Former President Donald Trump pleaded not guilty this week to federal criminal charges related to his alleged mishandling of classified documents after his departure from the White House in 2021. The unprecedented charges against Trump and his subsequent plea raise the question: How common is it for defendants in federal criminal cases to plead not guilty, go to trial and ultimately be acquitted?
The U.S. Justice Department’s indictment of former President Donald Trump, and his subsequent plea of not guilty, prompted Pew Research Center to examine how many defendants in federal criminal cases are acquitted in a typical year. The analysis builds on an earlier Center analysis that examined trial and acquittal rates in federal and state courts.
All statistics cited in this analysis come from the Judicial Business 2022 report by the Administrative Office of the U.S. Courts. Information about the total number of defendants in federal criminal cases in the United States, as well as how their cases ended, is drawn from Table D-4. Information about defendants in the Southern District of Florida is drawn from Table D-7 and Table D-9.
The statistics in this analysis include all defendants charged in U.S. district courts with felonies and serious misdemeanors, as well as some defendants charged with petty offenses. They do not include federal defendants whose cases were handled by magistrate judges or the much broader universe of defendants in state courts. Defendants who enter pleas of “no contest,” in which they accept criminal punishment but do not admit guilt, are also excluded.
This analysis is based on the 2022 federal fiscal year, which began Oct. 1, 2021, and ended Sept. 30, 2022.
In fiscal year 2022, only 290 of 71,954 defendants in federal criminal cases – about 0.4% – went to trial and were acquitted, according to a Pew Research Center analysis of the latest available statistics from the federal judiciary. Another 1,379 went to trial and were found guilty (1.9%).
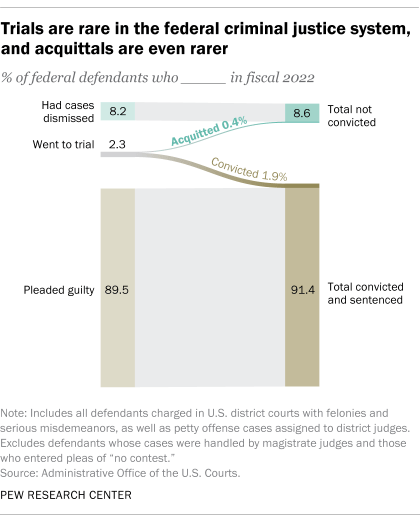
The overwhelming majority of defendants in federal criminal cases that year did not go to trial at all. About nine-in-ten (89.5%) pleaded guilty, while another 8.2% had their case dismissed at some point in the judicial process, according to the data from the Administrative Office of the U.S. Courts.
These statistics include all defendants charged in U.S. district courts with felonies and serious misdemeanors, as well as some defendants charged with petty offenses. They do not include federal defendants whose cases were handled by magistrate judges or the much broader universe of defendants in state courts. Defendants who entered pleas of “no contest,” in which they accept criminal punishment but do not admit guilt, are also excluded. The 2022 federal fiscal year began Oct. 1, 2021, and ended Sept. 30, 2022.
The U.S. Justice Department indicted Trump earlier this month on 37 counts relating to seven criminal charges: willful retention of national defense information, conspiracy to obstruct justice, withholding a document or record, corruptly concealing a document or record, concealing a document in a federal investigation, scheme to conceal, and false statements and representations.
Trump’s case is being heard in the U.S. District Court for the Southern District of Florida, where acquittal rates look similar to the national average. In fiscal 2022, only 12 of 1,944 total defendants in the Southern District of Florida – about 0.6% – were acquitted at trial. As was the case nationally, the vast majority of defendants in Florida’s Southern District (86.2%) pleaded guilty that year, while 10.7% had their cases dismissed.
It’s not clear from the federal judiciary’s statistics how many other defendants nationally or in the Southern District of Florida faced the same or similar charges that Trump is facing or how those cases ended.
Broadly speaking, however, the charges against Trump are rare. In fiscal 2022, more than eight-in-ten federal criminal defendants in the United States faced charges related to one of four other broad categories of crime: drug offenses (31%), immigration offenses (25%), firearms and explosives offenses (16%) or property offenses (11%). In Florida’s Southern District, too, more than eight-in-ten defendants faced charges related to these four categories.
Trump, of course, is not a typical federal defendant. He is the first former president ever to face federal criminal charges and is running for president again in 2024. The federal case against Trump is still in its early stages, and it’s unclear when – or whether – it will proceed to trial.



