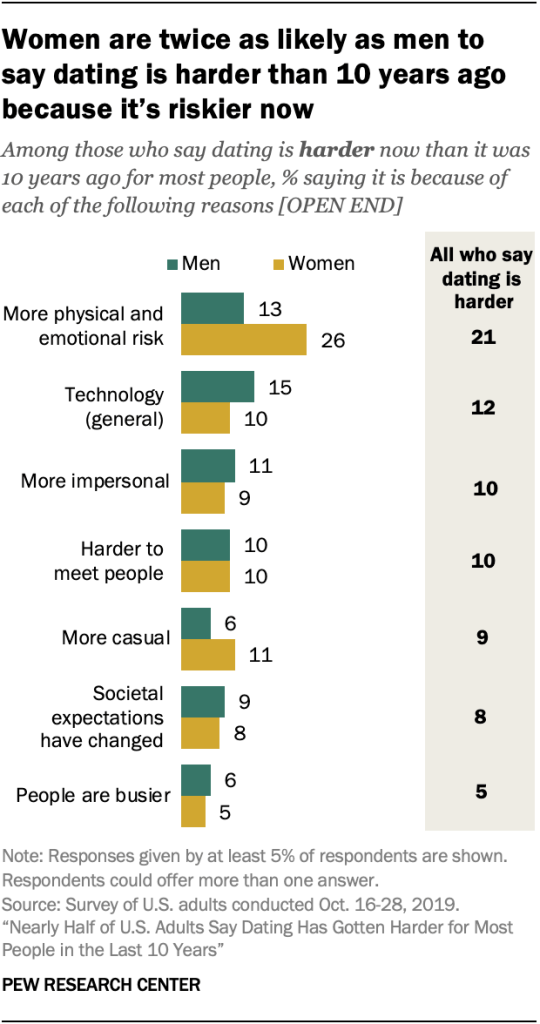Dating has always come with challenges. But the advent of dating apps and other new technologies – as well as the #MeToo movement – presents a new set of norms and expectations for American singles looking for casual or committed relationships, according to a recent Pew Research Center survey.
Some 15% of U.S. adults say they are single and looking for a committed relationship or casual dates. Among them, most say they are dissatisfied with their dating lives, according to the survey, which was conducted in October 2019 – before the coronavirus pandemic shook up the dating scene. Here are some additional key findings from the study.
Pew Research Center conducted this study to understand Americans’ attitudes toward and personal experiences with dating and relationships. These findings are based on a survey conducted Oct. 16-28, 2019, among 4,860 U.S. adults. This includes those who took part as members of the Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP), an online survey panel that is recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses, as well as respondents from the Ipsos KnowledgePanel who indicated that they identify as lesbian, gay or bisexual (LGB).
Recruiting ATP panelists by phone or mail ensures that nearly all U.S. adults have a chance of selection. This gives us confidence that any sample can represent the whole U.S. adult population (see our Methods 101 explainer on random sampling). To further ensure that each ATP survey reflects a balanced cross-section of the nation, the data is weighted to match the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education and other categories.
For more, see the report’s methodology about the project. You can also find the questions asked and the answers the public provided in this topline.
Nearly half (47%) of all Americans say dating is harder today than it was 10 years ago. A third of adults (33%) say dating is about the same as it was a decade ago, and 19% say it’s easier. Women are much more likely than men to say dating has gotten harder (55% vs. 39%).
Among those who say dating is harder today, 21% think it is because of increased risk, including physical risks as well as the risk of getting scammed or lied to. Women are twice as likely as men to cite increased risk as a reason why dating is harder (26% vs. 13%).
Other reasons why people think dating is harder include technology (12%), the idea that dating has become more impersonal (10%), the more casual nature of dating today (9%), and changing societal expectations, moral or gender roles (8%).
Technology tops the list of reasons why people think dating has gotten easier in the last decade. Among those who say dating is easier today, 41% point to technology, followed by 29% who say it’s easier to meet people now and 10% who cite changing gender roles and societal expectations.
