Chapter 1: Overview
 As the 2012 presidential candidates prepare their closing arguments to America’s middle class, they are courting a group that has endured a lost decade for economic well-being. Since 2000, the middle class has shrunk in size, fallen backward in income and wealth, and shed some—but by no means all—of its characteristic faith in the future.
As the 2012 presidential candidates prepare their closing arguments to America’s middle class, they are courting a group that has endured a lost decade for economic well-being. Since 2000, the middle class has shrunk in size, fallen backward in income and wealth, and shed some—but by no means all—of its characteristic faith in the future.
These stark assessments are based on findings from a new nationally representative Pew Research Center survey that includes 1,287 adults who describe themselves as middle class, supplemented by the Center’s analysis of data from the U.S. Census Bureau and Federal Reserve Board of Governors.
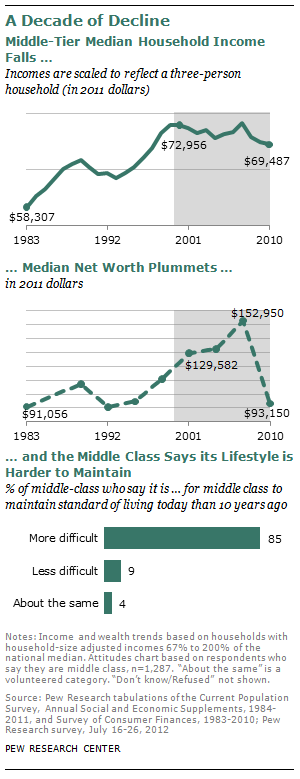
Fully 85% of self-described middle-class adults say it is more difficult now than it was a decade ago for middle-class people to maintain their standard of living. Of those who feel this way, 62% say “a lot” of the blame lies with Congress, while 54% say the same about banks and financial institutions, 47% about large corporations, 44% about the Bush administration, 39% about foreign competition and 34% about the Obama administration. Just 8% blame the middle class itself a lot.
Their downbeat take on their economic situation comes at the end of a decade in which, for the first time since the end of World War II, mean family incomes declined for Americans in all income tiers. But the middle-income tier—defined in this Pew Research analysis as all adults whose annual household income is two-thirds to double the national
median 1 —is the only one that also shrunk in size, a trend that has continued over the past four decades.
 In 2011, this middle-income tier included 51% of all adults; back in 1971, using the same income boundaries, it had included 61%. 2 The hollowing of the middle has been accompanied by a dispersion of the population into the economic tiers both above and below. The upper-income tier rose to 20% of adults in 2011, up from 14% in 1971; the lower-income tier rose to 29%, up from 25%. However, over the same period, only the upper-income tier increased its share in the nation’s household income pie. It now takes in 46%, up from 29% four decades ago. The middle tier now takes in 45%, down from 62% four decades ago. The lower tier takes in 9%, down from 10% four decades ago.
In 2011, this middle-income tier included 51% of all adults; back in 1971, using the same income boundaries, it had included 61%. 2 The hollowing of the middle has been accompanied by a dispersion of the population into the economic tiers both above and below. The upper-income tier rose to 20% of adults in 2011, up from 14% in 1971; the lower-income tier rose to 29%, up from 25%. However, over the same period, only the upper-income tier increased its share in the nation’s household income pie. It now takes in 46%, up from 29% four decades ago. The middle tier now takes in 45%, down from 62% four decades ago. The lower tier takes in 9%, down from 10% four decades ago.
For the middle-income group, the “lost decade” of the 2000s has been even worse for wealth loss than for income loss. The median income of the middle-income tier fell 5%, but median wealth (assets minus debt) declined by 28%, to $93,150 from $129,582. 3 During this period, the median wealth of the upper-income tier was essentially unchanged—it rose by 1%, to $574,788 from $569,905. Meantime, the wealth of the lower-income tier plunged by 45%, albeit from a much smaller base, to $10,151 from $18,421.
