Some say Christianity in India dates back to the earliest followers of Jesus in the first century C.E. Today, there are millions of Christians in the country, although they make up just 2.4% of India’s massive population. South India is home to about half of the Christians in the country, and Christians make up a relatively large share of people in India’s more sparsely populated Northeast, where the vast majority of Christians belong to tribal communities.
Here are eight key findings about Christians in India, according to a recent Pew Research Center report.
Pew Research Center conducted this analysis to take a closer look at the Christian population in India. It is based on the 2021 report “Religion in India: Tolerance and Segregation,” the Center’s most comprehensive, in-depth exploration of Indian public opinion to date. For this report, we completed 29,999 face-to-face interviews in 17 languages with adults ages 18 and older living in 26 Indian states and three union territories. The sample included interviews with 22,975 Hindus, 3,336 Muslims, 1,782 Sikhs, 1,011 Christians, 719 Buddhists and 109 Jains. An additional 67 respondents belong to other religions or are religiously unaffiliated. Interviews for this nationally representative survey were conducted from Nov. 17, 2019, to March 23, 2020.
Respondents were selected using a probability-based sample design that would allow for robust analysis of all major religious groups in India, as well as all major regional zones. Six groups were targeted for oversampling as part of the survey design: Muslims, Christians, Sikhs, Buddhists, Jains and those living in the Northeast region. Data was weighted to account for the different probabilities of selection among respondents and to align with demographic benchmarks for the Indian adult population from the 2011 census.
Here are the questions used for this report, along with responses, and its methodology.
Among Indians, 0.4% of adults are Hindu converts to Christianity. Conversion is a contentious issue in India, and nine states have enacted laws against proselytism as of early 2021. While Christianity is a proselytizing religion, many other religions in India are non-proselytizing, and religious conversion is rare in the country. Overall, just 2% of respondents report a different religion than the one in which they were raised, including 0.4% who are converts to Christianity. Christian converts in India mostly are former Hindus, but the survey also finds that Hindus tend to gain as many people as they lose through religious switching (0.7% of respondents were raised Hindu and now identify as something else, while 0.8% were raised as something else but now identify as Hindu). Christian converts in India are disproportionately located in the South, while some are also located in the East. Most converts say they belong to lower castes – that is, they identify with Scheduled Castes (sometimes known as Dalits), Scheduled Tribes or Other Backward Classes. Most converts also come from poor backgrounds – i.e., they report recently struggling to pay for food or other necessities.
There is no clear majority denomination among Indian Christians. While many Indian Christians identify as Catholic (37%), a variety of other denominations are present in India. For example, 13% of Indian Christians are Baptists, 7% identify with the Church of North India and another 7% identify with the Church of South India.
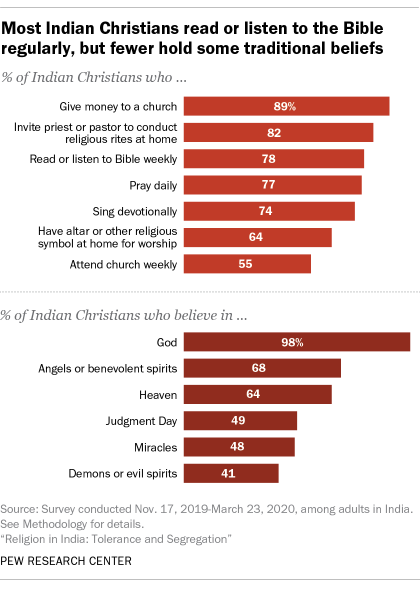
Three-quarters of Indian Christians (76%) say religion is very important in their lives, and Indian Christians engage in a variety of traditional beliefs and practices. Nearly all Indian Christians (98%) say they believe in God, and Christians in India are more likely than most other religious communities to say they pray daily (77%). Most Indian Christians also attend church weekly (55%), and an overwhelming share give money to a church (89%). At the same time, even though 78% of Indian Christians say they read or listen to the Bible at least weekly, smaller shares say they hold several traditional beliefs rooted in the Bible, including belief in Judgment Day (49%) and miracles (48%).
