What teachers, teens and the U.S. public say about current curriculum debates
Pew Research Center conducted this study to better understand how public K-12 teachers, teens and the American public see topics related to race, sexual orientation and gender identity playing out in the classroom.
The bulk of the analysis in this report is based on an online survey of 2,531 U.S. public K-12 teachers conducted from Oct. 17 to Nov. 14, 2023. The teachers surveyed are members of RAND’s American Teacher Panel, a nationally representative panel of public school K-12 teachers recruited through MDR Education. Survey data is weighted to state and national teacher characteristics to account for differences in sampling and response to ensure they are representative of the target population.
For the questions for the general public, we surveyed 5,029 U.S. adults from Nov. 9 to Nov. 16, 2023. The adults surveyed are members of the Ipsos KnowledgePanel, a nationally representative online survey panel. Panel members are randomly recruited through probability-based sampling, and households are provided with access to the Internet and hardware if needed. To ensure that the results of this survey reflect a balanced cross section of the nation, the data is weighted to match the U.S. adult population by gender, age, education, race and ethnicity and other categories.
For questions for teens, we conducted an online survey of 1,453 U.S. teens from Sept. 26 to Oct. 23, 2023, through Ipsos. Ipsos recruited the teens via their parents, who were part of its KnowledgePanel. The survey was weighted to be representative of U.S. teens ages 13 to 17 who live with their parents by age, gender, race and ethnicity, household income, and other categories. The survey on teens was reviewed and approved by an external institutional review board (IRB), Advarra, an independent committee of experts specializing in helping to protect the rights of research participants.
Here are the questions used for this report, along with responses, and the survey methodology.
Throughout the report, references to White, Black and Asian adults include those who are not Hispanic and identify as only one race. Hispanics are of any race. The views and experiences of teachers and teens who are Asian American or part of other racial and ethnic groups are not analyzed separately in this report due to sample limitations. Data for these groups is incorporated into the general population figures throughout the report.
All references to party affiliation include those who lean toward that party. Republicans include those who identify as Republicans and those who say they lean toward the Republican Party. Democrats include those who identify as Democrats and those who say they lean toward the Democratic Party.
Political leaning of school districts is based on whether the majority of those residing in the school district voted for Republican Donald Trump or Democrat Joe Biden in the 2020 presidential election.
Amid national debates about what schools are teaching, we asked public K-12 teachers, teens and the American public how they see topics related to race, sexual orientation and gender identity playing out in the classroom.
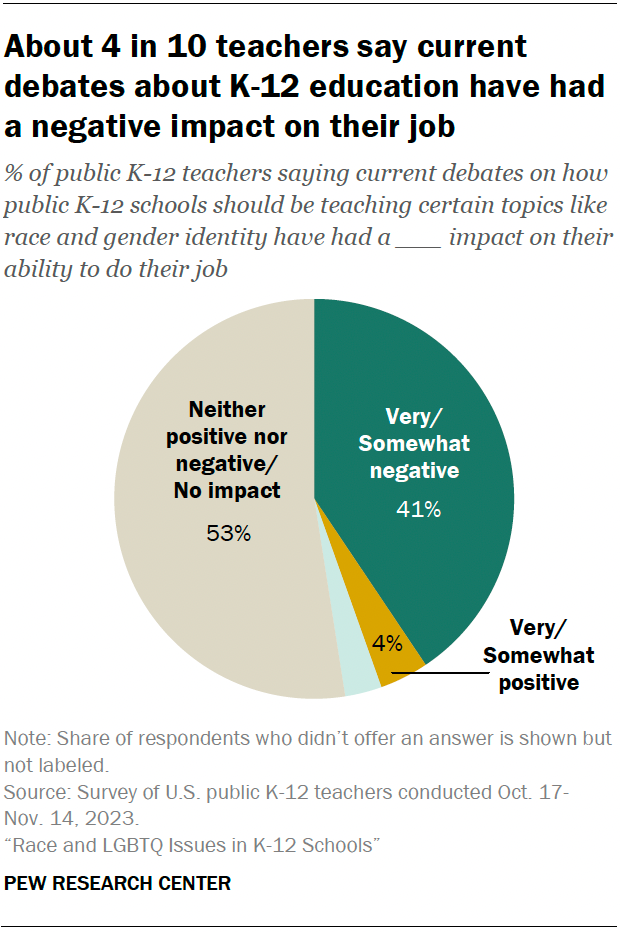
A sizeable share of teachers (41%) say these debates have had a negative impact on their ability to do their job. Just 4% say these debates have had a positive impact, while 53% say the impact has been neither positive nor negative or that these debates have had no impact.
And 71% of teachers say teachers themselves don’t have enough influence over what’s taught in public schools in their area.
