laptop and 54% said they got news on a mobile device. Beyond that, 35% reported that they get news in this way “frequently” on their desktop or laptop, and 21% on a mobile device (cellphone or tablet).
Digital Natives
Commercial
While commercial digital native sites remain a relatively small part of the economics of the news industry, their digital audience figures compete with those of much larger legacy news organizations. In April, May, and June of 2013, for example The Huffington Post averaged 45 million unique monthly visitors, putting it second only to Yahoo among the top news sites. Buzzfeed.com also fared well with 17 million monthly unique visitors, putting it at roughly the same as The Washington Post with 19 million monthly unique visitors.
Nonprofit
Audiences of noncommercial digital native news organizations vary widely and can be hard to determine because of syndication and partnership arrangements with other news outlets. On the national level, for example, ProPublica, an investigative journalism nonprofit site founded in 2007, had 544,799 unique visitors to its site in October 2012, according to a Knight Foundation report. While that is a 176% increase over October 2010, it probably misses a fair amount as the organization syndicates its content to various news organizations.
There are also regionally oriented outlets like the New England Center for Investigative Reporting with far fewer visitors per month: 2,362 unique visitors in October 2012, according to self-reported data in the Knight report. Still, that was up 87% from October 2010.
At the local level, MinnPost attracted 268,955 unique visitors in October 2012, according to the report, while The Lens, which focuses on New Orleans and Gulf Coast news, reported just 20,177 unique visitors in October 2012 (though again a huge increase – 375% – over October 2010). The variation in these data speaks to both the diversity in the scope of noncommercial digital start-ups as well as the degree to which collaboration and syndicated content may mean that site visits is not the best way to assess total audience.
Economics
Cable
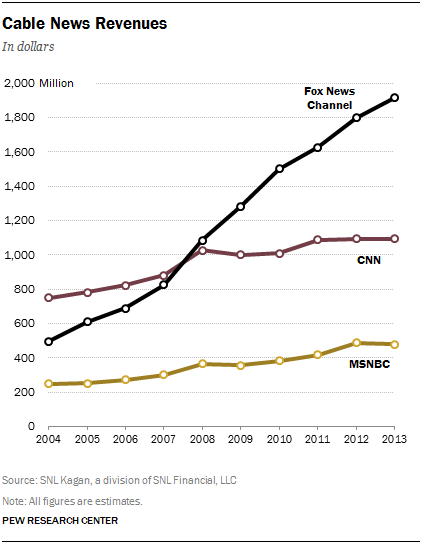
The year 2013 was a relatively weak one for economic growth among the cable news outlets. Fox News was projected to increase its total revenue, according to research firm SNL Kagan, by 5% to $1.89 billion. CNN was projected to increase just 2% to $1.11 billion, and MSNBC was projected to decline by 2% to $475 million. Both CNN and MSNBC experienced advertising revenue losses year over year.
Revenue from license fees, which cable channels charge to providers in exchange for the right to carry their programming, continued to grow in 2013, according to projections, becoming a larger part of the revenue pie for the news channels. For CNN, license fee revenue now accounts for 64% of its total intake. For Fox, it is 58%. And for MSNBC, it makes up 51% of total revenue.
Local TV
Local TV stations make the vast majority of their revenue from on-air advertising, which typically follows a cyclical pattern of increases in election years and decrease in non-election years. In 2013, total local TV ad revenue was expected to decline 2.5% from election-year 2012, according to BIA/Kelsey, amounting to $19.7 billion. But this is less of a decline than in 2011, when advertising revenues dropped by about 8% from the year before, and in 2009, when the decline was 22%.
To calculate ad revenue going just to news-producing stations (i.e. stations that include news programming,) we have to go back one year to 2012, the most recent year that BIA has final station-level data. For that year, news-producing stations took in $17.3 billion in total ad revenue, compared with $20.2 billion in the industry over all.