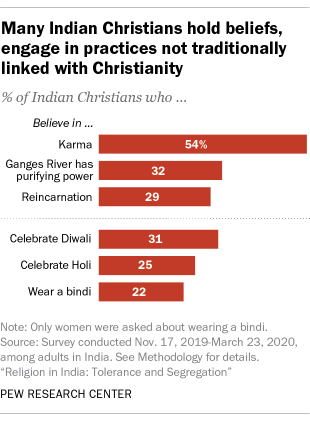
Substantial shares of Indian Christians follow religious practices and beliefs not traditionally associated with Christianity. Most Indian Christians say they believe in karma (54%), which is not rooted in the Christian religion. And many Indian Christians also believe in reincarnation (29%) and that the Ganges River has the power to purify (32%), both of which are core teachings in Hinduism. It is also somewhat common for Indian Christians to observe customs tied to other religions, like celebrating Diwali (31%) or wearing a forehead marking called a bindi (22%), most often worn by Hindu, Buddhist and Jain women.
Indian Christians disproportionally identify with lower castes (74%), including 57% with Scheduled Castes (SC) or Scheduled Tribes (ST). India’s caste system is a social hierarchy that can dictate class and social life, including whom a person can marry. Today, regardless of their religion, Indians nearly universally identify with a caste category. Among Christians, 33% identify as SC, while 24% identify as ST. And Christians are somewhat more likely than the Indian population overall to say there is widespread caste discrimination in India. For example, among Indians overall, 20% say there is widespread discrimination against SCs in India, compared with 31% among Christians who say the same. A smaller share of Christians (18%) say there is a lot of discrimination against Christians in India, and even fewer say they have personally faced recent discrimination based on their caste (11%) or religion (10%).
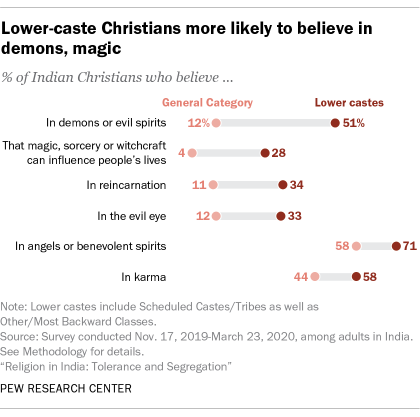
Lower-caste Indian Christians are much more likely than upper-caste (also called General Category) Christians to hold both Christian and non-Christian beliefs. Indian Christians who belong to SCs, STs and other lower castes tend to believe in angels and demons at significantly higher rates than upper-caste Christians. For example, roughly half of lower-caste Christians (51%) believe in demons or evil spirits, while just 12% of higher-caste Christians hold this belief. Lower-caste Christians also are more likely than General Category Christians to believe in spiritual forces not generally associated with Christianity, like karma (58% vs. 44%) and the evil eye (33% vs. 12%).
Overall, Indian Christians are less prone toward religious segregation than some other groups. For instance, Christians are less likely than other religious groups to say that stopping interreligious marriage is “very important.”Among Christians, 37% say stopping the interreligious marriage of Christian women is very important, while 35% say the same about Christian men. In contrast, roughly two-thirds of Hindus and an even greater share of Muslims say it is crucial to stop such marriages by men and women in their respective communities. In addition, fewer Christians (22%) than Hindus (47%) and Muslims (45%) say all of their close friends share their religion. In part, these attitudes may reflect Christians’ regional concentration in the South, where opposition to interreligious marriage is generally less widespread and religious segregation overall is less pronounced.
Politically, Christians favor the opposing Indian National Congress (INC) over the ruling Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP), which is led by Prime Minister Narendra Modi and is often described as promoting a Hindu nationalist ideology. A plurality of Christian voters (30%) say they voted for the INC in the 2019 parliamentary elections, which roughly matches the shares of Muslims and Sikhs who voted for the INC. Just one-in-ten Indian Christian voters say they voted for the BJP in 2019, the lowest share among all of India’s major religious groups. Once again, the voting patterns of Christians in India mirror the political preferences of Southern Indians more generally. In the 2019 parliamentary elections, the BJP received its lowest vote share in the South, including among Hindus; many people in the South, including Christians, voted for regional parties.
Note: Here are the questions used for this report, along with responses, and its methodology.