Majorities of teens credit social media with strengthening their friendships and providing support while also noting the emotionally charged side of these platforms

Pew Research Center conducted this study to better understand the experiences American teens are having with social media. For this analysis, we surveyed 1,316 U.S. teens. The survey was conducted online by Ipsos from April 14 to May 4, 2022.
This research was reviewed and approved by an external institutional review board (IRB), Advarra, which is an independent committee of experts that specializes in helping to protect the rights of research participants.
Ipsos recruited the teens via their parents who were a part of its KnowledgePanel, a probability-based web panel recruited primarily through national, random sampling of residential addresses. The survey is weighted to be representative of U.S. teens ages 13 to 17 who live with parents by age, gender, race, ethnicity, household income and other categories.
This report also includes quotes from teen focus groups. Pew Research Center worked with PSB Insights to conduct four live, online focus groups with a total of 16 U.S. 13- to 17-year-olds. The focus groups were conducted Jan. 12-13, 2022.
Here are the questions used for this report, along with responses. Here is the survey methodology and the focus groups methodology.
Society has long fretted about technology’s impact on youth. But unlike radio and television, the hyperconnected nature of social media has led to new anxieties, including worries that these platforms may be negatively impacting teenagers’ mental health. Just this year, the White House announced plans to combat potential harms teens may face when using social media.
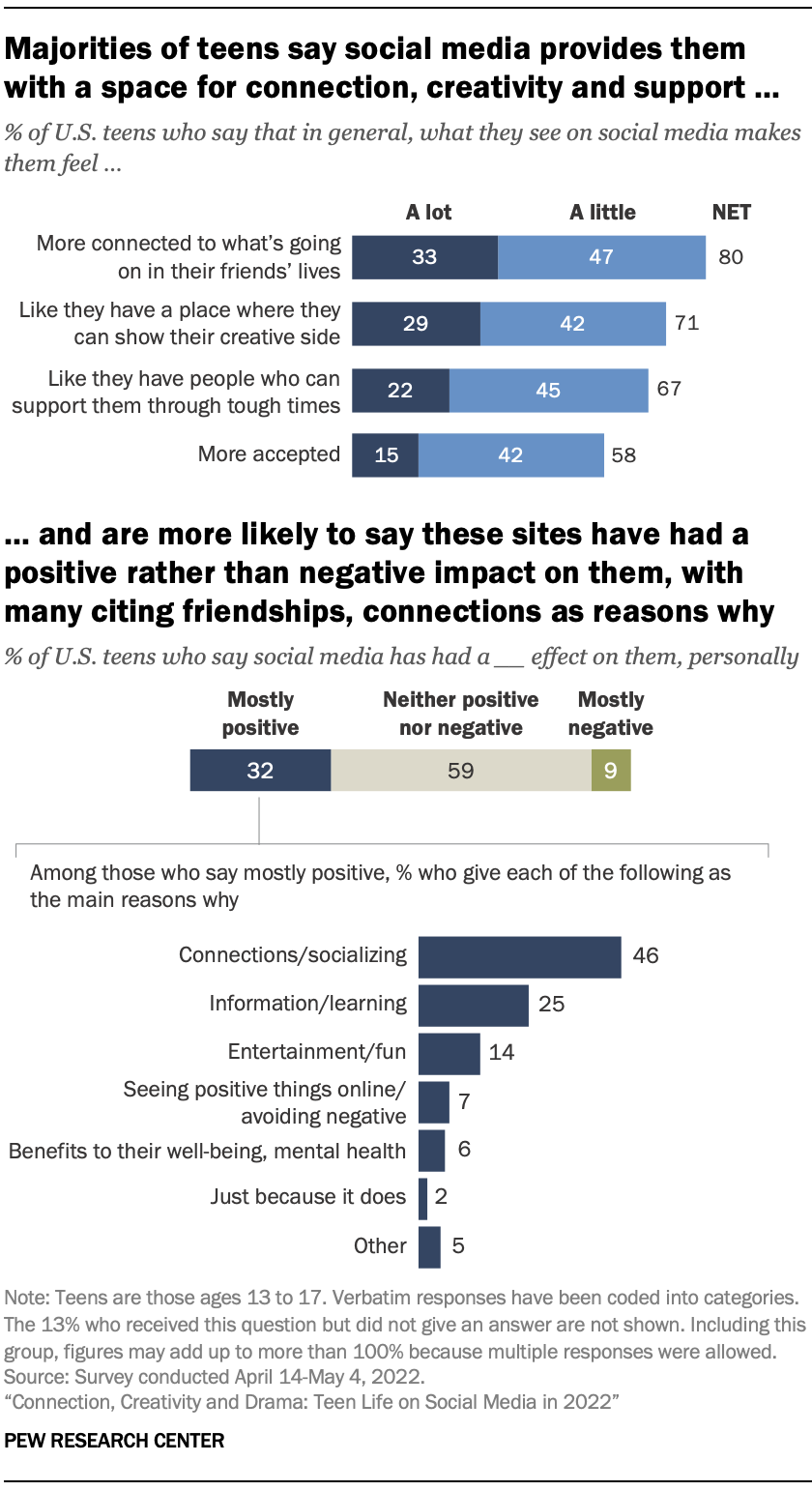
Despite these concerns, teens themselves paint a more nuanced picture of adolescent life on social media. It is one in which majorities credit these platforms with deepening connections and providing a support network when they need it, while smaller – though notable – shares acknowledge the drama and pressures that can come along with using social media, according to a Pew Research Center survey of U.S. teens ages 13 to 17 conducted April 14 to May 4, 2022.1