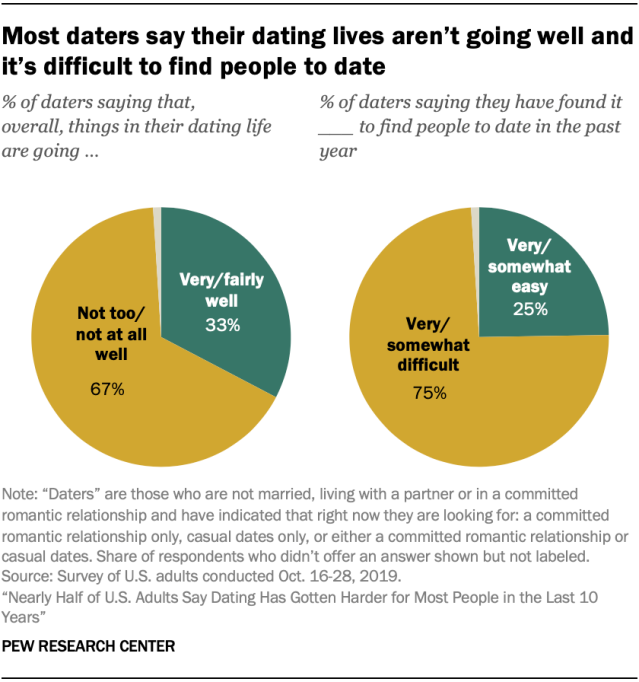
Most daters don’t feel like their dating life is going well and say it’s been hard to find people to date. Two-thirds of those who are single and looking for a relationship or dates say their dating life is going not too or not at all well (67%), while 33% say it’s going very or fairly well. Majorities of daters across gender, age, race and ethnicity, education, sexual orientation and marital history say their dating life isn’t going well.
Three-quarters of daters say it’s been difficult to find people to date in the past year, according to the pre-coronavirus survey. Among the top reasons cited are finding someone looking for the same type of relationship (53%), finding it hard to approach people (46%) and finding someone who meets their expectations (43%).
Substantial shares of daters also report other obstacles, including the limited number of people in their area (37%), being too busy (34%) and people not being interested in dating them (30%).
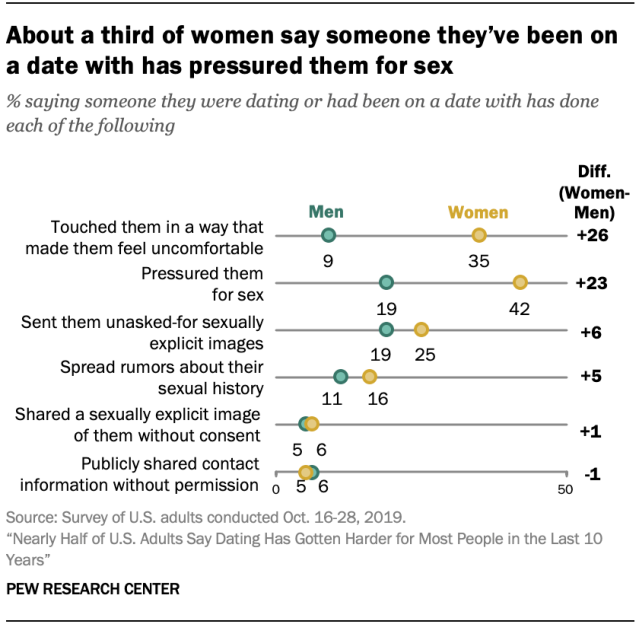
A majority (57%) of women – and 35% of men – say they have experienced some kind of harassing behavior from someone they were dating or had been on a date with. Women are much more likely than men to say they have been pressured for sex (42% vs. 19%) or have been touched in a way that made them feel uncomfortable (35% vs. 9%). While the gender gap is smaller, women are also more likely than men to say someone they have been on a date with sent them unwanted sexually explicit images or spread rumors about their sexual history.
Some 42% of women younger than 40 say someone they’ve been on a date with has sent them unwanted sexually explicit images, compared with 26% of men in this age group. And while 23% of women younger than 40 say someone they have been on a date with has spread rumors about their sexual history, 16% of younger men say the same. There is no gender gap on these questions among those older than 40.