This year, Pew Research also estimated what portion of the $17.3 billion in ad revenues at these news-producing stations is connected to the news programming. Local TV news directors, in an annual survey by Bob Papper, attributed 48.6% of 2012 stations’ revenues to news. That would amount to $8.4 billion in all. Other sources of revenues for the local TV industry have been growing. Retransmission payments have been increasing rapidly in the past decade, according to data from the investment firm Veronis Suhler Stevenson. In 2011, the last year for which there were final data, retransmission revenues equaled almost $1.5 billion, more than 70 times higher than they had been in 2003 ($20 million). And VSS projects that revenue will more than double—to about $3.7 billion—by 2016. In 2013 alone, 21st Century Fox— created after the split-up of News Corp. — doubled its retransmission revenues. And Nexstar, which owns 108 local stations, reported a 66% increase in its retransmission fee revenues for the fourth quarter 2013, which now account for about 23% of its total revenues.
Digital revenues for the local TV market were forecast to grow 23% in 2013, following 17% growth the previous year, according to Borrell Associates. But, the typical local TV station makes only about 4% of its total revenue from online and mobile ads, according to Borrell Associates.
Newspapers (updated April 22, 2014)
The Newspaper Association of America has stopped compiling quarterly reports on advertising revenue. According to its annual numbers, which were released in April 2014, overall revenue for newspapers in 2013 was $37.6 billion, a decrease of 2.6% from 2012. Within that total, combined print and digital ad revenue decreased by 7%—to $20.7 billion. While daily and Sunday print ad revenue dropped 8.6%, digital advertising edged up by 1.5%. That is a slowdown from the 3.7% digital ad growth rate in 2012.
The news was better with circulation revenue which was up 3.7% in 2013, slightly lower than the growth rate in 2012, 4.6%. Many companies continue to add digital subscriptions and raise rates for a combination of print and digital access. The biggest paywall gains tend to come in the first year with revenues flattening in following years. Many companies are also building other revenue sources like digital marketing services for local businesses, contract printing or events and newsletters. Direct marketing revenue increased by 2.4% in 2013 while new and other revenue increased 5%, in 2013, according to the NAA, but both only constituted a fraction of the total revenue picture.
News Magazines
For a third year in a row, news magazines faced a difficult print advertising environment. Combined ad pages (considered a better measure than ad revenue) for the five magazines studied in this report were down 13% in 2013, following a decline of 12.5% in 2012, and about three times the rate of decline in 2011, according to the Publishers Information Bureau. Again, hardest hit was The Week, which suffered a 20% drop in ad pages. The Atlantic fell 17%, The Economist 16%, and Time about 11%, while The New Yorker managed to keep its ad pages losses in single digits (7%). For print magazines, the number of ad pages sold across the industry over all was down in 2013 (4.1%), after a steep decline in 2012 (8.2%).
Network TV
According to Kantar Media, ad revenue for network television evening news programs increased 2% in the first three quarters of 2013 to $401 million. ABC’s World News decreased 3% to $130 million, the CBS Evening News saw an 11% increase to $116 million and NBC Nightly News remained steady at $155 million. Revenue for network television morning shows increased 7% in the first three quarters of 2013. At ABC’s Good Morning America revenues increased 12% to $260 million and CBS This Morning fell 2% to $108 million. At NBC’s Today show, revenue increased 6% to $504 million.
Digital
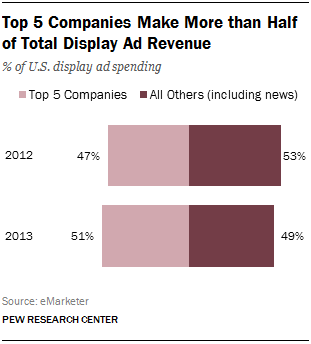
Total digital ad spending rose to $42.6 billion in 2013, a 15.7% increase over 2012. But the bigger news was that display made up almost as much of that total as search (which is not a source of revenue for news organizations.) In 2013 display ads accounted for about 42% of the total, or $17.7 billion, according to eMarketer, and are projected to outpace search by 2015.