Eight-in-ten teens say that what they see on social media makes them feel more connected to what’s going on in their friends’ lives, while 71% say it makes them feel like they have a place where they can show their creative side. And 67% say these platforms make them feel as if they have people who can support them through tough times. A smaller share – though still a majority – say the same for feeling more accepted. These positive sentiments are expressed by teens across demographic groups.
When asked about the overall impact of social media on them personally, more teens say its effect has been mostly positive (32%) than say it has been mostly negative (9%). The largest share describes its impact in neutral terms: 59% believe social media has had neither a positive nor a negative effect on them. For teens who view social media’s effect on them as mostly positive, many describe maintaining friendships, building connections, or accessing information as main reasons they feel this way, with one teen saying:
“It connects me with the world, provides an outlet to learn things I otherwise wouldn’t have access to, and allows me to discover and explore interests.” – Teen girl
While these youth describe the benefits they get from social media, this positivity is not unanimous. Indeed, 38% of teens say they feel overwhelmed by all the drama they see on social media, while about three-in-ten say these platforms have made them feel like their friends are leaving them out of things (31%) or have felt pressure to post content that will get lots of likes or comments (29%). Another 23% say these platforms make them feel worse about their own life.
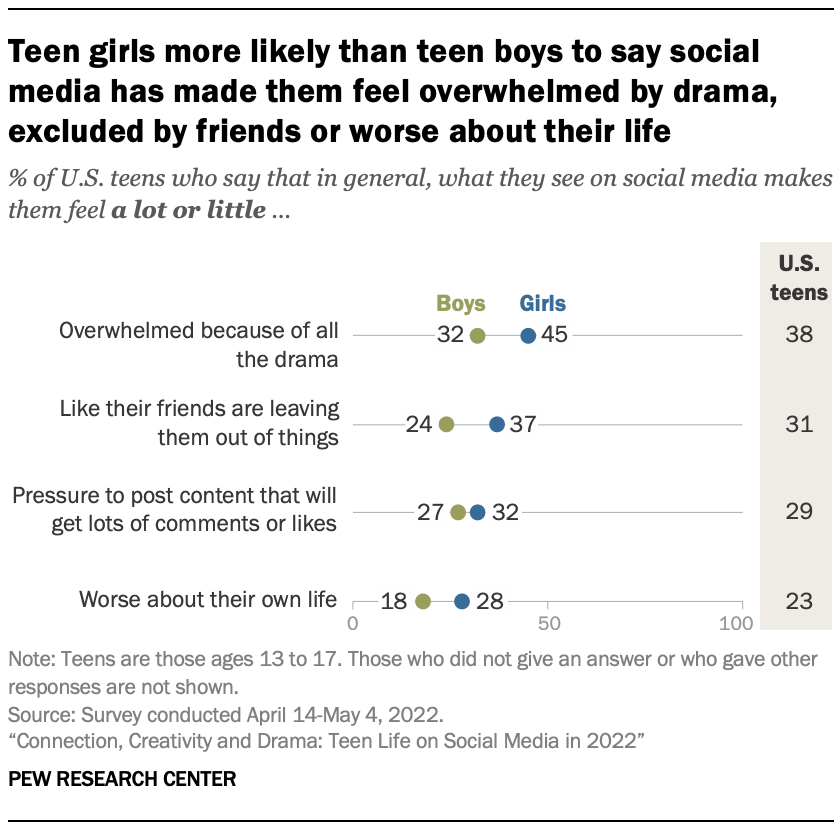
Teen girls report encountering some of these pressures at higher rates. Some 45% of girls say they feel overwhelmed because of all the drama on social media, compared with 32% of boys. Girls are also more likely than boys to say social media has made them feel like their friends are leaving them out of things (37% vs. 24%) or worse about their own lives (28% vs. 18%).