Which Presidential Candidate Is Better for the Middle Class?
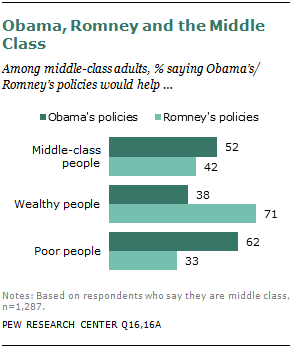 As the 2012 presidential campaign heads toward the party conventions and the fall climax, no group has been the target of more electioneering appeals than America’s beleaguered middle class. The Pew Research survey finds that neither candidate has sealed the deal with middle-class adults but that President Obama is in somewhat better shape than his Republican challenger, Mitt Romney. 4
As the 2012 presidential campaign heads toward the party conventions and the fall climax, no group has been the target of more electioneering appeals than America’s beleaguered middle class. The Pew Research survey finds that neither candidate has sealed the deal with middle-class adults but that President Obama is in somewhat better shape than his Republican challenger, Mitt Romney. 4
About half (52%) of adults who self-identify as middle class say they believe Obama’s policies in a second term would help the middle class, while 39% say they would not help. By comparison, 42% say that Romney’s election would help the middle class, while 40% say it would not help. There is much more variance in the judgments of the middle class about the likely impact of the two candidates’ policies on the wealthy and the poor. Fully seven-in-ten (71%) middle-class respondents say Romney’s policies would help the wealthy, while just a third (33%) say they would help the poor. Judgments about Obama tilt the opposite way. Roughly four-in-ten (38%) middle-class respondents say his policies would help the wealthy, and about six-in-ten (62%) say they would help the poor.
Who Is Middle Class?
In addition to looking at a “statistical middle” derived from government data, this report looks at those who self-identify as middle class, based on a Pew Research Center national survey of 2,508 adults. In the survey, 49% of adults describe themselves as middle class; 53% said the same in a similar survey in early 2008, when what is now known as the Great Recession was gathering steam. That recession, according to the National Bureau of Economic Research, began in December 2007 and ended in June 2009.
 The 2012 survey finds an increase in those who self-identify as being in the lower or lower-middle class—32% place themselves in these categories, up from 25% in 2008. And 17% now say they are in the upper or upper-middle class, down from 21% in 2008.
The 2012 survey finds an increase in those who self-identify as being in the lower or lower-middle class—32% place themselves in these categories, up from 25% in 2008. And 17% now say they are in the upper or upper-middle class, down from 21% in 2008.
Noteworthy patterns by race, age and gender are present in all of these self-categorizations.
Similar shares of whites (51%), blacks (48%) and Hispanics (47%) say they are middle class, even though government data show that whites have a higher median income and much more wealth than blacks or Hispanics.
Adults ages 65 and older (63%) are more inclined than all other age groups to call themselves middle class and less inclined to say they are lower class (20%). Meantime, younger adults (those ages 18 to 29) are more likely to say they are in the lower or lower-middle class; fully 39% say this now, compared with 25% who said so in 2008.
Men (46%) are somewhat less likely than women (53%) to include themselves in the middle class. In 2008, a somewhat larger share of men (51%) said they were middle class, and 54% of women said they were.
Falling Behind, Moving Ahead
When middle-class Americans size up their personal economies, they see themselves as both moving ahead and falling behind. It all depends on the time frame. Over the short term, their evaluations tilt negative. Over the span of the past decade, they’re mixed. And over the full arc of their lives, they’re positive—albeit less so now than in the past.
The Great Recession officially ended three years ago, but most middle-class Americans are still feeling pinched. About six-in-ten (62%) say they had to reduce household spending in the past year because money was tight, compared with 53% who said so in 2008.