In turn, a majority of teachers (58%) say their state government has too much influence over this. And more say the federal government, the local school board and parents have too much influence than say they don’t have enough.
Most of the findings in this report come from a survey of 2,531 U.S. public K-12 teachers conducted Oct. 17-Nov. 14, 2023, using the RAND American Teacher Panel.1 The survey looks at teachers’ views on:
- Race and LGBTQ issues in the classroom (Chapter 1)
- Current debates over what schools should be teaching and the role of key groups (Chapter 2)
It follows a fall 2022 survey of K-12 parents that explored similar topics.
This report also includes some findings from a survey of U.S. teens ages 13 to 17 (Chapter 3) and a survey of U.S. adults (Chapter 4). For details about these surveys, refer to the Methodology section of this report. Among the key findings:
- 38% of teens say they feel comfortable when topics related to racism or racial inequality come up in class (among those who say these topics have come up). A smaller share (29%) say they feel comfortable when topics related to sexual orientation or gender identity come up.
- Among the American public, more say parents should be able to opt their children out of learning about LGBTQ issues than say the same about topics related to race (54% vs. 34%).
What do teachers think students should learn about slavery and gender identity?
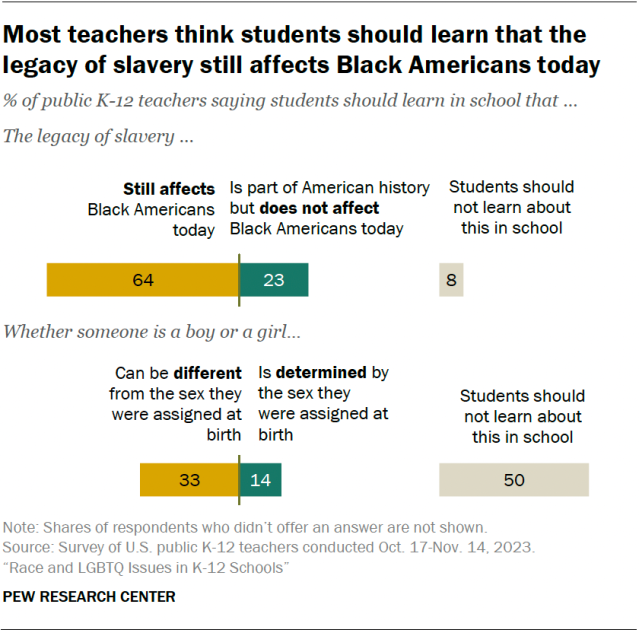
We asked public K-12 teachers what they think students should learn in school about two topics in particular:
- Whether the legacy of slavery still affects the position of Black people in American society today.
- Whether a person’s gender can be different from or is determined by their sex at birth.
For these questions, elementary, middle and high school teachers were asked about elementary, middle and high school students, respectively.
The legacy of slavery
Most teachers (64%) say students should learn that the legacy of slavery still affects the position of Black people in American society today.
About a quarter (23%) say students should learn that slavery is part of American history but no longer affects the position of Black people in American society. Just 8% say students shouldn’t learn about this topic in school at all.
Majorities of elementary, middle and high school teachers say students should learn that the legacy of slavery still has an impact on the lives of Black Americans.
Gender identity
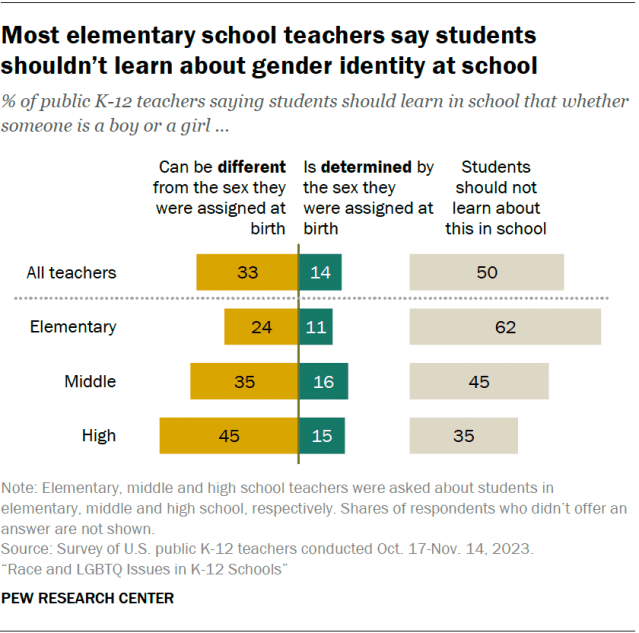
When it comes to teaching about gender identity – specifically whether a person’s gender can be different from or is determined by their sex assigned at birth – half of public K-12 teachers say students shouldn’t learn about this in school.
