Indian adults nearly universally say it is important for women to have the same rights as men, including eight-in-ten who say this is very important. At the same time, however, there are circumstances when Indians feel men should receive preferential treatment: 80% agree with the idea that “when there are few jobs, men should have more rights to a job than women,” according to a new Pew Research Center report.
The report, based on a face-to-face survey of 29,999 Indian adults fielded between late 2019 and early 2020, before the COVID-19 pandemic, looks at how Indians view gender roles at home and in society more generally. The survey, which was also the basis for a 2021 report on religion in India, was conducted by local interviewers in 17 languages and covered nearly all of India’s states and union territories.
Here are key findings from the report.
Pew Research Center conducted this analysis to find out how Indians view gender roles in families and society. It is based on the March 2022 report “How Indians View Gender Roles in Families and Society,” and is part of the Center’s most comprehensive, in-depth exploration of Indian public opinion to date. For this report, we surveyed 29,999 Indian adults ages 18 and older living in 26 Indian states and three union territories. The sample included interviews with 22,975 Hindus, 3,336 Muslims, 1,782 Sikhs, 1,011 Christians, 719 Buddhists, 109 Jains and 67 respondents who belong to another religion or are religiously unaffiliated. Many findings from the survey in India were previously published in “Religion in India: Tolerance and Segregation,” which looked in detail at religious and national identity, religious beliefs and practices, and attitudes among religious communities. The survey also included several questions on gender roles in Indian society, but these questions were not analyzed in the previous report and are now being published for the first time. Interviews for this nationally representative survey were conducted face-to-face in 17 languages from Nov. 17, 2019, to March 23, 2020.
Respondents were selected using a probability-based sample design that would allow for robust analysis of all major religious groups in India, as well as all major regional zones. Data was weighted to account for the different probabilities of selection among respondents, and to align with demographic benchmarks for the Indian adult population from the 2011 census.
Here are the questions used in this analysis, along with responses, and its methodology.
International survey data referenced in this analysis can be found at the following links: 2019 Global Attitudes Survey, 2015 Global Attitudes Survey, Central and Eastern Europe, Latin America. Each survey’s methodology can also be found via these links.
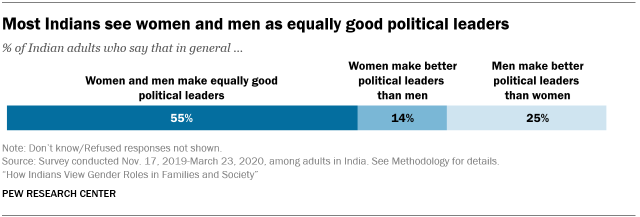
Indians broadly accept women as political leaders. India has a long history of women holding political power, from the 1966 election of Indira Gandhi, one of the world’s first woman prime ministers, to other well-known figures, such as Jayalalitha, Mamata Banerjee and Sushma Swaraj.
The survey results reflect this comfort with women in politics. Most adults say that women and men make equally good political leaders (55%) or that women generally make better leaders than men (14%). Only a quarter of Indian adults take the position that men tend to make better political leaders than women.
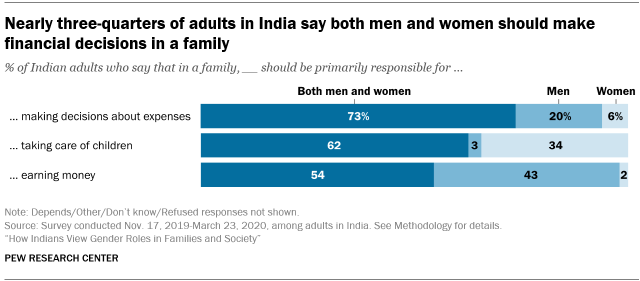
While most Indians say that men and women should share some family responsibilities, many still support traditional gender roles. For instance, 62% of adults say both men and women should be responsible for taking care of children, while roughly a third of adults (34%) feel that child care should be handled primarily by women. Similarly, a slim majority (54%) say that both men and women in families should be responsible for earning money, yet many Indians (43%) see this as mainly the obligation of men.
Meanwhile, nearly nine-in-ten Indians (87%) completely or mostly agree with the notion that “a wife must always obey her husband.” This includes a majority of Indians (64%) who completely agree with this sentiment. Women are only modestly less likely than men to say that wives should obey their husbands in all situations, and most Indian women express total agreement with this sentiment (61% vs. 67% among men). (Throughout this report, differences in opinion between men and women are modest. In other words, Indian women typically are not much more likely than Indian men to express egalitarian views on gender roles.)
