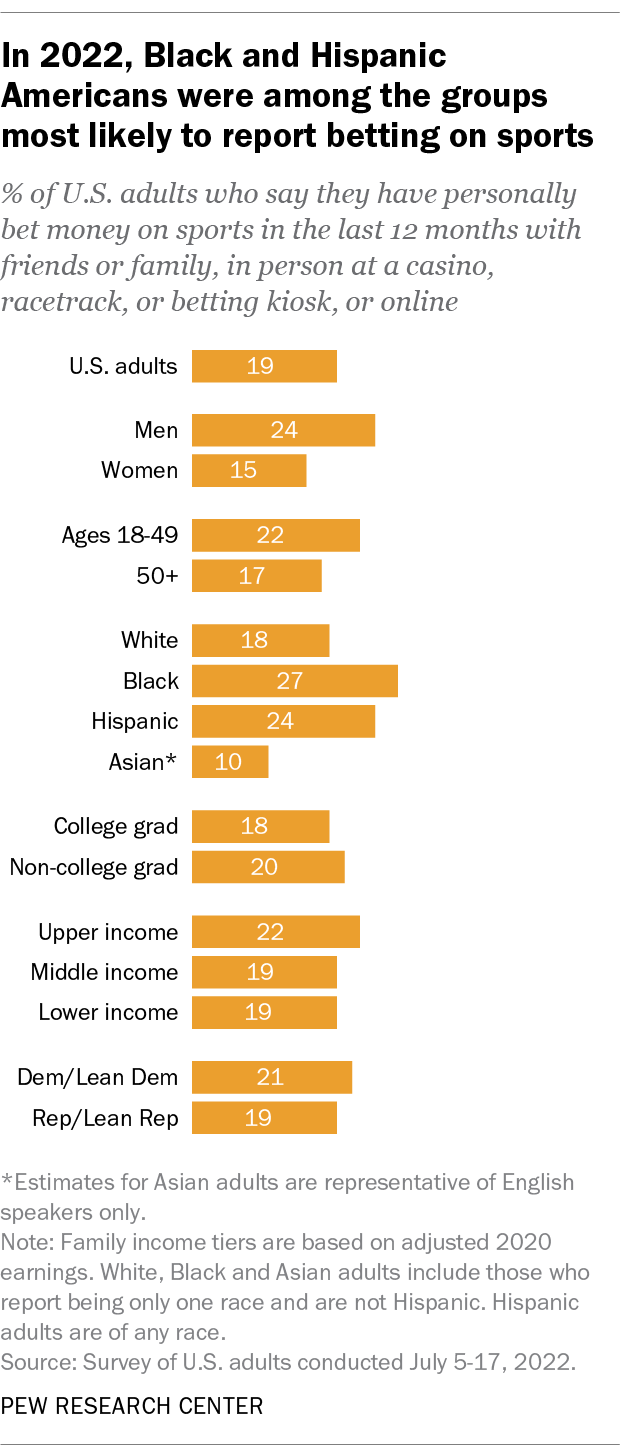Many Americans participate in sports in some way, whether they play, cheer on their favorite teams or gamble on outcomes.
Ahead of March Madness – the annual men’s and women’s college basketball tournaments – here are five facts about Americans’ experiences with and interest in sports, drawn from Pew Research Center surveys.
Ahead of this year’s NCAA Division I basketball tournaments, Pew Research Center explored Americans’ experiences with and interest in sports.
This analysis is based on recent Center surveys. Links to these surveys, including information about the field dates, sample sizes and other methodological details, are available in the text.
About half of Americans (48%) say they took part in organized, competitive sports in high school or college, according to a February 2022 Center survey. This includes 39% who participated in high school, 2% who participated in college and 7% who participated at both levels.
Men are more likely than women to say they played high school or college sports (56% vs. 41%).
There are also notable age differences among women: Adults under 50 are more likely than their older counterparts to have played high school or college sports (48% vs. 33%). These age differences among women may be partly due to Title IX, which became law in 1972. The law prohibits schools that receive federal funding from discriminating based on sex – including in the athletic opportunities they provide.
