At least since the Bharatiya Janata Party’s (BJP) electoral victories in 2014, the term “Hindu nationalism” has been frequently invoked in both Indian and Western media, with Prime Minister Narendra Modi and his ruling party often described as promoting a Hindu nationalist agenda. But there is no widely accepted definition of what the term means, and little data exists on how common Hindu nationalist attitudes are in India and how they vary across the country.
A new Pew Research Center survey of nearly 30,000 Indian adults sought to measure multiple dimensions of Hindu nationalism by asking people how important certain attributes or behaviors are to “true” Indian identity. This survey was conducted several months after the BJP’s victory in the 2019 parliamentary elections and before the COVID-19 pandemic.
Pew Research Center conducted this analysis to shed more light on nationalism in India. It is based on the 2021 report “Religion in India: Tolerance and Segregation,” the Center’s most comprehensive, in-depth exploration of Indian public opinion to date. For this report, we completed 29,999 face-to-face interviews in 17 languages with adults ages 18 and older living in 26 Indian states and three union territories. The sample included interviews with 22,975 Hindus, 3,336 Muslims, 1,782 Sikhs, 1,011 Christians, 719 Buddhists and 109 Jains. An additional 67 respondents belong to other religions or are religiously unaffiliated. Interviews for this nationally representative survey were conducted from Nov. 17, 2019, to March 23, 2020.
Respondents were selected using a probability-based sample design that would allow for robust analysis of all major religious groups in India, as well as all major regional zones. Six groups were targeted for oversampling as part of the survey design: Muslims, Christians, Sikhs, Buddhists, Jains and those living in the Northeast region. Data was weighted to account for the different probabilities of selection among respondents and to align with demographic benchmarks for the Indian adult population from the 2011 census.
Here are the questions used for this report, along with responses, and its methodology.
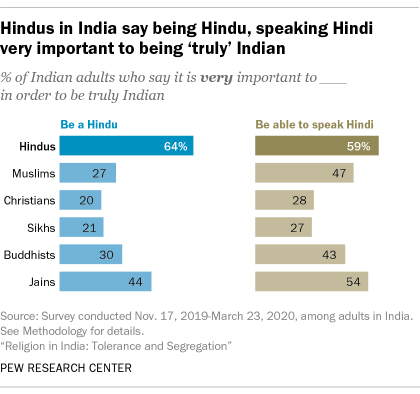
Hindus are far more likely than members of other religious groups to link Indian and Hindu identities: Nearly two-thirds of Hindus (64%) say it is very important to be Hindu to be truly Indian. Far fewer respondents among other religious communities in the country answer the same way, including 27% of Muslims who say being Hindu is very important to being truly Indian.
Hindu nationalism in India also has a linguistic dimension. Hindus are more likely than other Indians to associate national identity with the Hindi language. While India has dozens of major languages, a majority of Hindus (59%) feel that being able to speak Hindi is very important to being truly Indian. Hindus who link their religion with national identity tend also to link the Hindi language with being authentically Indian.
Altogether, about half of Hindus (51%) say being Hindu and speaking Hindi are both very important to being truly Indian. A substantial share of Jains (36%) also express both these sentiments, but Buddhists (25%), Muslims (23%), Sikhs (18%) and Christians (15%) are less inclined to offer these definitions of national identity. By contrast, large majorities of Indians across all major religions generally agree that respecting elders, respecting all religions, and respecting the country’s institutions and laws are each paramount to being truly Indian.
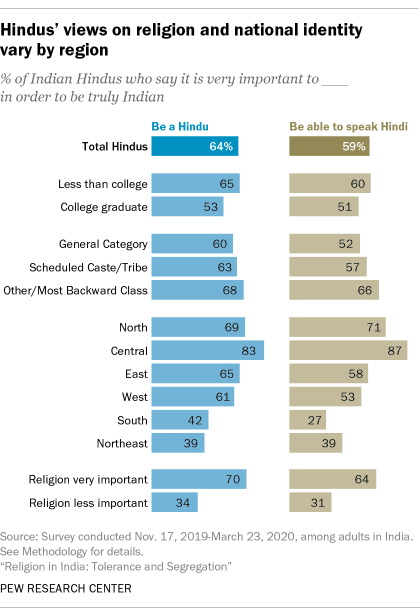
Among Hindus, opinion varies widely in different parts of the country on the importance of Hindu identity and speaking Hindi in relation to national identity. Hindus in the Northern (69%) and Central (83%) regions are the most likely to say being a Hindu is very important to be truly Indian, while Hindus in the South (42%) and Northeast (39%) express the weakest association between national and religious identities. Similarly, Hindus in the Northern (71%) and Central (87%) regions – which include the country’s “Hindi belt,” where Hindi is most prevalent – are the most likely to say it is very important to be able to speak Hindi to be truly Indian.
Hindus with a college degree are less likely to connect language and religion with national identity. Roughly half of Hindu college graduates (53%) tie being Hindu with being truly Indian, compared with nearly two-thirds of other Hindus (65%). Religious observance plays a role as well: Among Hindus who say religion is very important in their lives, 70% say being Hindu is very important to being truly Indian, compared with 34% among less religiously committed Hindus.
These beliefs about Hindu nationalism are strongly reflected in political behavior. Roughly half of Hindus who say they voted in the 2019 election say they voted for the ruling BJP (49%), but support for the BJP is considerably higher among those who say both being Hindu and speaking Hindi are very important to be truly Indian. Six-in-ten Hindu voters who place great importance on both of these attributes say they voted for the BJP in the 2019 parliamentary election. By comparison, 33% of those who say neither being Hindu nor being able to speak Hindi is very important to national identity reported voting for the party.
Although this group of Hindu BJP voters may see a special place for Hindus in India, they are just as likely as other Hindus to say respecting other religions is crucial to being truly Indian. And they are even more likely to say that religious diversity benefits India. Nearly two-thirds (65%) of this group – Hindus who say that being a Hindu and speaking Hindi are very important to be truly Indian and who voted for the BJP in 2019 – say religious diversity is a good thing for the country, compared with about half (47%) of other Hindu voters who say the same.
At the same time, Hindus who express this combination of Hindu nationalist positions also are more inclined to support a religiously segregated India – by opposing interreligious marriage, for instance. More than eight-in-ten in this group (83%) say it is very important to stop Hindu women from marrying into another religion, compared with roughly six-in-ten (61%) among other Hindu voters.
Note: Here are the questions used for this report, along with responses, and its methodology.