 The downbeat short-term perspective is not surprising in light of the heavy economic blows delivered by the Great Recession of 2007-2009 and the sluggish recovery since. About four-in-ten (42%) middle-class adults say their household’s financial situation is worse now than it was before the recession, while 32% say they are in better shape; an additional 23% volunteered that their finances are unchanged. Of those who say they’re in worse shape, about half (51%) say it will take at least five years to recover, including 8% who predict they will never recover.
The downbeat short-term perspective is not surprising in light of the heavy economic blows delivered by the Great Recession of 2007-2009 and the sluggish recovery since. About four-in-ten (42%) middle-class adults say their household’s financial situation is worse now than it was before the recession, while 32% say they are in better shape; an additional 23% volunteered that their finances are unchanged. Of those who say they’re in worse shape, about half (51%) say it will take at least five years to recover, including 8% who predict they will never recover.
Asked to compare their financial situation now with what it was 10 years ago, the evaluations of the middle class are more evenly divided. Some 44% say they are more financially secure than they had been, and 42% say less. (An additional 12% volunteered that it’s about the same.)
Over the longer term, the evaluations grow more positive. Six-in-ten (60%) say their standard of living is better than that of their parents at the same age, 24% say it is the same and just 13% say it is worse. However, these evaluations were even rosier four years ago, when 67% said they were doing better than their parents at the same age.
Does Hard Work Pay Off?
In addition to their scaled-back judgments about how they are doing personally, Americans have a bit less faith in their long-held beliefs about the efficacy of hard work.
Two-thirds of the middle class (67%) agree that “most people who want to get ahead can make it if they are willing to work hard,” while 29% agree that “hard work and determination are no guarantee of success for most people.” Among the general public, the shares are similar—63% say hard work pays off, while 34% say it does not necessarily lead to success. The Pew Research Center has asked this question 10 times since 1994, when 68% of the public agreed that hard work would pay off. The proportion saying so peaked in 1999, when roughly three-quarters (74%) expressed that view.
Looking Ahead with Muted Hope
 Middle-class Americans look to the economic future—their own, their children’s, and the nation’s—with a mix of apprehension and muted optimism.
Middle-class Americans look to the economic future—their own, their children’s, and the nation’s—with a mix of apprehension and muted optimism.
About a quarter (23%) say they are very confident that they will have enough income and assets to last throughout their retirement years; an additional 43% say they are somewhat confident and 32% say they are not too or not at all confident.
As for their children’s economic future, some 43% of those in the middle class expect that their children’s standard of living will be better than their own, while 26% think it will be worse and 21% think it will be about the same. Four years ago, in response to the same question, the middle class had higher hopes for their offspring, with 51% predicting they would have a better standard of living and 19% thinking it would be worse.
As for the nation as a whole, the verdict from the middle class is likewise muted. Only about one-in-ten (11%) say they are very optimistic about the country’s long-term economic future, 44% are somewhat optimistic and 41% are somewhat or very pessimistic.
Does Partisan Affiliation Influence Economic Perceptions?
As is true of the population overall, more members of the middle class identify with or lean toward the Democratic Party (50%) than with the Republican Party (39%), with 11% declining to take sides. These partisan affiliations are correlated with the economic attitudes and perceptions of survey respondents in ways that often run contrary to their actual economic circumstances, a pattern evident in many Pew Research surveys conducted since 2008, when the recession took hold and Barack Obama was elected president.
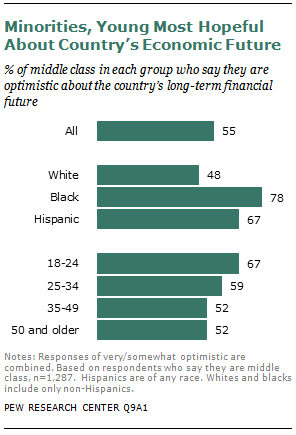 Many of the demographic groups that have fared the worst during the recession—including young adults (ages 18 to 24), blacks and Hispanics—have the most upbeat assessments of their own economic mobility, their children’s economic prospects and the nation’s economic future.