Many Americans say an increased focus on sexual harassment and assault has muddied the waters, especially for men, in the dating landscape. A majority of Americans (65%) say the increased focus on sexual harassment and assault over the last few years has made it harder for men to know how to interact with someone they’re on a date with. About one-in-four adults (24%) say it hasn’t made much of a difference, while 9% say it has made things easier for men.
Meanwhile, 43% of Americans say the attention paid to sexual harassment and assault has made it harder for women to know how to interact with someone they’re on a date with, compared with 38% who say it hasn’t made much of a difference and 17% who say it’s easier for women.
Men are more likely than women to think the focus on sexual harassment and assault has made it harder for men to know how to act on dates. Republicans and Republican-leaning independents are more likely than Democrats and Democratic leaners to say this. Older men are also more likely than their younger counterparts to hold this view: Three-quarters of men 50 and older say it’s harder for single-and-looking men to know how to behave, compared with 63% of men younger than 50.
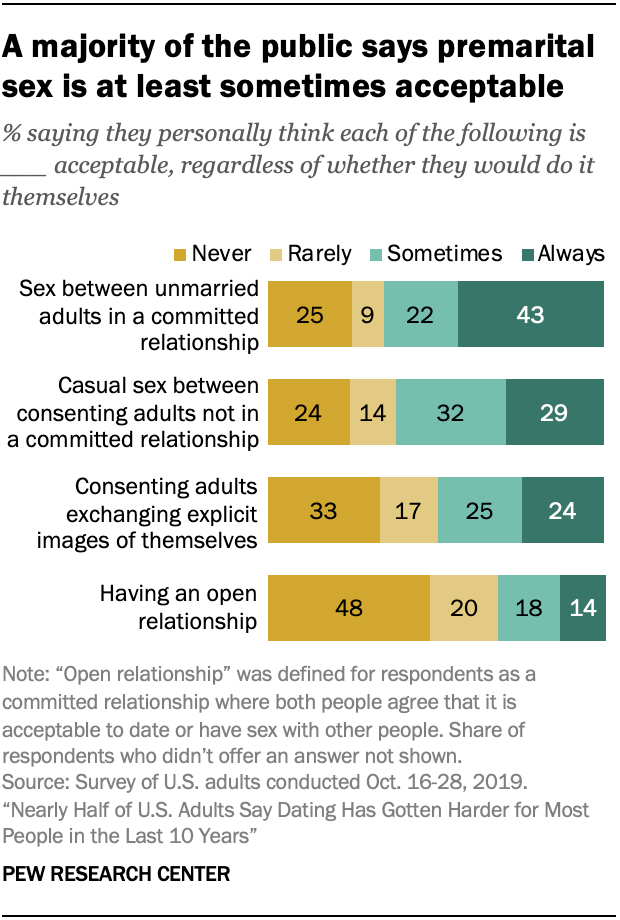
Premarital sex is largely seen as acceptable, but more Americans see open relationships and sex on the first date as taboo. Most adults (65%) say sex between unmarried adults in a committed relationship can be acceptable, and about six-in-ten (62%) say casual sex between consenting adults who aren’t in a committed relationship is acceptable at least sometimes. While men and women have similar views about premarital sex, men are much more likely than women to find casual sex acceptable (70% vs. 55%).
Americans are less accepting of other practices. For example, open relationships – that is, committed relationships where both people agree that it is acceptable to date or have sex with other people – are viewed as never or rarely acceptable by most Americans. About half of adults (48%) say having an open relationship is never acceptable, 20% say it’s rarely acceptable and 32% say it’s sometimes or always acceptable.
When it comes to consenting adults sharing sexually explicit images of themselves, about half of adults (49%) say it is at least sometimes acceptable, while a similar share (50%) say it is rarely or never acceptable. However, there are large age differences in views of this practice. Adults ages 18 to 29 are more than three times as likely as those 65 and older to say this is always or sometimes acceptable (70% vs. 21%). Younger adults are also more likely to say open relationships can be acceptable.
