Personal experiences with racial discrimination are common for black Americans. But certain segments within this group – most notably, those who are college educated or male – are more likely to say they’ve faced certain situations because of their race, according to a new Pew Research Center survey.
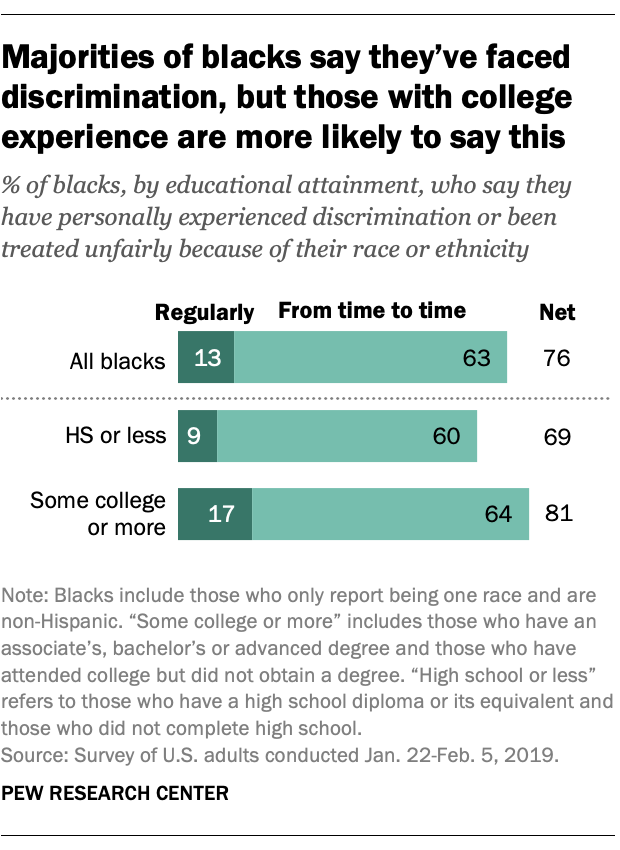 A majority of black adults say they have been discriminated against because of their race, but this varies by education. Roughly eight-in-ten blacks with at least some college experience (81%) say they’ve experienced racial discrimination, at least from time to time, including 17% who say this happens regularly. Among blacks with a high school education or less, these shares are lower – 69% and 9%, respectively.
A majority of black adults say they have been discriminated against because of their race, but this varies by education. Roughly eight-in-ten blacks with at least some college experience (81%) say they’ve experienced racial discrimination, at least from time to time, including 17% who say this happens regularly. Among blacks with a high school education or less, these shares are lower – 69% and 9%, respectively.
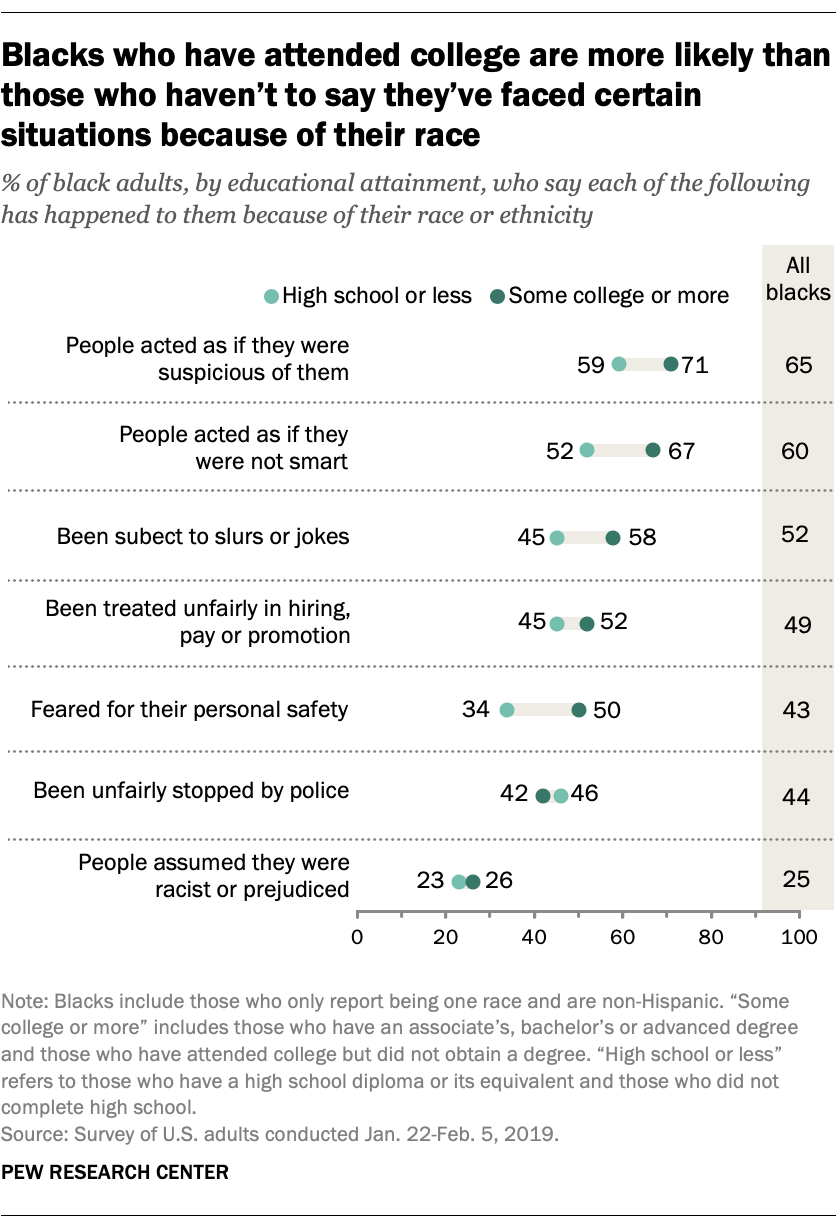 When asked about specific situations they may have experienced because of their race, blacks who have attended college are more likely than those without college experience to say they have faced a number of these incidents: people acting as if they were suspicious of them (71% vs. 59%), people acting as if they were not smart (67% vs. 52%) or being subjected to slurs or jokes (58% vs. 45%). Half of blacks with at least some college experience also say they have feared for their personal safety because of their race. That share drops to about a third (34%) among those with less education.
When asked about specific situations they may have experienced because of their race, blacks who have attended college are more likely than those without college experience to say they have faced a number of these incidents: people acting as if they were suspicious of them (71% vs. 59%), people acting as if they were not smart (67% vs. 52%) or being subjected to slurs or jokes (58% vs. 45%). Half of blacks with at least some college experience also say they have feared for their personal safety because of their race. That share drops to about a third (34%) among those with less education.
College-educated blacks are also more inclined to believe their race has negatively impacted their ability to succeed: 57% of blacks with at least some college experience believe being black has hurt their ability to get ahead, compared with 47% of those with a high school education or less.
This pattern has been consistent across multiple surveys. A 2016 Pew Research Center survey found similar educational gaps among blacks in experiences with discrimination. And a 2017 NPR poll found that being subjected to racial slurs or offensive comments was more common among blacks with a college degree than those with less education.
So why is this? Other researchers suggest that college-educated blacks are more likely to work in predominately white environments, which may lead to greater exposure to race-related prejudices or stresses. One scholar noted that college itself may offer blacks more opportunities to discuss race and discrimination through classes and organizations, thereby raising their awareness of these issues.