Many of the demographic groups that have fared the worst during the recession—including young adults (ages 18 to 24), blacks and Hispanics—have the most upbeat assessments of their own economic mobility, their children’s economic prospects and the nation’s economic future.
These groups are all heavily Democrats and supporters of President Obama. For example, young adults are more optimistic than older adults about the nation’s long-term economic future (67% of adults ages 18 to 24 vs. 52% of adults ages 35 and older), and blacks (78%) and Hispanics (67%) are more optimistic than whites (48%). The same patterns play out in many evaluations of personal finances.
Partisan differences also affect the way members of the middle class apportion blame for the economic difficulties the middle class has endured over the past decade. Sizable gaps exist on whether a lot of blame belongs with large corporations (Democrats 59% vs. Republicans 27%) and banks and other financial institutions (Democrats 62% vs. Republicans 40%). However, similar majorities of both groups blame Congress (63% for Democrats and 58% for Republicans).
Cost To Lead a Middle-class Life
 The survey also asked how much annual income a family of four would need to lead a middle-class lifestyle. The median response among those who consider themselves middle class is $70,000, meaning that half of middle-class adults say it would take more than $70,000 annually and half say it would take less than that amount.
The survey also asked how much annual income a family of four would need to lead a middle-class lifestyle. The median response among those who consider themselves middle class is $70,000, meaning that half of middle-class adults say it would take more than $70,000 annually and half say it would take less than that amount.
Public estimates of how much money it takes for a family of four to live a middle-class lifestyle are quite close to the Pew Research Center’s analysis based on U.S. Census Bureau data that the median income for a four-person household is $68,274. 5
As expected from the varying cost of living across the country, the annual family income seen as necessary for a middle-class lifestyle is a median of $85,000 in the East and $60,000 in the Midwest (with a median of $70,000 in both the South and the West). Similarly, the median among middle-class adults living in rural areas is $55,000; among suburban and urban dwellers, it is $75,000 and $70,000, respectively.
Income Trends from Government Data
The economic narrative the middle class tells about itself through its responses to the Pew Research survey is consistent with the story told by government economic and demographic trend data. For the half century following World War II, American families enjoyed rising prosperity in every decade—a streak that ended in the decade from 2000 to 2010, when inflation-adjusted family income fell for the middle income as well as for all other income groups, according to U.S. Census Bureau data. 6

A Pew Research Center analysis of long-term census data also finds that those in the upper-income tier now take in a much larger share of U.S. aggregate household income than they did four decades ago, while those in the middle tier take in a much lower share. (For the purpose of this analysis, the middle tier is defined as those living in households with an annual income
that is 67% to 200% of the national median; the upper tier is made up of those in households above the 200% threshold, and the lower tier is made up of those below the 67% threshold.)

The Pew Research analysis finds that upper-income households accounted for 46% of U.S. aggregate household income in 2010, compared with 29% in 1970. Middle-income households claimed 45% of aggregate income in 2010, compared with 62% in 1970. Lower-income households had 9% of aggregate income in 2010 and 10% in 1970.
 These shifts result from two trends: larger income gains for upper-income households than for others and a decline in the share of adults who live in middle-income households. From 1970 to 2010, median incomes rose 43% for upper-income households, 34% for middle-income households and 29% for lower-income households. Over the same four decades, the share of the adult population living in upper-income households rose to 20% from 14%; for middle-income households, it fell to 51% from 61%; and for lower-income households, it rose to 29% from 25%.
These shifts result from two trends: larger income gains for upper-income households than for others and a decline in the share of adults who live in middle-income households. From 1970 to 2010, median incomes rose 43% for upper-income households, 34% for middle-income households and 29% for lower-income households. Over the same four decades, the share of the adult population living in upper-income households rose to 20% from 14%; for middle-income households, it fell to 51% from 61%; and for lower-income households, it rose to 29% from 25%.