A third of teachers think students should learn that someone can be a boy or a girl even if that is different from the sex they were assigned at birth.
A smaller share (14%) say students should learn that whether someone is a boy or a girl is determined by their sex at birth.
Views differ among elementary, middle and high school teachers. But teachers across the three levels are more likely to say students should learn that a person’s gender can be different from their sex at birth than to say students should learn gender is determined by sex at birth.
Most elementary school teachers (62%) say students shouldn’t learn about gender identity in school. This is much larger than the shares of middle and high school teachers who say the same (45% and 35%).
What parents and teens say
Parents of K-12 students are more divided on what their children should learn in school about these topics.
In the 2022 survey, 49% of parents said they’d rather their children learn that the legacy of slavery still affects the position of Black people in American society today, while 42% said they’d rather their children learn that slavery no longer affects Black Americans.
When it comes to gender identity, 31% of parents said they’d rather their children learn that gender can be different from sex at birth. An identical share said they would rather their children learn gender is determined by sex at birth. Another 37% of parents said their children shouldn’t learn about gender identity in school.
Teens, like parents, are more divided than teachers on these questions. About half of teens (48%) say they’d rather learn that the legacy of slavery still affects the position of Black Americans today. Four-in-ten would prefer to learn that slavery no longer affects Black Americans.
And teens are about evenly divided when it comes to what they prefer to learn about gender identity. A quarter say they’d rather learn that a person’s gender can be different from their sex at birth; 26% would prefer to learn that gender is determined by sex at birth. About half (48%) say they shouldn’t learn about gender identity in school.
For more on teens’ views about what they prefer to learn in school about each of these topics, read Chapter 3 of this report.
Should parents be able to opt their children out of learning about certain topics?
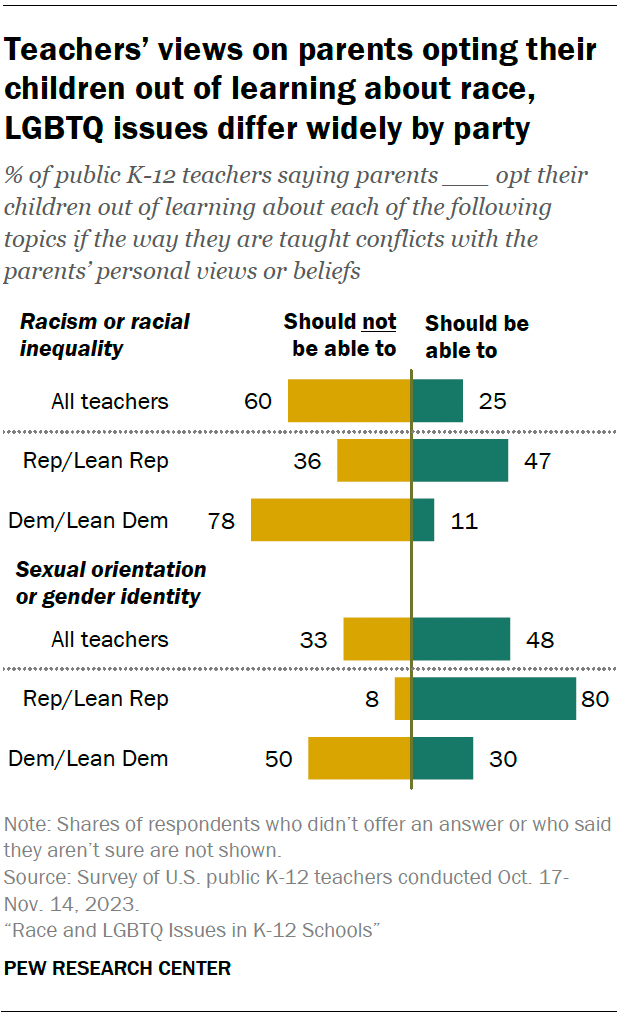
Most public K-12 teachers (60%) say parents should not be able to opt their children out of learning about racism or racial inequality in school, even if the way these topics are taught conflicts with the parents’ beliefs. A quarter say parents should be able to opt their children out of learning about these topics.
In contrast, more say parents should be able to opt their children out of learning about sexual orientation or gender identity (48%) than say parents should not be able to do this (33%).
On topics related to both race and LGBTQ issues, elementary and middle school teachers are more likely than high school teachers to say parents should be able to opt their children out.