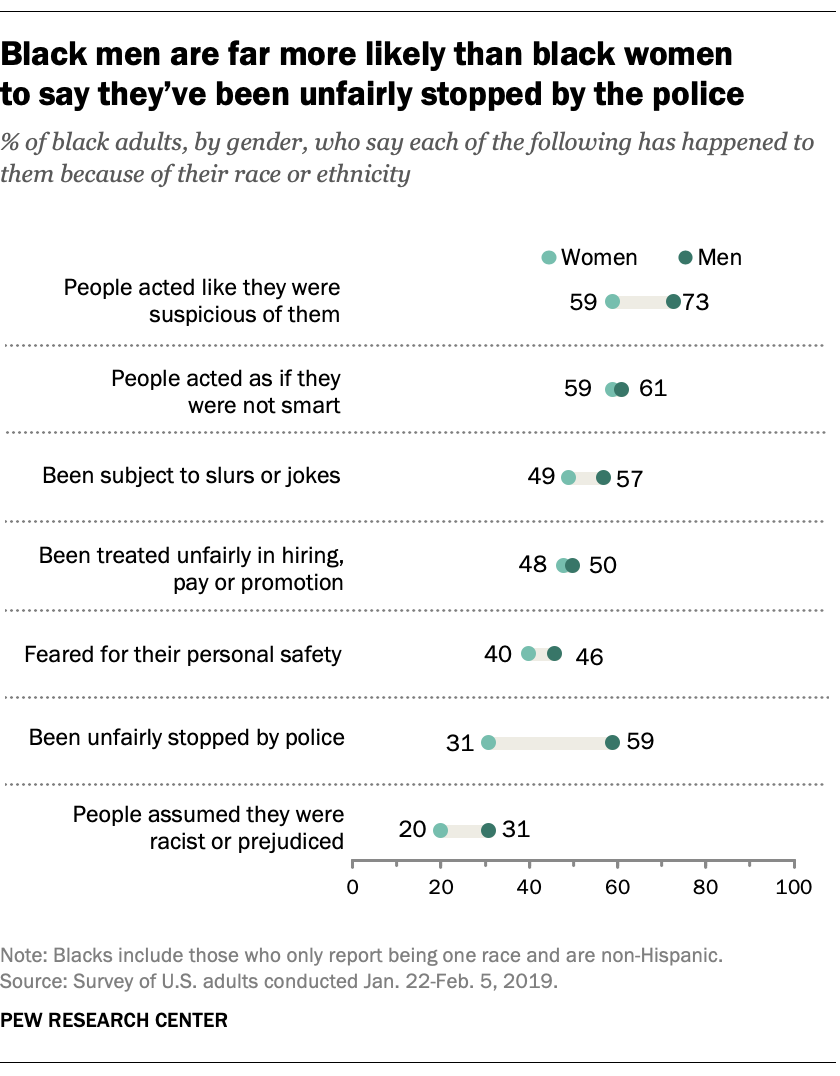 Beyond educational differences, experiences with certain forms of discrimination also differ by gender. This is most evident in reported interactions with law enforcement. In the new survey, 59% of black men say they have been unfairly stopped by the police because of their race, compared with 31% of black women. Black men are also more likely than black women to say people have acted as if they were suspicious of them, that they’ve been subjected to slurs or jokes, or that someone assumed they were racist or prejudiced because of their racial background.
Beyond educational differences, experiences with certain forms of discrimination also differ by gender. This is most evident in reported interactions with law enforcement. In the new survey, 59% of black men say they have been unfairly stopped by the police because of their race, compared with 31% of black women. Black men are also more likely than black women to say people have acted as if they were suspicious of them, that they’ve been subjected to slurs or jokes, or that someone assumed they were racist or prejudiced because of their racial background.
Still, some experiences are equally common for both groups. Among blacks, similar shares of men and women say they have feared for their personal safety, that people have acted as if they were not smart, or that they’ve been treated unfairly in hiring, pay or promotion because of their race. There are also no gender differences when it comes to general experiences with racial discrimination.
Other factors are not strongly associated with facing specific types of discrimination. Black adults under the age of 50 are just as likely as those 50 and older to say they’ve faced certain situations because of their race. For example, 54% of blacks ages 18 to 49 say they have been subject to slurs or jokes because of their race, which is similar to the share among those 50 and older (50%). Additionally, skin tone is not necessarily correlated with encountering these types of situations. More specifically, blacks who identify as having lighter skin are about as likely as those with a deeper complexion to say they’ve faced specific situations because of their race.