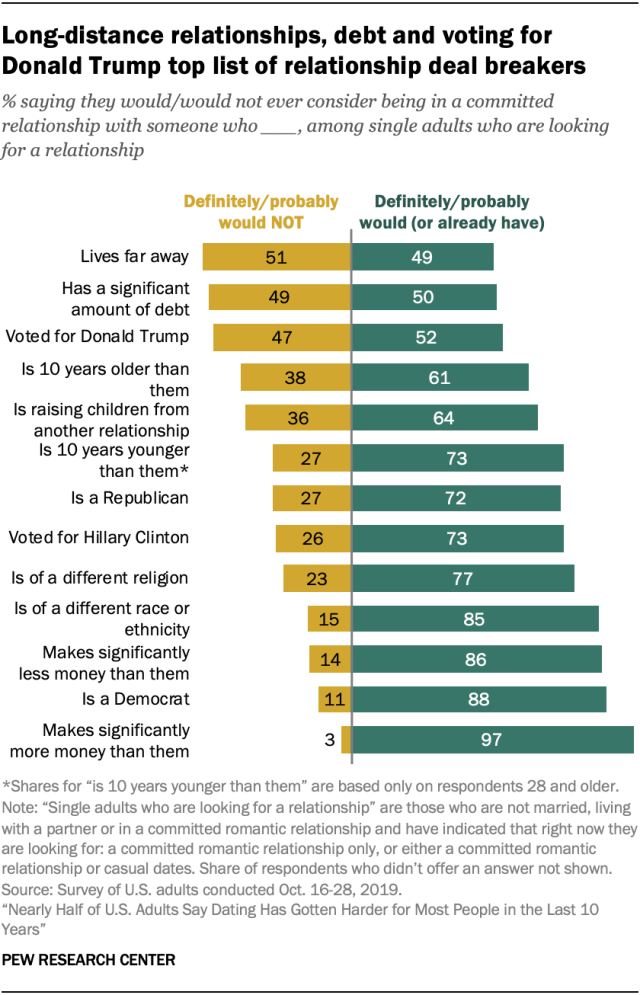
Many singles are open to dating someone who is different from them, but certain characteristics would give some people pause. Distance, debt and voting for Donald Trump top the list of reasons singles looking for a relationship wouldn’t consider a potential partner, but there are other considerations, too. For example, 38% say dating someone 10 years older than them would give them pause, and 36% say the same about dating someone who is raising children from another relationship. Some of those looking for a relationship also say they definitely or probably wouldn’t consider being in a relationship with someone who is a Republican (27% of all daters), someone who voted for Hillary Clinton (26%), someone who practices a different religion (23%) or someone who is a different race or ethnicity (15%). Among daters looking for a relationship who are 28 and older, 27% say they definitely or probably wouldn’t consider a relationship with someone 10 years younger than them.
There are some differences in these attitudes by gender, political party and age. For example, single women looking for a relationship are roughly three times as likely as men to say they wouldn’t consider a relationship with someone who makes significantly less money than them (24% vs. 7%). Republicans are more likely than Democrats to say they probably or definitely wouldn’t consider a committed relationship with someone of a different race or ethnicity (21% vs. 12%). And when it comes to debt, 59% of adults 40 and older say they probably or definitely wouldn’t consider a committed relationship with someone who has significant debt, compared with 41% of people younger than 40.
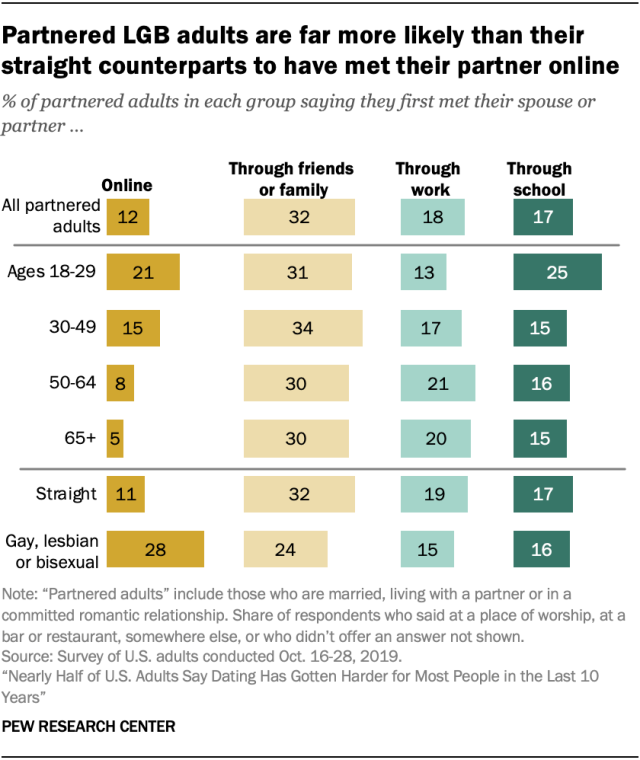
While meeting partners through personal networks is still the most common kind of introduction, about one-in-ten partnered adults (12%) say they met their partner online. About a third (32%) of adults who are married, living with a partner or are in a committed relationship say friends and family helped them find their match. Smaller shares say they met through work (18%), through school (17%), online (12%), at a bar or restaurant (8%), at a place of worship (5%) or somewhere else (8%).