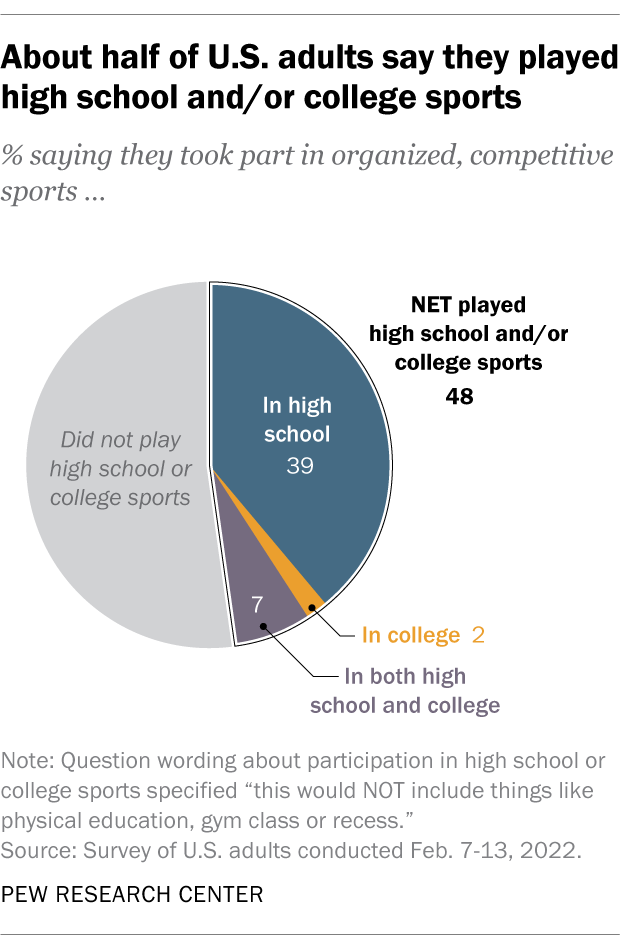
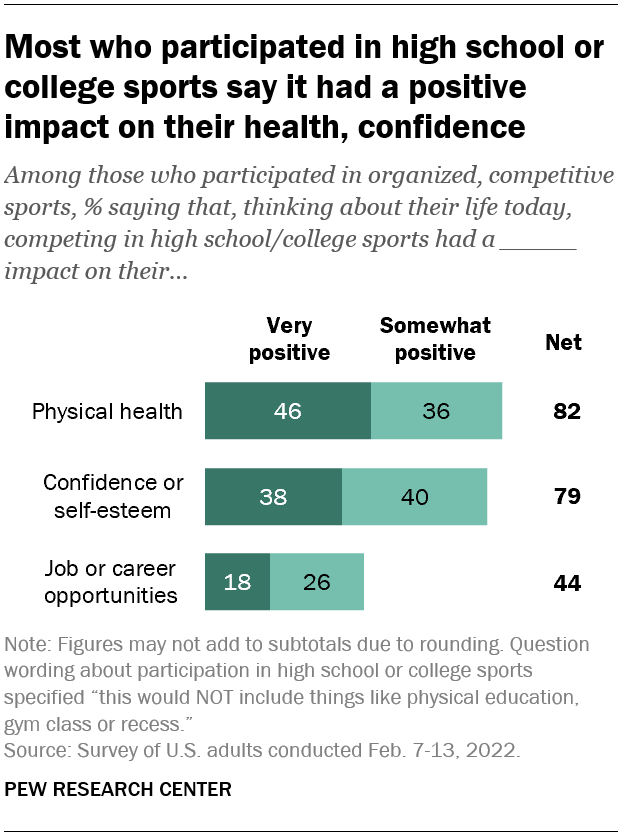
Most Americans who played sports in high school or college say their athletic experiences improved their physical health and confidence, according to the same survey. Some 82% of adults who played sports say doing so had a very or somewhat positive impact on their physical health, including 46% who say it had a very positive impact. And 79% say playing sports had a positive impact on their confidence or self-esteem, with 38% saying it had a very positive impact.
A smaller share of these Americans say playing sports had a positive impact on their job or career opportunities. Still, the share who say this far outpaces the share who say it had a negative impact (44% vs. 3%).
In all three areas – physical health, confidence and job opportunities – former college athletes are more likely than former high school athletes to say that playing sports had a very positive impact.
