In recent years, a host of new ways have emerged for people with little or no formal science training to take part in scientific research projects. Such citizen science often entails crowdsourcing data collection related to natural phenomena such as birds and astronomical objects – and, lately, the COVID-19 pandemic – but it can encompass a wide range of other activities.
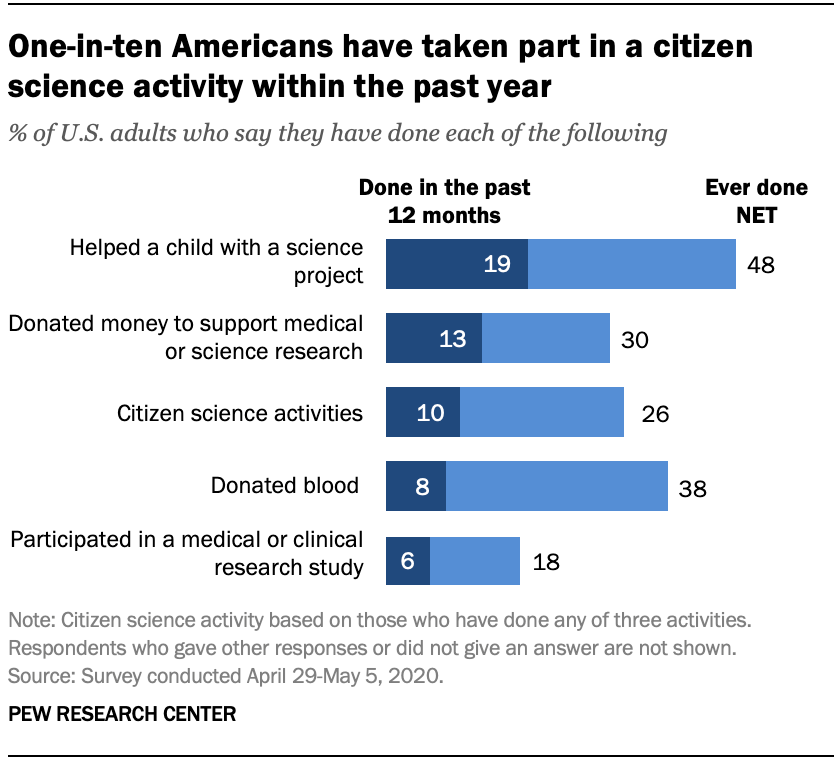 One-in-ten U.S. adults say they have taken part in an activity classified as citizen science in the past year, and 26% say they have ever done so, according to a Pew Research Center survey conducted April 29-May 5.
One-in-ten U.S. adults say they have taken part in an activity classified as citizen science in the past year, and 26% say they have ever done so, according to a Pew Research Center survey conducted April 29-May 5.
The Center survey combined responses to three questions to better capture the range of citizen science activities. The survey asked respondents if they had made observations or collected data samples as part of a science research project, contributed to a science-related online crowdsourcing activity, or participated in “a maker movement or hack-a-thon,” in which citizens seek to adapt and invent through hands-on use of science, technology and engineering tools.
This analysis about Americans’ behavioral engagement with science and scientific research is based on a survey of 10,957 U.S. adults conducted from April 29 to May 5, 2020. Everyone who took part is a member of Pew Research Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP), an online survey panel that is recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses. This way nearly all U.S. adults have a chance of selection. The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education and other categories. Read more about the ATP’s methodology.
Here are the questions used for this report, along with responses, as well as its methodology.