When asked how often they decide not to post on social media out of fear of it being using against them, older teen girls stand out. For example, half of 15- to 17-year-old girls say they often or sometimes decide not to post something on social media because they worry others might use it to embarrass them, compared with smaller shares of younger girls or boys.
These are some of the key findings from a Pew Research Center online survey of 1,316 U.S. teens conducted from April 14 to May 4, 2022.
Teens are more likely to view social media as having a negative effect on others than themselves
The strong presence of social media in many teenagers’ lives begs the question: What impact, if any, are these sites having on today’s youth?
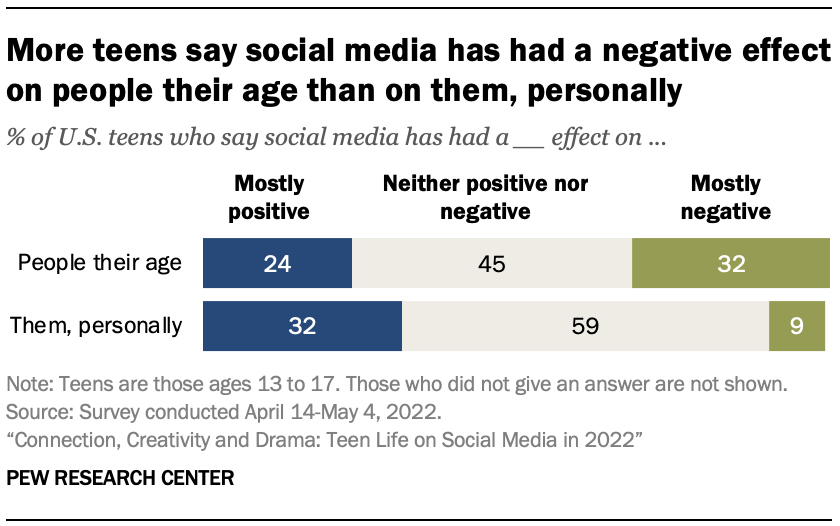
Even as teens tend to view the impact of social media on their own lives in more positive than negative terms, they are more critical of its influence on their peers. While 9% of teens think social media has had a mostly negative effect on them personally, that share rises to 32% when the same question is framed about people their age.
There are also gaps when looking at the positive side of these platforms. Some 32% of teens say social media has had a positive effect on them personally, compared with a smaller share (24%) who say the same about these platforms’ impact on teens more broadly.
Still, regardless of whether teens are assessing social media’s impact on themselves or others, the most common way they describe its effect is as neither positive nor negative.