How teachers’ views compare with the public’s views
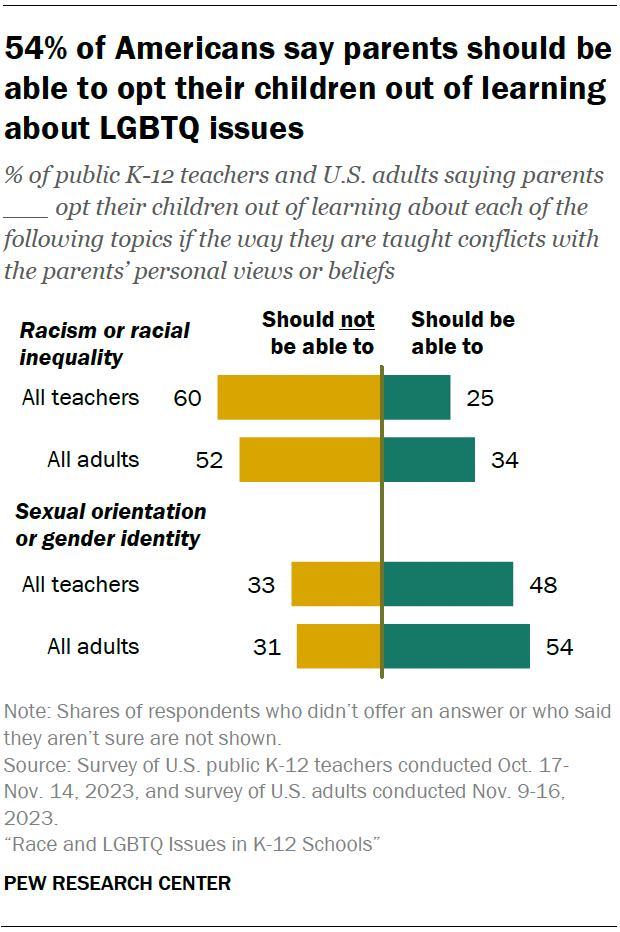
Like teachers, Americans overall are more likely to say parents should be able to opt their children out of learning about sexual orientation or gender identity (54%) than to say they should be able to opt their children out of learning about racism or racial inequality (34%).
Across both issues, Americans overall are somewhat more likely than teachers to say parents should be able to opt their children out.
For more on the public’s views, read Chapter 4 of this report.
How often do topics related to race and LGBTQ issues come up in the classroom?
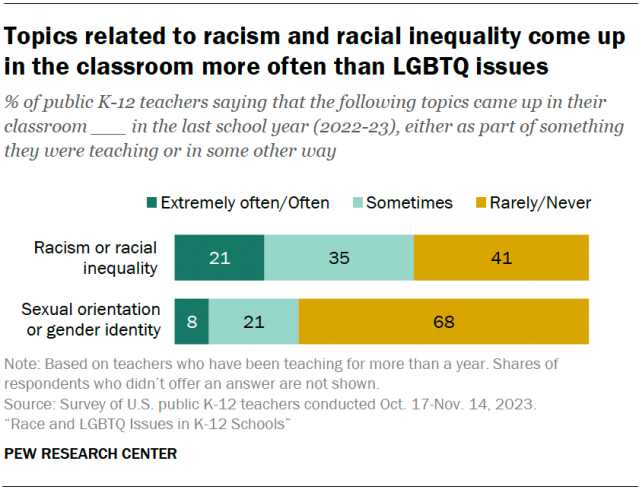
Most teachers who’ve been teaching for more than a year (68%) say the topics of sexual orientation and gender identity rarely or never came up in their classroom in the 2022-23 school year. About one-in-five (21%) say these topics came up sometimes, and 8% say they came up often or extremely often.
Topics related to racism or racial inequality come up more frequently. A majority of teachers (56%) say these topics came up at least sometimes in their classroom, with 21% saying they came up often or extremely often.
These topics are more likely to come up in secondary school than in elementary school classrooms.
How do teachers’ views differ by party?
As is the case among parents of K-12 students and the general public, teachers’ views on how topics related to race and LGBTQ issues should play out in the classroom differ by political affiliation.
- What students should learn about slavery: 85% of Democratic and Democratic-leaning teachers say students should learn that the legacy of slavery still affects the position of Black people in American society today. This compares with 35% of Republican and Republican-leaning teachers who say the same.
- What students should learn about gender identity: Democratic teachers are far more likely than Republican teachers to say students should learn that a person’s gender can be different from the sex they were assigned at birth (53% vs. 5%). Most Republican teachers (69%) say students shouldn’t learn about gender identity in school.
- Parents opting their children out of learning about these topics: 80% of Republican teachers say parents should be able to opt their children out of learning about LGBTQ issues, compared with 30% of Democratic teachers. And while 47% of Republican teachers say parents should be able to opt their children out of learning about racism and racial inequality, just 11% of Democratic teachers say this.
A majority of public K-12 teachers (58%) identify with or lean toward the Democratic Party. About a third (35%) identify with or lean toward the GOP. Americans overall are more evenly divided: 47% are Democrats or Democratic leaners, and 45% are Republicans or Republican leaners.