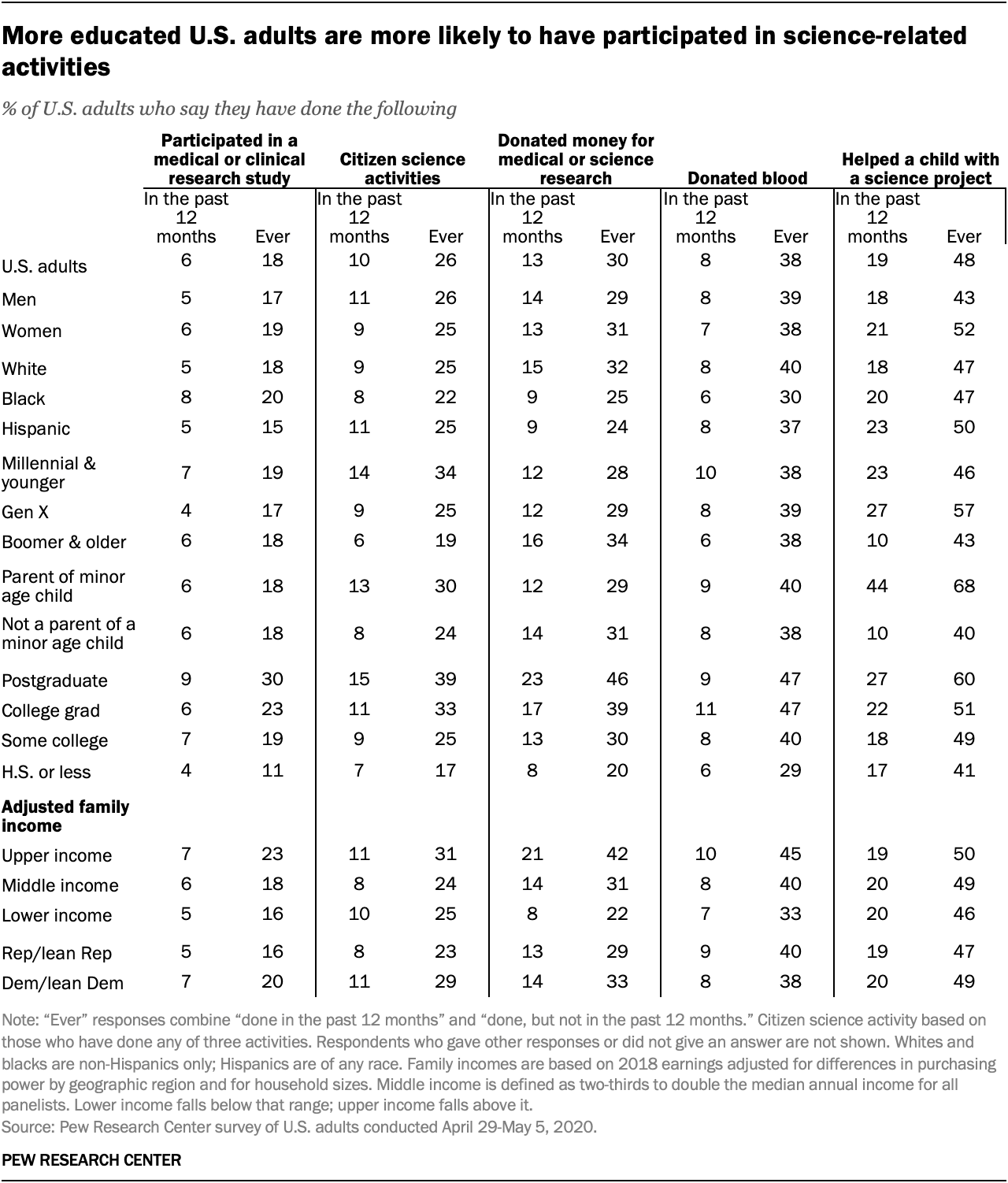
Other ways people have engaged with science and scientific research over the past year include taking part in a clinical or medical research study (6%) and giving money to support medical or science research (13%). For comparison, about two-in-ten adults (19%) and 44% of parents with a minor-age child say they have helped a child with a science project in the past year.