Teens reflect on parents’ concerns and assessments of teen life on social media
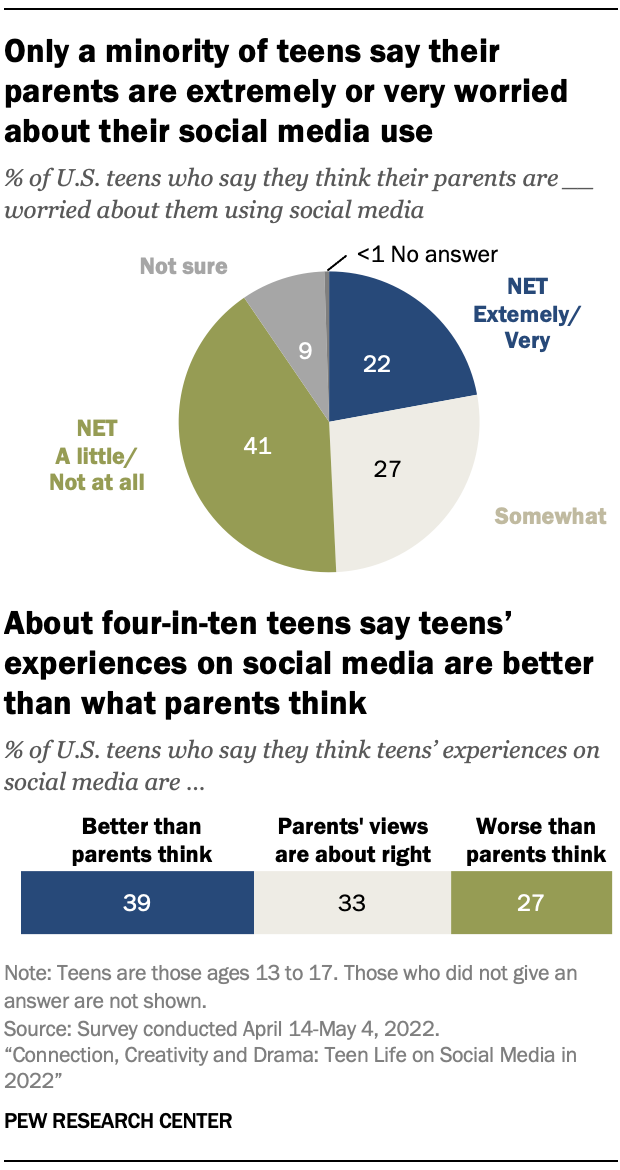
Parents are often on the front lines in navigating challenges their children may face when using social media. While previous Center surveys reflect parents’ anxieties about social media, only a minority of teens in this survey describe their parents as being highly concerned about their use of these sites.
Some 22% believe their parents are extremely or very worried about them using social media, while another 27% say their parents are somewhat worried. However, many teens – 41% – say their parents are worried only a little or not at all. And 9% say they aren’t sure about the level of concern their parents have over their social media use. These youth also weighed in on whether parents overall – not just their own – have an accurate picture of what it’s like to be a teenager on social media. Some 39% say teens’ experiences are better than parents think, while 27% say things on social media are worse for teens than parents think. Still, one-third believe parents’ assessments are about right.
Teens who have a more positive outlook about social media are more likely to say these platforms benefit them
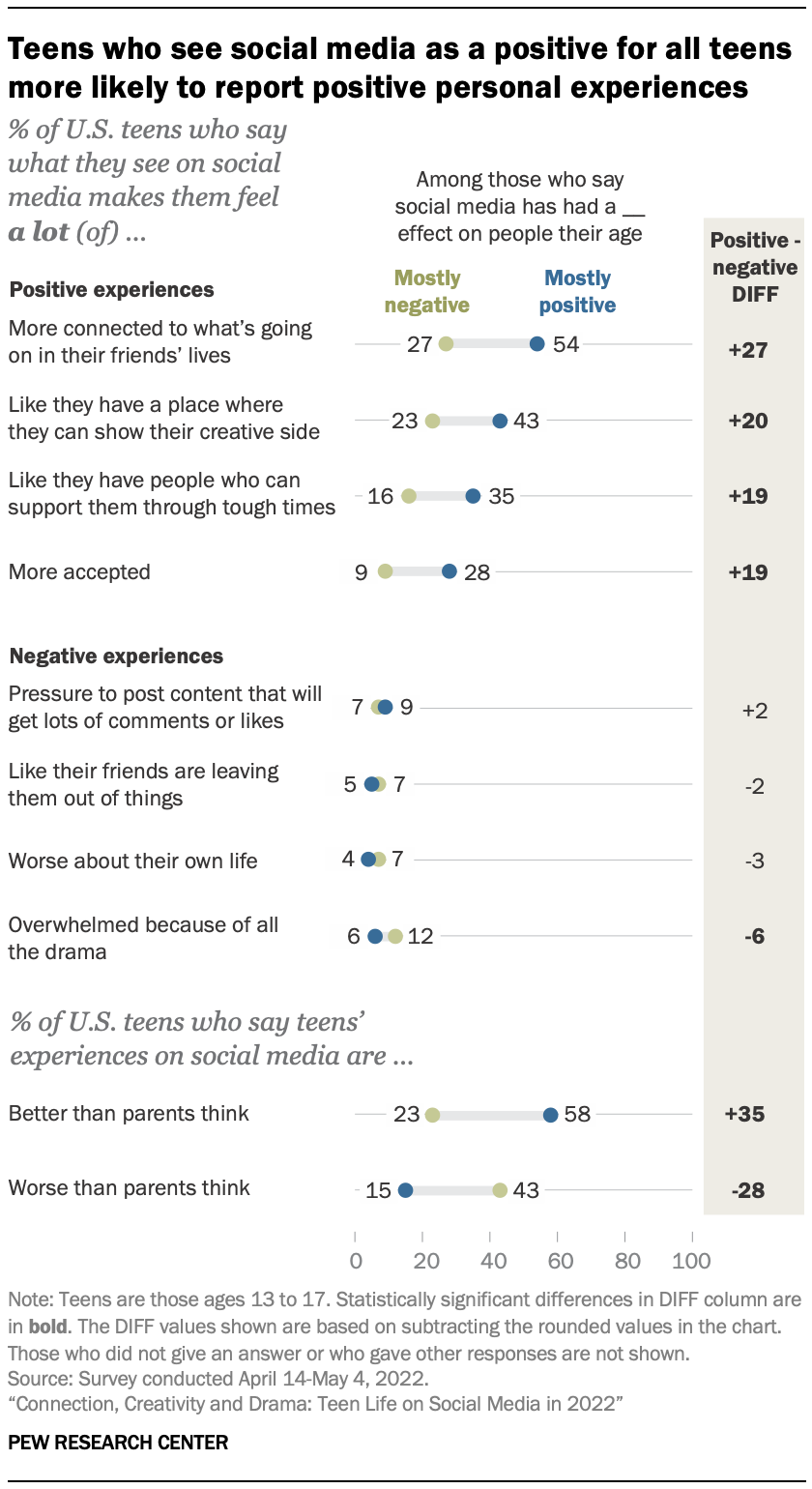
Teens who see social media as having a mostly positive effect on people their age are more likely than teens who see mostly negative effects to say teens’ experiences on social media are better than parents think. They are also more likely to say they have had positive experiences while personally using these platforms.
Whether teens see social media’s effects as positive or negative relates to their perspective on whether parents’ views stack up to reality. About six-in-ten teens who say that social media has had a mostly positive effect on people their age say teens’ experiences on social media are better than parents think, while a plurality of teens who say social media has been mostly negative for people their age say teens’ experiences on social media are worse than parents think.
Teens who have a more positive view of social media’s effect on their peers report more positive personal experiences with these platforms. More than half (54%) of teens who see social media as having a mostly positive effect on people their age say that what they see on social media makes them feel a lot more connected to what’s going on in their friends’ lives. About four-in-ten say they feel a lot like they have a place where they can show their creative side. Some 35% of teens who see the effect as mostly positive say social media makes them feel a lot like they have people who can support them through tough times, and 28% say it makes them feel a lot more accepted. By comparison, much smaller shares – about or quarter or fewer – of teens who see social media as having a negative effect say what they see on social media makes them feel each of these positive experiences a lot.
While teens who have a positive outlook on the impact of social media are more likely to report personally benefiting from these sites, they tend to say they’ve experienced the more negative side in similar proportions as those who rate these sites’ effect on teens negatively. There is one exception: 12% of teens who believe social media has a mostly negative effect on teens say they feel overwhelmed by all of the drama on these platforms a lot, compared with 6% of those who see its impact as mostly positive.
Online activism is not common on social media among teens; only a minority of teens are highly concerned about digital privacy
Beyond broad measurement of social media, this survey also tackled two popular topics in the debates around social media: online activism and digital privacy.