Winners and Losers
 Even as the share of Americans in the middle has declined, the income status has improved for some demographic groups and deteriorated for others. This report classified groups into winners and losers by comparing changes over time in their shares in the upper- and lower-income tiers.
Even as the share of Americans in the middle has declined, the income status has improved for some demographic groups and deteriorated for others. This report classified groups into winners and losers by comparing changes over time in their shares in the upper- and lower-income tiers.
From 2001 to 2011, there were distinct differences by age: Adults ages 65 and older were the greatest winners, while other age groups were economic losers. The widowed and currently married were winners, while those who never married or who were divorced or separated were economic losers. Age helps explain some differences by marital status. Widowed and currently married adults tend to be older than those who never married. Adults with only a high school diploma were among the groups that lost the most ground, although college graduates also experienced a small loss.
Over the longer term—1971 to 2011—older adults fared better than younger ones, married adults fared better than the unmarried, and college-educated adults fared better than those with less education.
Wealth, Assets and Debt
 The net worth of middle-income families—that is, the sum of assets minus debts—also took a hit during the past decade, according to data for 2001 to 2010 from the Federal Reserve’s Survey of Consumer Finances. Median net worth fell 28%, to $93,150, erasing two decades of gains.
The net worth of middle-income families—that is, the sum of assets minus debts—also took a hit during the past decade, according to data for 2001 to 2010 from the Federal Reserve’s Survey of Consumer Finances. Median net worth fell 28%, to $93,150, erasing two decades of gains.
Wealth of middle-income families had been unchanged from 1983 to 1992, then grew sharply—by 43%—from 1992 to 2001, and continued to grow in the 2001-2007 period, by 18%. Net worth of middle-income families dropped 39% in the later years of the decade as the housing market crash and Great Recession wiped out the previous advances. Over the 1983 to 2010 period, only upper-income families registered strong increases in wealth.
Breaking apart the two components of net worth—assets and liabilities—the value of assets grew more than the level of debt in dollar terms from 1983 to 2001 and from 2001 to 2007 for all families and for middle-income families. For middle-income families, though, the rate of increase in debt was larger than the rate of increase in assets during both periods. From 2007 to 2010, mean debt level for middle-income families fell 11%, or $11,040, but the value of their assets fell even more, by 19%, or $75,621.
One reason that upper-income families fared better than others is that they are less dependent on home equity, which has been the main source of declines in wealth since 2006. Home equity accounted for at most 24% of the mean assets of upper-income families from 1983 to 2010, compared with at least 40% of the assets of middle-income families during the same period.
About the Authors
This report was edited by Paul Taylor, executive vice president of the Pew Research Center and director of its Social & Demographic Trends project, who also co-wrote Chapter 1. Senior editor Rich Morin led the team that drafted the questionnaire; he also co-wrote Chapter 3 with research assistant Eileen Patten and wrote Chapter 5. Senior writer D’Vera Cohn co-wrote Chapter 1 and wrote Chapter 2; senior researcher Cary Funk wrote Chapter 4. Chapters 6 and 7 were written by associate director for research Rakesh Kochhar and senior research associate Richard Fry. Research assistant Seth Motel and Patten helped with the preparation of charts, and Patten formatted the final report. Patten and Motel also numbers-checked the report. Social & Demographics Trend project associate director Kim Parker and research associate Wendy Wang assisted on all aspects of the research project. Marcia Kramer copy-edited the report.
About the Report
The remainder of this report is organized as follows: Chapter 2 provides a detailed demographic profile of those who described themselves as middle class in the Pew Research survey. Chapter 3 reports how well middle-class Americans say they have fared financially in the past decade. Chapter 4 examines social mobility, including whether middle-class Americans believe they have done better or worse in life than their parents, their expectations for their children, and asks Americans how much money is needed to lead a middle-class life. Chapter 5 examines the politics of the middle class, including their judgments about the political parties and presidential candidates on matters related to the middle class. Chapter 6 uses an income-based definition of the middle tier derived from U.S. Census Bureau data to analyze economic and demographic trends over the past 60 years, with a special focus on the past decade. Chapter 7 also uses government data to conduct a detailed analysis of trends in both wealth and income from 1983 to 2011, with a special focus on the decline in wealth since 2007 among different income groups.
