A growing share of people around the world see U.S. power and influence as a “major threat” to their country, and these views are linked with attitudes toward President Donald Trump and the United States as a whole, according to Pew Research Center surveys conducted in 22 nations since 2013.
 A median of 45% across the surveyed nations see U.S. power and influence as a major threat, up from 38% in the same countries during Trump’s first year as president in 2017 and 25% in 2013, during the administration of Barack Obama. The long-term increase in the share of people who see American power as a threat has occurred alongside declines in the shares of people who say they have confidence in the U.S. president to do the right thing regarding world affairs and who have a favorable view of the United States. (For more about global views toward the U.S. president and the country he leads, see “Trump’s International Ratings Remain Low, Especially Among Key Allies.”)
A median of 45% across the surveyed nations see U.S. power and influence as a major threat, up from 38% in the same countries during Trump’s first year as president in 2017 and 25% in 2013, during the administration of Barack Obama. The long-term increase in the share of people who see American power as a threat has occurred alongside declines in the shares of people who say they have confidence in the U.S. president to do the right thing regarding world affairs and who have a favorable view of the United States. (For more about global views toward the U.S. president and the country he leads, see “Trump’s International Ratings Remain Low, Especially Among Key Allies.”)
Despite these changes, U.S. power and influence still ranks below other perceived threats around the world. Considerably larger shares of people point to global climate change (seen as a major threat by a median of 67%), the Islamic militant group known as ISIS (cited by 62%) and cyberattacks (cited by 61%). U.S. power and influence, in fact, is not seen as the top threat in any of the countries surveyed.
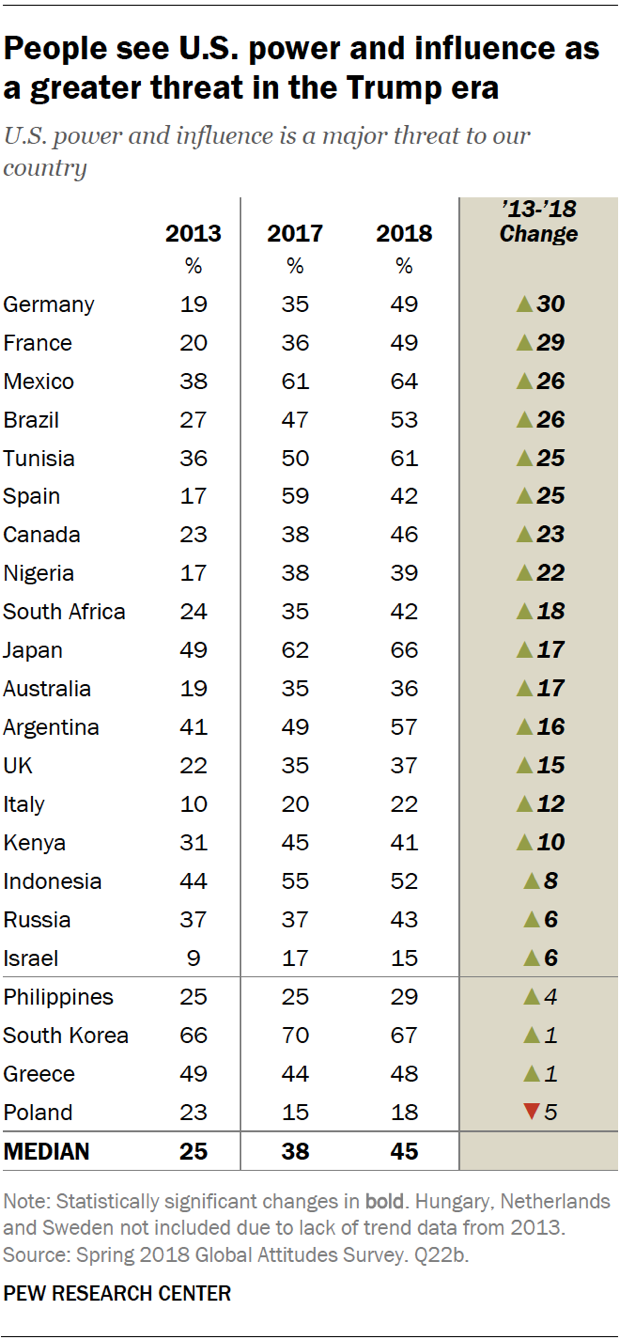 Still, in 18 of the 22 countries, there were statistically significant increases in the share of people who see American power and influence as a major threat between 2013 and 2018. That includes increases of 30 percentage points in Germany, 29 points in France, and 26 points in Brazil and Mexico. And while these shares rose substantially in many countries after Trump’s election, they increased further in several nations between Trump’s first and second year in office.
Still, in 18 of the 22 countries, there were statistically significant increases in the share of people who see American power and influence as a major threat between 2013 and 2018. That includes increases of 30 percentage points in Germany, 29 points in France, and 26 points in Brazil and Mexico. And while these shares rose substantially in many countries after Trump’s election, they increased further in several nations between Trump’s first and second year in office.
In Germany and France, for instance, the share of people who see U.S. power and influence as a major threat went up by 14 and 13 percentage points, respectively, between 2017 and 2018. Other notable year-over-year increases occurred in Tunisia (11 points), Canada and Argentina (8 points each), South Africa (7 points) and Brazil and Russia (6 points each).
Other nations bucked this trend, however. In Spain, for example, the share of people who see American power as a major threat fell by 17 points between 2017 and 2018 (from 59% to 42%). Still, people in Spain remain much more likely to see the U.S. as a threat today than in 2013.
Overall, there are 10 nations surveyed where roughly half or more now see U.S. power as a major threat, with the biggest shares saying this in South Korea (67%), Japan (66%) and Mexico (64%).
In South Korea, equal shares point to U.S. power and influence and to North Korea’s nuclear program as a major threat to their nation (each is cited by 67% of the public). However, several other perceived threats to South Koreans outrank U.S. power and influence, including global climate change (named by 86% of South Koreans), China’s power and influence (cited by 82%), cyberattacks from other countries (cited by 81%) and the condition of the global economy (cited by 74%). South Koreans have long perceived American power as a major threat to their country: 66% said this in 2013 and 70% said it in 2017.
In many of the surveyed countries, concerns about American power and influence are connected with views of Trump: People who have little or no confidence in the U.S. president to do the right thing regarding world affairs are more likely than those who have confidence in Trump to see U.S. power and influence as a top threat to their country. This includes several longtime U.S. allies, including Canada, the UK and Australia.
The same pattern appears when it comes to views of the U.S. in general, as opposed to its president. In most surveyed nations, people who have a more unfavorable view of the U.S. are also more likely to say that American power and influence is a threat to their nation.