While the ascent of display is a good thing for news organizations, the dominance of large tech companies remains an issue. In 2012 the top five display advertising companies made 47% of all display ad revenue on the web; in 2013 that proportion increased to 51%. And while Google had been on top, Facebook overtook the search giant in 2013, taking in 17.9% of all display ad revenue to Google’s 16.9%.
Commercial
Much of the for-profit digital news landscape is occupied by private or unincorporated concerns that do not disclose detailed financial figures. But based on publicly available estimates and reports, Pew Research analysts identified a minimum of roughly $500 million in annual ad revenue from a range of digital news sites. Even that estimate does not include outlets that had been identified, but for whom no revenue estimates were found. That $500 million figure would account for roughly 1% of all known news ad revenue across U.S. media sectors. While the actual figure is almost certainly higher, even if it were doubled, it would still account for a small fraction of all news revenue in the U.S.
Nonprofit
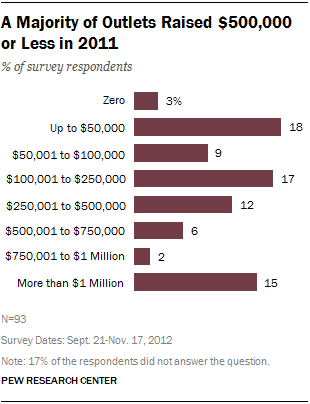
About one-fifth of nonprofits (21%) surveyed by the Pew Research Center in 2012 said they generated $50,000 or less in annual revenue in 2011, the latest year for which data were available, and 26% took in between $50,001 and $250,000. Foundations have been prominent sources of funding, particularly in the form of start-up grants. For many outlets, this initial funding has been difficult to replace. Nearly two-thirds of the survey respondents (61%) began with a start-up grant that accounted for at least one-third of their original funding, and a majority of those grants were for $100,000 or more. Yet less than a third of those outlets had the funding renewed. As with the audience for digital native noncommercial sites, discussed above, the economics for these sites also vary, but a 2013 report by the Pew Research Center finds on average total income is quite small and heavily reliant on foundations.
Audio
Traditional AM/FM radio remains heavily reliant on “spot” advertising (ads aired during radio broadcasts) for its revenue, which saw virtually no year-over-year change in the third quarter of 2013 (the most current data available) compared with the third quarter of 2012. Digital and off-air advertising saw increases of 15% and 3% respectively, but is just a drop in the network advertising bucket.
Sirius XM, the only satellite radio provider in the U.S., grew its revenue in 2013 as well. In 2013, Sirius XM had $3.8 billion in revenue, up from $3.4 billion in 2012, an 11.7% increase. This follows several years of growth in subscriber revenue after the merger of the two companies (Sirius and XM) in 2007.
News Investment
Local TV
Staffing levels in the local TV sector were expected to be stable in 2013, according to the yearly Hofstra University survey. A majority of news directors expected no change in staff size in 2013, while just a third said they anticipated adding more staff, about the same as the year before. And only 2.5% said they expected to have to cut staff, fewer than the year before.
The average amount of weekday local TV news programming declined by six minutes in 2012, the last year for which data exist, to five hours and 24 minutes, according to the same survey. This follows four straight years of increases in the hours of news, but still puts the average hours at 5.4 in 2012, up 46% from what is was in 2003 (3.7 hours). And weekend programming continued to add time: up 11% on Saturday and 6% on Sunday on average.
One area seeing more news is in the very early 4:30 a.m. time slot. The number of stations airing news at 4:30 a.m. increased 11% in 2013 to 271, up from 245 in 2012, according to Nielsen data. Those stations cut across 120 markets, up from 113 in 2012.
Cable
Under Jeff Zucker, CNN, already a sizable global news operation, was projected to increase its spending more than either Fox or MSNBC in 2013. SNL Kagan estimated that CNN would grow its news investment by 11% to $757 million in 2013, compared to Fox’s increase of 4% (to $848.5 million) and MSNBC’s scale-back by 4% (to $272 million).
CNN still maintains by far the largest bureau system among the three major news channels with 33 around the world, though the organization laid off at least 40 journalists in late 2013 and lists one fewer domestic bureau than it had the previous year. (Fox lists two fewer bureaus than it did a year earlier, and no updated information was available from NBC News.)