About the Data
The income, wealth and demographic data come from two primary sources. The demographic and household income data reported in Chapter 6 are derived from the Current Population Survey, Annual Social and Economic Supplements (ASEC) conducted in March of every year. Income is reported for the year prior to the survey year (e.g., 2010 income is reported in the 2011 survey). The specific files used in this report are from March 1971 to March 2011, the latest year for which ASEC data are available. Conducted jointly by the U.S. Census Bureau and the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the CPS is a monthly survey of approximately 55,000 households and is the source of the nation’s official statistics on unemployment. Additionally, the mean family income numbers in Chapter 6 are derived from the U.S. Census Bureau’s Historical Income Tables. The wealth data in Chapter 7 are derived from the Survey of Consumer Finances (SCF), which is sponsored by the Federal Reserve Board of Governors and the Department of Treasury. It has been conducted every three years since 1983 and is designed to provide detailed information on the finances of U.S. families. The SCF sample typically consists of approximately 4,500 families, but the 2010 survey included about 6,500 families. For more details, see Appendix 2.
The general public survey is based on telephone interviews conducted July 16-26, 2012, with a nationally representative sample of 2,508 adults ages 18 and older, including 1,287 respondents who identified themselves as “middle class.” The survey included an oversample of 407 non-Hispanic blacks and 377 Hispanics. A total of 1,505 interviews were completed with respondents contacted by landline telephone and 1,003 with those contacted on their cellular phone. Data are weighted to produce a final sample that is representative of the general population of adults in the continental United States. Survey interviews were conducted in English and Spanish under the direction of Princeton Survey Research Associates International. Margin of sampling error is plus or minus 2.8 percentage points for results based on the total sample, 3.9 percentage points for those in the middle class, 5.7 percentage points for non-Hispanic blacks and 5.5 percentage points for the Hispanic subsamples at the 95% confidence level. For more details, see Appendix 3.
Notes on Terminology
Race/Ethnicity: Hispanics are of any race. Whites and blacks include only non-Hispanics.
Education: “High school or less” refers to those who either did not finish high school or who graduated high school (with a regular diploma or its equivalent, such as a GED) but did not obtain any college education. The educational level “some college” refers to those who do not have a four-year college degree, but have completed some college credits, including those who received associate degrees. “College graduate” refers to anyone with at least a bachelor’s degree, including those with a graduate or professional degree.
Net Worth: The difference between the value of assets owned by a household (such as home, stocks and savings accounts) and its liabilities (such as mortgages, credit card debt and loans for education). The terms “net worth” and “wealth” are used interchangeably in this report.
Income Tiers: Analysis based on census data refers to lower-, middle- and upper-income groups, or tiers. Using income as the criterion, the middle tier is defined as those living in households with an annual income that is two-thirds to double (67% to 200%) the national median; the upper tier is made up of those in households above the 200% threshold, and the lower tier is made up of those below the 67% threshold. The assignment of a household to a tier depends on what its income expressed in 2011 dollars is estimated to be after it is scaled to a three-person household (see Appendix 2 for details on the adjustment process).
Social Classes: In survey-based analysis, assignment into the lower, middle or upper classes is based on a respondent’s answer to the following question: “If you were asked to use one of these commonly used names for the social classes, which would you say you belong in? The upper class, upper-middle class, middle class, lower-middle class or lower class?” Respondents who say they are upper or upper-middle are combined into a single “upper-class” category; respondents who say they are lower or lower-middle are combined into a single “lower-class” category. The size of the middle group, whether based on household income in 2010 or based on self-described class in the 2012 survey, turns out to be nearly identical.


 Video Key Findings from the Survey
Video Key Findings from the Survey