Meeting online is more common among younger adults and those who live in urban and suburban areas, as well as those who are lesbian, gay or bisexual (LGB). About one-in-five partnered adults ages 18 to 29 (21%) say they met their partner online, compared with 15% or fewer among their older counterparts. And while 28% of partnered LGB adults say they met their partner online, 11% of those who are straight say the same.
Among those who met their partner online, 61% say they met through a dating app, while 21% met on a social media site or app, 10% met on an online discussion forum, 3% met on a texting or messaging app and 3% through online gaming.
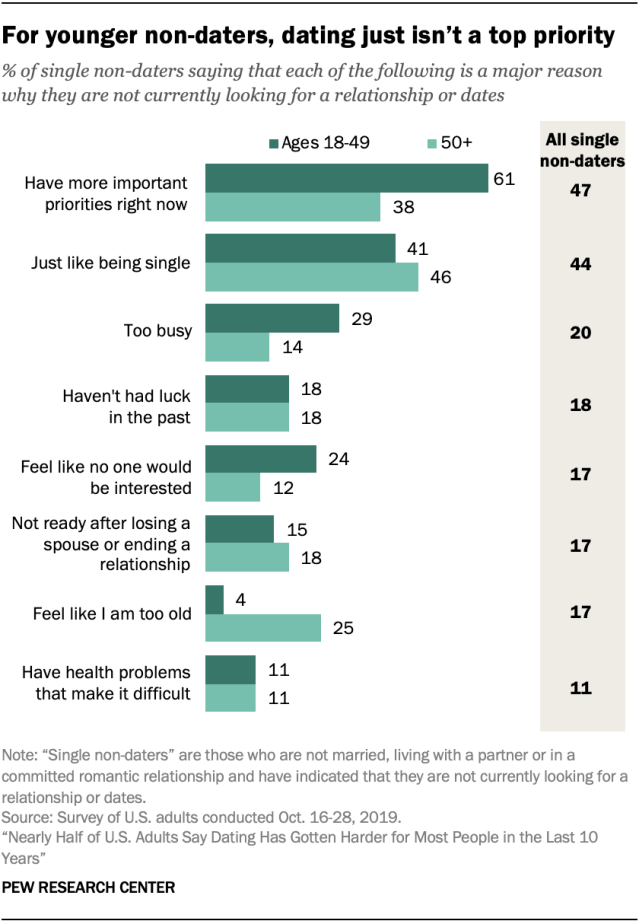
Half of singles say they aren’t currently looking for a relationship or dates. Among these single non-daters, 47% say a major reason why they aren’t currently looking for a relationship or dates is that they have more important priorities, while 44% say they just like being single. Other factors include being too busy (20%), not having had luck in the past (18%), feeling like no one would be interested in dating them (17%), not being ready to date after losing a spouse or ending a relationship (17%), feeling too old to date (17%) and having health problems that make dating difficult (11%).
While these answers are mostly similar for men and women, there is one notable exception: Male non-daters are about twice as likely as female non-daters to say a major reason they aren’t looking to date is the feeling that no one would be interested in dating them (26% vs. 12%).
There is also some variation by age. For example, 61% of non-daters younger than 50 say that a major reason they aren’t looking to date is that they have more important priorities, compared with 38% of older non-daters. And a quarter of non-daters ages 50 and older – including 30% of those 65 and up – say a major reason is they that feel too old to date.
Note: Here are the questions asked for this report, along with responses, and its methodology.