Newspapers
During 2012, the most recent year for which figures are available, full-time professional newsroom employment at newspaper organizations fell by 2,600 jobs, or 6.4%. The total of 38,000 jobs is down 33.2% from its 1989 peak of 56,900, according to the annual census of the American Society of News Editors. Most of that loss was in the last six years. When the organization’s census for 2013 is released, more job losses are likely.
According to various sources, including media accounts, several major companies eliminated hundreds of newspaper jobs in 2013—including two companies that began investing more heavily in local television stations. Gannett is estimated to have cut about 400 newspaper jobs while the Tribune Co. announced about 700 cuts, not all of them in the newsroom. Media reports put newsroom layoffs at The Plain Dealer in Cleveland at about 50 and at The Oregonian in Portland at about 35 in 2013.
In one eye-catching cutback, The Chicago Sun-Times laid off its entire 28-person photography department in 2013, but hired back four photographers in December. Even Aaron Kushner, a California publisher who attracted considerable attention for hiring scores of journalists and investing heavily in print journalism, implemented about 70 layoffs at The Orange County Register and The Press-Enterprise in Riverside early in 2014.
Digital Native
Commercial
One of the noteworthy developments in 2013 (and early 2014) was the growth of editorial jobs in the expanding world of big commercial digital native news outlets. Rapidly growing Buzzfeed added approximately 170 editorial jobs last year, Gawker’s editorial staff grew to 132, almost double what it was two years earlier. Mashable lured former New York Times editor Jim Roberts to oversee its robust investment in news coverage while Yahoo News hired several high profile Times journalists to build up its original content. Henry Blodget’s Business Insider hired 15 new people to grow its editorial staff to 70. The founder of eBay, Pierre Omidyar, is building its growing staff at the fledgling First Look Media around Glenn Greenwald, while Ezra Klein’s Project X at Vox Media is signing up former Washington Post staffers at a brisk clip. Vice Media, which has expanded from a Montreal punk magazine to a worldwide news operation, now has more than 1,100 total global employees (that includes all staff positions), and as of the deadline for this report, had hired nearly 50 U.S. new employees in 2014 alone.
Not all of the news was good. AOL’s network of Patch hyperlocal sites at one time employed about 1,000 reporters and editors but that had been cut back to fewer than 100 by early 2014, signaling the failure of the most ambitious effort to create a universe of digital community news sites under one roof.
News Magazines
In January 2013, Time magazine cut six positions as part of broader wave of layoffs (500 jobs) at Time Inc., the publishing division that houses Time magazine. Those cuts were part of a mandate from Time Warner CEO Jeff Bewkes to shave $100 million from the publishing division’s annual costs. In late 2013, soon after Nancy Gibbs replaced Rick Stengel as Time’s managing editor (becoming the first women to hold that position), Time announced 11 new hires and three promotions. However, in February 2014 Time Inc. proceeded with another round of reductions, reportedly 500 jobs, as part of a restructuring plan to spin off from its parent company, Time Warner.
Audio
News in traditional radio is a hard category to define, one measure being the number of stations that carry news content only. While the number of all-news radio stations in the U.S. remains small, 37 in 2012, according to the latest data available, that number was unchanged from 2011.
Ownership
Local TV
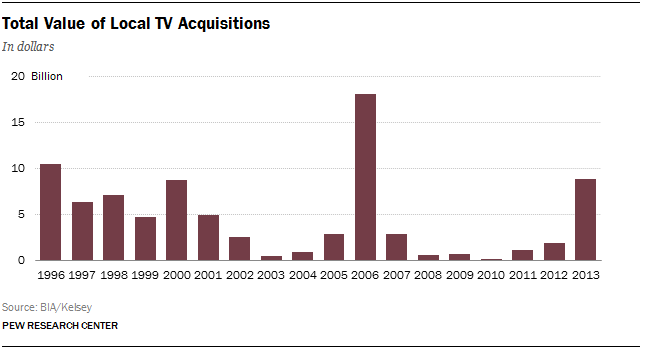
Local TV station sales exploded in 2013. Nearly 300 TV stations were sold, up 205% from 2012, according to BIA/Kelsey. Likewise, the total value of these transactions was up, a 367% increase in 2013 from 2012, reaching $8.8 billion.