Only small shares of teens are engaging in online activism on social media, but experiences and views vary by political affiliation
On topics from MAGA to Black Lives Matter, social media platforms have become an important way for people of all ages to share information, mobilize and discuss issues that are important to them.
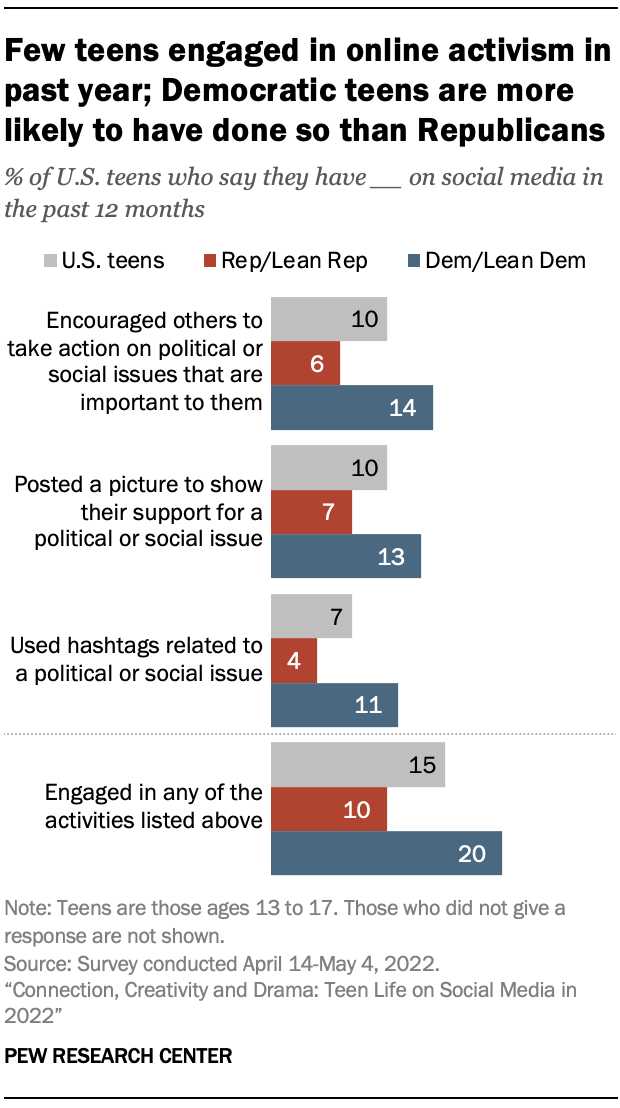
But this survey reveals that only a minority of teens say they have been civically active on social media in the past year via one of the three means asked about at the time of the survey. One-in-ten teens say they have encouraged others to take action on political or social issues that are important to them or have posted a picture to show their support for a political or social issue in the past 12 months. Some 7% say the same about using hashtags related to a political or social cause on social media during this period. Taken together, 15% of teens have engaged in at least one of these activities on social media in the past 12 months.
While majorities of both Democrats and Republicans have not used social media in this way, there are some notable partisan differences among those who engage in activism. For example, 14% of teens who identify as Democrats or who lean toward the Democratic Party say they have used social media to encourage others to take action on political or social issues that are important to them in the past 12 months, compared with 6% of teens who are Republicans or GOP leaners. And larger shares of Democrats than Republicans say they have posted pictures or used hashtags to show support for a political or social issue in the past year. In total, Democratic teens are twice as likely as Republican teens to have engaged in any of these activities during this time (20% vs. 10%).