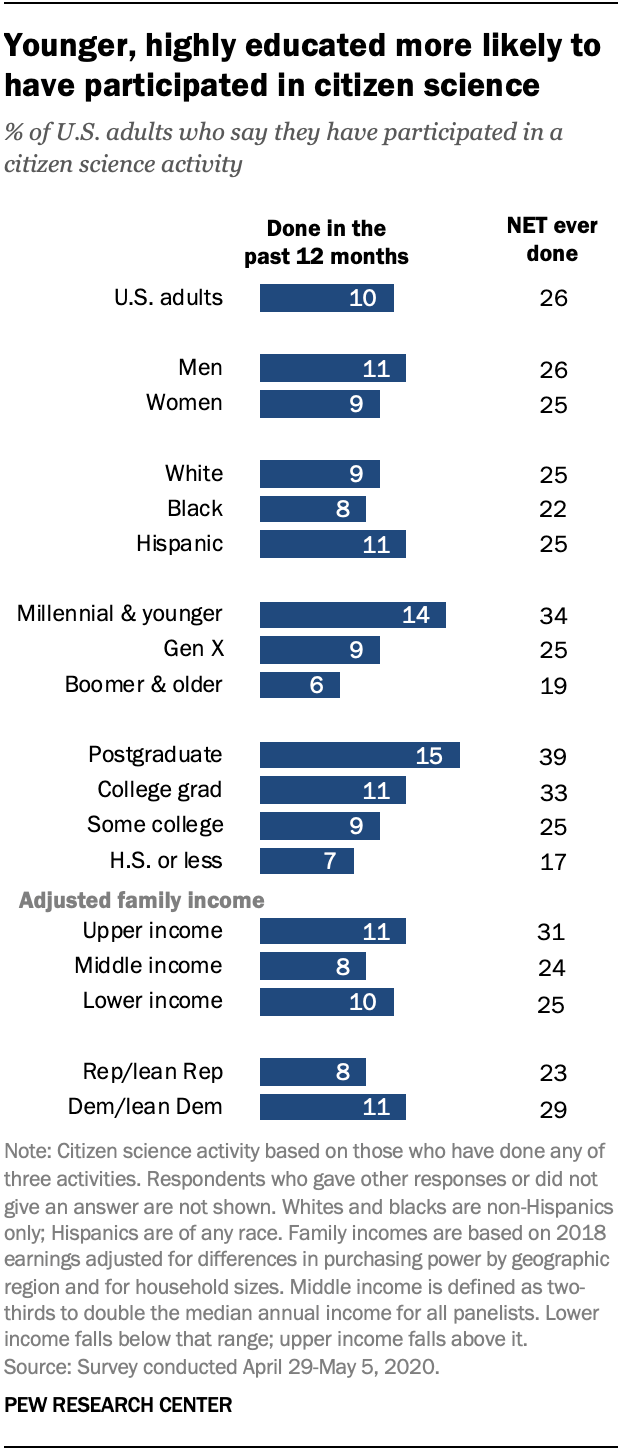 Younger generations and Americans with a postgraduate degree are more likely to have participated in some kind of citizen science activity.
Younger generations and Americans with a postgraduate degree are more likely to have participated in some kind of citizen science activity.
One-in-seven Millennial and Generation Z adults (14%) have taken part in a citizen science project over the past year, and a total of 34% have done so at some point in the past. By contrast, Baby Boomer and older adults are about half as likely to say they have participated in a citizen science activity in the past year.
People with higher levels of education are more likely to have engaged in all five science-related activities on the survey, including citizen science. Among those with a postgraduate degree, 15% have done a citizen science activity in the past year, compared with 7% of those with a high school diploma or less. (For more information, see the detailed table below.)
While a recent Center study found a growing divide between political groups over their trust in scientists, citizen science tends to cut across party lines; 8% of Republicans and those who lean to the Republican Party say they took part in a citizen science project over the past year, as did 11% of Democrats and Democratic leaners.
Note: Here are the questions used for this report, along with responses, as well as its methodology.