About the Pew Internet & American Life Project
The Project is a non-profit, non-partisan initiative of the Pew Research Center that is funded by the Pew Charitable Trusts to do research about the social impact of the internet. The Project takes no positions on policy issues. Its reports and data can be found at https://legacy.pewresearch.org/internet/.
December 2006 Tracking Survey
Final Topline, 1/5/07
Data for November 30 – December 30, 2006
Princeton Survey Research Associates International for the Pew Internet & American Life Project
Sample: n = 2,373 adults 18 and older
Interviewing dates: 11.30.06 – 12.30.06
- Margin of error is plus or minus 2 percentage points for results based on total sample [n=2,373]
- Margin of error is plus or minus 3 percentage points for results based on total internet users [n=1,623]
Asked of internet users
WEB1 Please tell me if you ever use the internet to do any of the following things. Do you ever use the internet to…/Did you happen to do this yesterday, or not?2
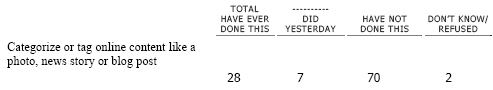
Methodology
This report is based on the findings of a daily tracking survey on Americans’ use of the Internet. The results in this report are based on data from telephone interviews conducted by Princeton Survey Research Associates International between November 30 to December 30, 2006, among a sample of 2,373 adults, 18 and older. For results based on the total sample, one can say with 95% confidence that the error attributable to sampling and other random effects is plus or minus 2.3 percentage points. For results based Internet users (n=1623), the margin of sampling error is plus or minus 2.7 percentage points. In addition to sampling error, question wording and practical difficulties in conducting telephone surveys may introduce some error or bias into the findings of opinion polls.
The sample for this survey is a random digit sample of telephone numbers selected from telephone exchanges in the continental United States. The random digit aspect of the sample is used to avoid “listing” bias and provides representation of both listed and unlisted numbers (including not-yet-listed numbers). The design of the sample achieves this representation by random generation of the last two digits of telephone numbers selected on the basis of their area code, telephone exchange, and bank number.
New sample was released daily and was kept in the field for at least five days. The sample was released in replicates, which are representative subsamples of the larger population. This ensures that complete call procedures were followed for the entire sample. At least 10 attempts were made to complete an interview at sampled households. The calls were staggered over times of day and days of the week to maximize the chances of making contact with a potential respondent. Each household received at least one daytime call in an attempt to find someone at home. In each contacted household, interviewers asked to speak with the youngest male currently at home. If no male was available, interviewers asked to speak with the youngest female at home. This systematic respondent selection technique has been shown to produce samples that closely mirror the population in terms of age and gender. All interviews completed on any given day were considered to be the final sample for that day.
Non-response in telephone interviews produces some known biases in survey-derived estimates because participation tends to vary for different subgroups of the population, and these subgroups are likely to vary also on questions of substantive interest. In order to compensate for these known biases, the sample data are weighted in analysis. The demographic weighting parameters are derived from a special analysis of the most recently available Census Bureau’s March 2006 Annual Social and Economic Supplement. This analysis produces population parameters for the demographic characteristics of adults age 18 or older, living in households that contain a telephone. These parameters are then compared with the sample characteristics to construct sample weights. The weights are derived using an iterative technique that simultaneously balances the distribution of all weighting parameters.
The final response rate is 27 percent.
Appendix: How tagging is done at key sites
Tagging is done somewhat differently at different websites. Here are some links that illustrate more fully how the tagging process is done:
- At Flickr – a photo sharing site: http://flickr.com/learn_more.gne
- At Del.icio.us – a browser bookmarking site: http://del.icio.us/help/tags
- At Technorati – a blog search engine: http://technorati.com/help/tags.html
- At Furl – a browser tool that allows content to be archived and labeled: http://www.furl.net/faq.jsp#howNotBook
- At Yahoo – how tags work in Yahoo’s MyWeb browser feature: http://help.yahoo.com/help/us/ysearch/myweb2/index.html, particularly the section labeled “Tagging, Saving, and Sharing”
- At YouTube – a video-sharing site: http://www.google.com/support/youtube/bin/answer.py?answer=55769&query=tagging&topic=&type=
- A Wikipedia entry on tagging: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tag_%28metadata%29