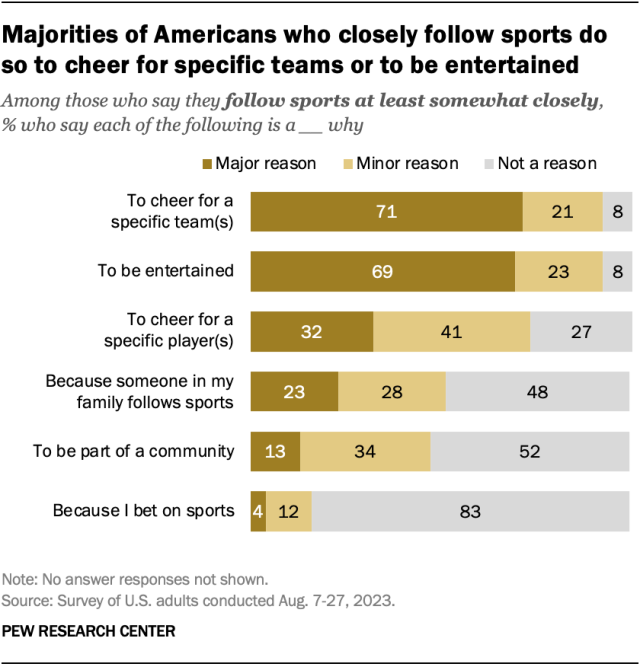
Nearly four-in-ten Americans (38%) follow professional or college sports at least somewhat closely, according to a 2023 Center survey. This includes 16% who follow sports extremely or very closely. And 7% of U.S. adults are what might be called “superfans”: They follow sports extremely or very closely and talk about sports with other people at least daily.
About seven-in-ten Americans who follow sports at least somewhat closely say a major reason they do so is to cheer for a specific team or teams (71%) or to be entertained (69%). Much smaller shares say a major reason is to cheer for a specific player or players (32%), because someone in their family follows sports (23%), or for one of the other reasons included in the survey.
Still, a majority of Americans (62%) say they follow sports not too or not at all closely. Among this group, 69% say a major reason they don’t follow sports is that they’re just not interested.
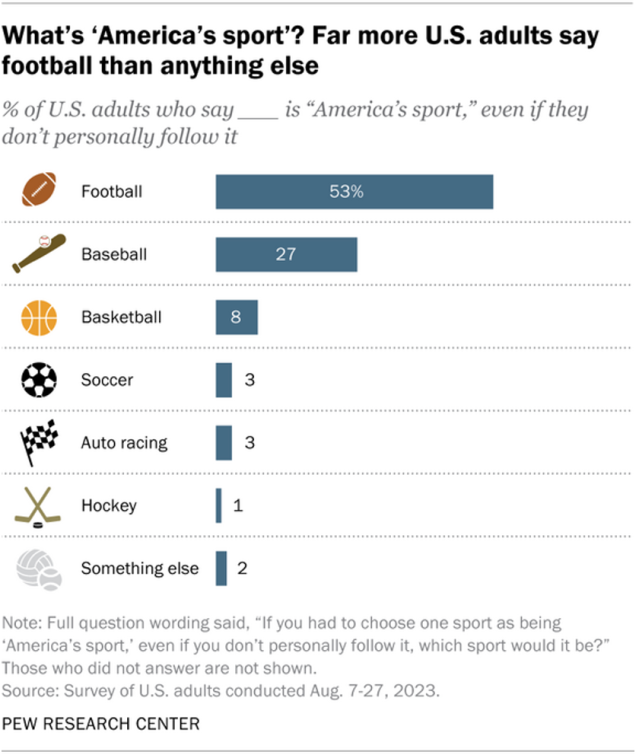
When asked to choose one sport as “America’s sport,” more than half of U.S. adults (53%) choose football, according to the same survey. Another 27% say it’s baseball, while 8% pick basketball, 3% pick soccer, 3% choose auto racing and 1% choose hockey.
Football is the most common choice in every major demographic group, but there are some differences by race and ethnicity. For example, White Americans are more likely than those in other racial and ethnic groups to say baseball is America’s sport. Hispanic Americans are more likely than others to pick soccer, and Black and Asian Americans are more likely to choose basketball.
In a July 2022 Center survey, 19% of Americans said they had bet money on sports in the past year. This includes betting with friends and family, in person at a casino or other gambling venue, or online with a betting app. Men, adults under 50, and Black and Hispanic adults were particularly likely to say they’d bet on sports in the previous year.
The survey was conducted more than four years after the Supreme Court effectively legalized commercial sports betting in the United States. Most adults (57%) said the legalization of sports betting in much of the country was neither a good nor bad thing for society, while 34% said it was a bad thing. Only 8% said it was a good thing.
Despite the widespread availability of commercial sports gambling today, betting rarely motivates people to follow sports, according to our 2023 survey. Among those who follow sports at least somewhat closely, 83% say betting is not a reason for doing so. Another 12% say betting is a minor reason they follow sports, and just 4% say it’s a major reason.