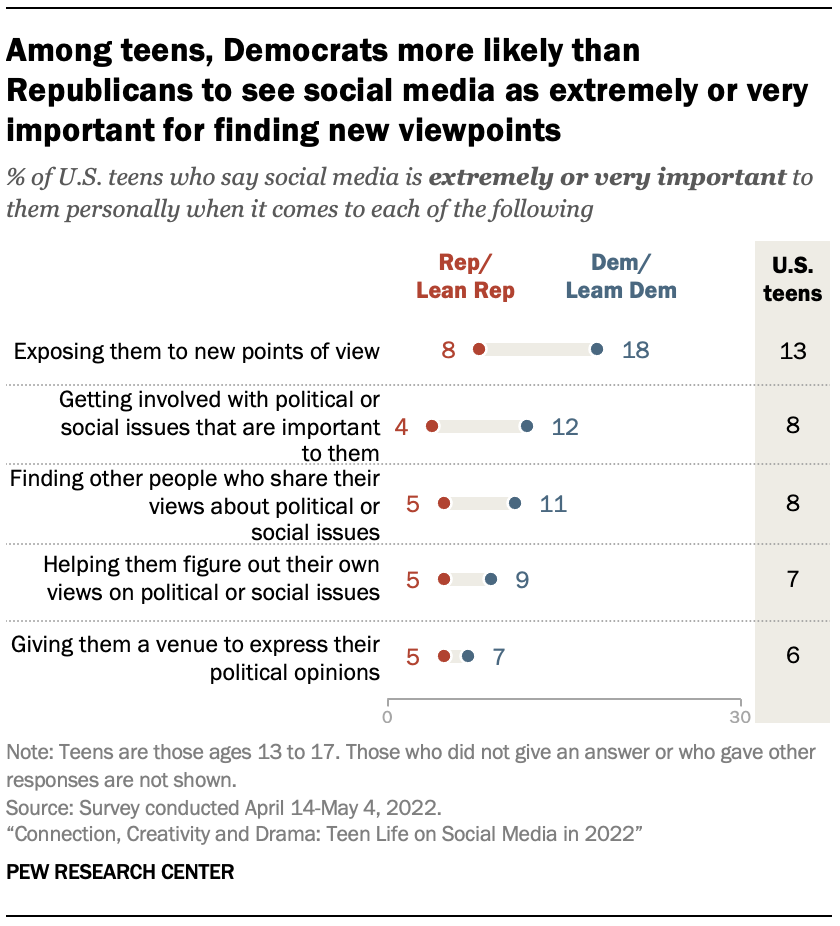
Not only do small shares of teens participate in these types of activities on social media, relatively few say these platforms play a critical role in how they interact with political and social issues.
About one-in-ten or fewer teens say social media is extremely or very important to them personally when it comes to exposing them to new viewpoints, getting involved with issues that are important to them, finding other people who share their views, helping them figure out their own views on an issue or giving them a venue to express their political opinions.
Just as Democratic teens are more likely than Republican teens to engage in these forms of online activism, they also see social media as a more integral tool for civic engagement. For example, 18% of Democratic teens say social media is extremely or very important to them when it comes to exposing them to new points of view, compared with 8% of Republican teens. Democrats are also more likely than Republicans to say these platforms are at least very important to them for getting involved with issues that are important to them, finding others who share their views or helping them figure out their own way of thinking.
And when asked about what people should do more broadly, Democratic teens (22%) are more likely than Republican teens (12%) to say that regardless of whether they engage in online activism themselves, it is very or extremely important for people to speak out about political or social issues on social media.
Teens feel a lack of control over their personal data but aren’t too concerned about social media companies having this information
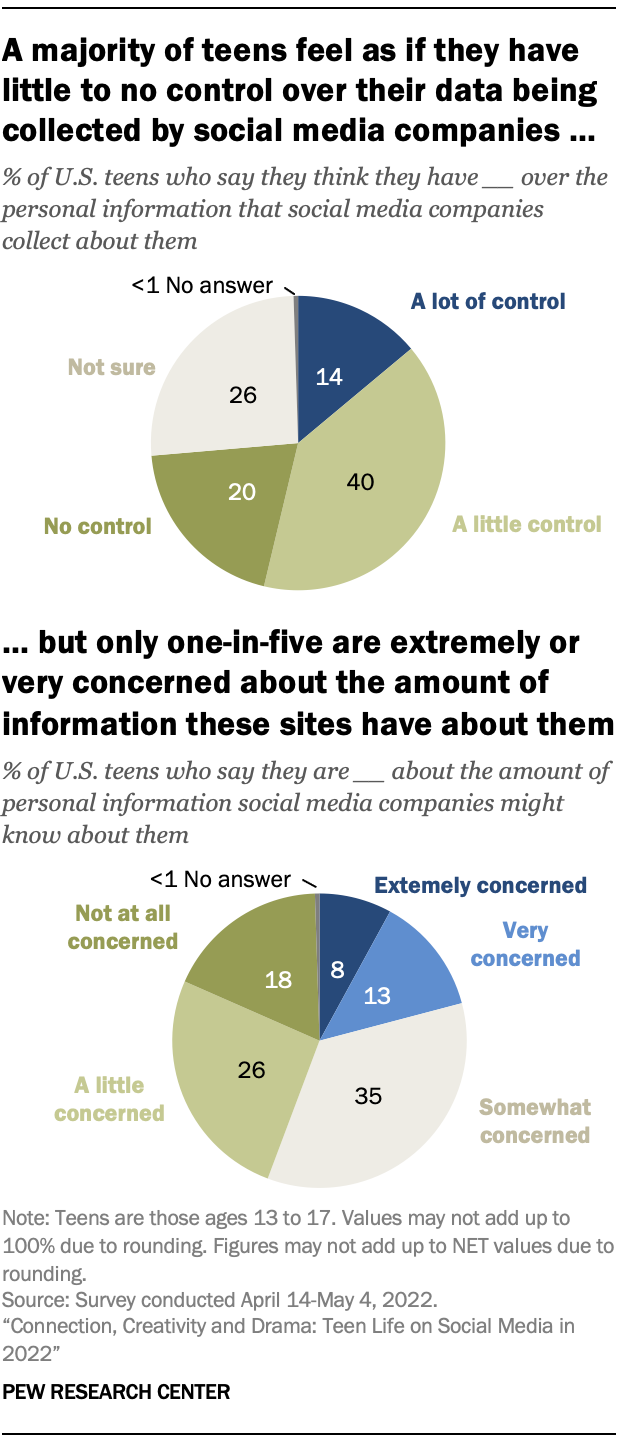
Amid the continued privacy discussions in the media and among policymakers, teens have nuanced views on the topic. Just 14% of teens report feeling a lot of control over the personal information that social media companies collect about them. Meanwhile, 60% of teens feel like they have little to no control. A further 26% say they are not sure how much control they have over companies’ collection of this information.
Despite feeling a lack of control over their data being collected by social media companies, teens are largely unconcerned. A fifth of teens (20%) say they feel very or extremely concerned about the amount of their personal information social media companies might have. Still, a notable segment of teens – 44% – say they have little or no concern about how much these companies might know about them.