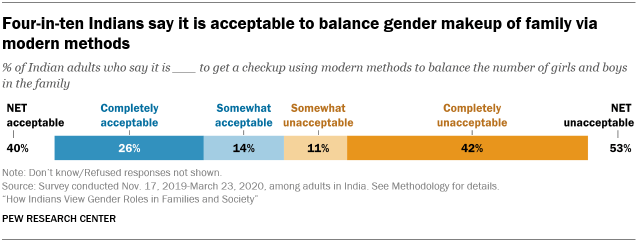
An overwhelming majority of Indian adults say it is very important for families to have both sons and daughters, and a substantial share are accepting of sex-selective abortion. Indians are united in the view that it is very important for a family to have at least one son (94%) and, separately, a daughter (90%). Historically in Indian society, though, families have tended to place higher value on their sons than their daughters, a custom broadly referred to as “son preference.” One enduring manifestation of son preference has been the illegal practice of sex-selective abortions – using ultrasound or other tests to learn the sex of a fetus and terminating the pregnancy if the fetus is female.
The survey finds that four-in-ten Indians say it is either “completely acceptable” or “somewhat acceptable” to “get a checkup using modern methods to balance the number of girls and boys in the family,” a euphemism that connotes sex-selective abortion. In contrast, roughly half of adults (53%) say that this practice is either somewhat or completely unacceptable.
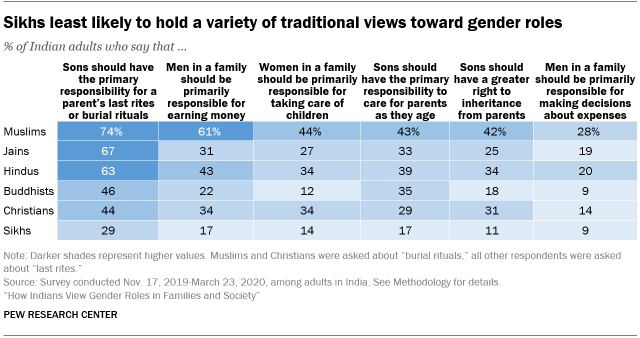
Most Indians (63%) say sons should be primarily responsible for parents’ last rites or burial rituals, although attitudes differ significantly across religious groups. Religious funeral practices for loved ones are widely seen as very important in India, and at least according to Hindu tradition, sons must perform last rites for a parent to ensure freedom for the soul in the afterlife.
Most Muslims (74%), Jains (67%) and Hindus (63%) say sons should be primarily responsible for funeral rituals, but far fewer Sikhs (29%), Christians (44%) and Buddhists (46%) expect this from sons. (Muslims and Christians were asked about “burial rituals,” while all other respondents were asked about “last rites.”) Instead, Sikhs, Christians and Buddhists are more likely to say that both sons and daughters should be responsible for their parents’ last rites. Very few Indians, regardless of religion, say daughters should be primarily responsible for funeral rituals.
Muslims are more likely than other Indians to support traditional gender roles in families, while Sikhs are often the least likely community to hold such views. For example, while most Indian Muslims (61%) say that men in a family should be primarily responsible for earning money, just 17% of Sikhs say this. And Muslims are more than twice as likely as Sikhs to assign sons the primary responsibility of caring for aging parents (43% vs. 17%).
Indians favor teaching boys to respect women as a way to improve women’s safety. As described in a previous Pew Research Center report, roughly three-quarters of Indian adults (76%) say violence against women is a “very big problem” in their country. Police cases registered as “crimes against women” nearly doubled between 2010 and 2019, and rapes and murders of women have led to massive protests across India. The survey asked respondents which of two options is more important to improve the safety of women in their community: teaching boys to respect all women or teaching girls to behave appropriately.
About half of Indians (51%) say it is more important to teach boys to respect all women, while roughly a quarter (26%) say it is more important to teach girls to behave appropriately. An additional quarter of Indian adults don’t take a clear position between those two options, instead voicing that some combination of the two approaches is necessary, that improved law and order through policing will improve the situation, or that women are already safe.
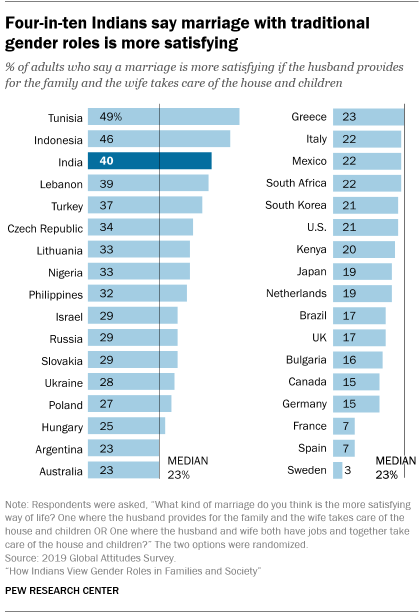
Compared with people in other countries around the world, Indians have relatively traditional views on gender roles. Although Indian adults are roughly in line with the global median in their support for equal rights for women, by two other measures the Indian public appears much more conservative, according to a series of other surveys conducted by the Center in recent years.
Only one out of 61 countries surveyed has a higher share of adults than in India who agree completely with the notion that men should have greater rights to a job than women when jobs are scarce. And just two out of 34 countries surveyed exceed India in the shares who say a marriage is more satisfying if the husband provides for the family and the wife takes care of the house and children. On this question, the percentage of Indians who take this view (40%) is well above the global median (23%).
Note: Here are the questions used in this analysis, along with responses, and its methodology.