Sinclair, which already owned more local stations than any other company, purchased 63 more in 2013, the most notable of which were seven stations from Allbritton Communications and 22 from Fisher Communications. Sinclair now operates 167 television stations in 77 markets. The Tribune Co. acquired Local TV Holdings for $2.73 billion (a total of 19 stations) and Gannett purchased Belo, adding 17 stations, in a $2.2 billion transaction. BIA/Kelsey attributes this growth to strong political advertising revenues from the previous year, retransmission consent revenues and continued historically low interest rates.
Network
The only major development in the ownership and executive level positions at the three network news divisions in 2013 was the joint venture between Disney/ABC with Univision to create a new cable channel, Fusion. They each own 50% of the channel.
Cable
A process that began in 2012 was completed in mid-2013 when News Corp.—parent of Fox News Channel and Fox Business Network—formally spit in two. The movie and TV division containing the news channels was renamed Twenty-First Century Fox Inc. with Rupert Murdoch continuing as chief executive.
In August of 2013, Qatar-based Al Jazeera Media Network launched a new channel aimed squarely at U.S. audiences—Al Jazeera America. It occupies the same space on the dial held by Current TV.
Newspapers
Within days in August of 2013, two venerable newspapers changed hands. Multi-millionaire and Red Sox owner John Henry bought The Boston Globe and another Massachusetts newspaper, The Worchester Telegram & Gazette, from The New York Times for $70 million. And, Amazon CEO Jeff Bezos acquired The Washington Post for $250 million. In other transactions, Warren Buffett’s Berkshire Hathaway acquired several more newspapers, The News & Record in Greensboro, N.C., and Tulsa World, among them. A. H. Belo sold one its four newspapers – The Press-Enterprise in Riverside, Calif., and plans to sell The Providence Journal in Rhode Island. That will leave just its flagship Dallas Morning News and the nearby Denton Record-Chronicle. Tribune Co., on the other hand, pulled eight of its papers off the market in 2013, after failing to fetch an attractive offer. Tribune now plans to spin them off into a separate company.
Commercial Digital Natives
Unlike other sectors studied here most commercial digital native sites are privately held companies and in 2013 saw little movement. One notable development, though, was AOL’s dropping of the hyperlocal news network Patch. Patch was founded by AOL CEO Tim Armstrong in 2007, at first independent of AOL but then acquired by it in 2009.
In 2009 and 2010, AOL hired 900 employees, Armstrong said, with half of them going to Patch. By early 2011, Patch sites were up and running in about 800 cities and towns across the U.S. Despite this aggressive growth, and plans being made to hire for 1,000 Patch sites by the end of 2011, Armstrong drew back, saying in early 2012, “We don’t have a massive number of Patches on a run-rate profitability, and some of them have bounced in and bounced out.”
Despite the early growth at Patch and investment by AOL the company’s business model quickly came under criticism. In May, 2012 Starboard Value (an investment firm that owned 5.3% of Patch at the time) released a report calling Patch’s business model unsustainable. The report offered some rare estimates of Patch’s finances, which showed that the company had lost $147 million in 2011 and only brought in $13 million in advertising revenue.
Over the course of 2013, Patch suffered more losses. In August 2013 AOL announced the closing of 400 of the 900 Patch sites that existed at the time. Finally, in early 2014, AOL dropped Patch entirely and sold majority ownership of the remaining sites to Hale Global.
News Magazines
In March 2013, Time Warner announced that it would spin off Time Inc. into a separate publicly traded company. In March of 2014, these plans seem to be in full effect as Time Inc. prepares to separate from Time Warner. In the meantime, Time Inc. has been integrating American Express Publishing, which it bought last year.