In their own words, teens share their thoughts about social media and the challenges and benefits of using it
“TikTok is more of a place to watch videos … then Instagram [is] more to see what my friends are up to and then Snapchat [is] a way of more direct communication.” – Teen girl
To inform and supplement this survey, the Center conducted a series of teen focus groups to better understand how teens were using social media and thinking about topics related to it. These focus groups highlight how nuanced teens’ views on social media truly are.
Teens share how different platforms serve different purposes as they navigate online life and that using these platforms can lead to a variety of emotions and experiences, from anxiety to excitement and from improved social connections to bullying:2
“I’ve liked, especially during the pandemic, being able to communicate with my friends more, since I couldn’t see them in person. And then also, having something to watch to entertain me, which was good, because we were just stuck at home.” – Teen girl
“Okay, for me, it is like bullies or like negative comments or stuff like that, you just see a lot of people hating under the comments, under your posts and stuff like that.” – Teen boy
“During the pandemic, I feel like less people were using social media in certain ways, because there wasn’t much to post, like going out. You’re just staying at home. But TikTok, everyone was on it, because it was their source of entertainment.” – Teen girl
As teens walk us through their perspectives, they also share how the pandemic changed (and didn’t change) their social media habits and what they think their lives would be like if social media disappeared overnight:
“I think it would be a little bit [messed up if social media disappeared]. I spend 99% of my time indoors in front of my computer, if I’m not playing games, I’m watching pirated videos. If I’m not watching videos, maybe I’m reading an article. I’m always online. And I hardly step out of my room. I have had issues with my dad. He said my room is too creepy. I should come outside and play with people but I’m not really good at making friends. So, it’s a bit hard on me.” – Teen boy
“[When] we were younger, [social media] didn’t have an effect on us and social media wasn’t as big as it is now. I feel like we were more free and more happy, and no stress or overthinking or insecure.” – Teen girl
For more quotes and themes from the focus groups, see Chapter 3.


