
After years of decline, the number of arrests made by U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) climbed to a three-year high in fiscal 2017, according to data from the agency. The biggest percentage increases were in Florida, northern Texas and Oklahoma.
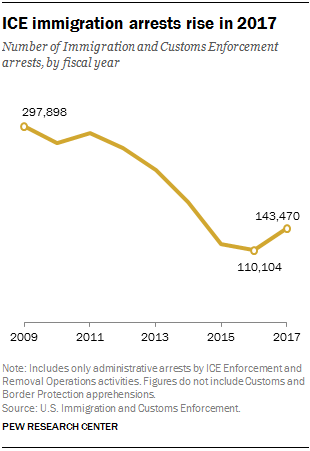
ICE Enforcement and Removal Operations made a total of 143,470 arrests in fiscal 2017, a 30% rise from fiscal 2016. The surge began after President Donald Trump took office in late January: From his Jan. 20 inauguration to the end of the fiscal year on Sept. 30, ICE made 110,568 arrests, 42% more than in the same time period in 2016.
Trump signed an executive order on Jan. 25 that expanded ICE’s enforcement focus to most immigrants in the U.S. without authorization, regardless of whether they have a criminal record. Under President Barack Obama, by contrast, ICE focused its enforcement efforts more narrowly, such as by prioritizing the arrests of those convicted of serious crimes.
Despite the overall rise in arrests in 2017, ICE made about twice as many arrests in fiscal 2009, the year Obama came into office (297,898). This total generally declined in subsequent years.
ICE reports arrests geographically by “areas of responsibility.” Although they are named for field offices in major cities, these areas can encompass large regions of the U.S., with some covering four or more states. The Miami area of responsibility, which covers all of Florida, Puerto Rico and the U.S. Virgin Islands, saw the largest percentage increase in ICE arrests between 2016 and 2017 (76%). Next were the Dallas and St. Paul regions (up 71% and 67%, respectively). Arrests increased by more than 50% in the New Orleans, Atlanta, Boston and Detroit regions as well.
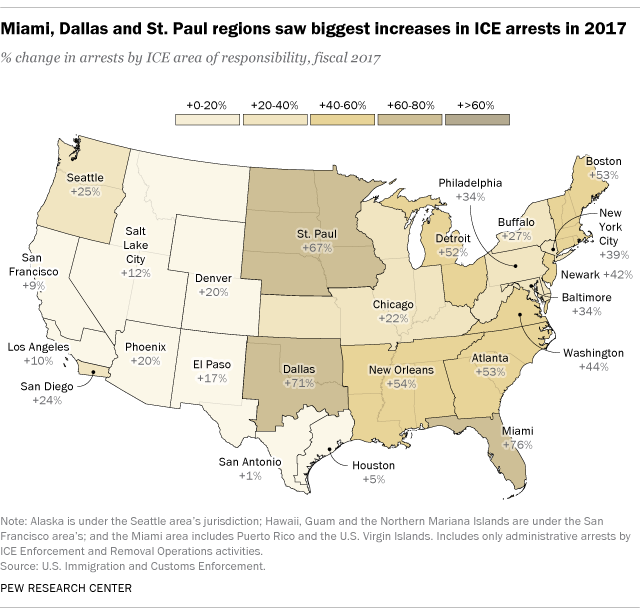 Other ICE regions, including those on the U.S.-Mexico border, saw relatively little change in arrests compared with the 30% increase nationally. The Phoenix and El Paso areas, for example, rose around 20% each. The San Antonio and Houston areas in particular saw almost no growth from 2016 to 2017 (up 1% and 5%, respectively). No region reported a decrease in arrests.
Other ICE regions, including those on the U.S.-Mexico border, saw relatively little change in arrests compared with the 30% increase nationally. The Phoenix and El Paso areas, for example, rose around 20% each. The San Antonio and Houston areas in particular saw almost no growth from 2016 to 2017 (up 1% and 5%, respectively). No region reported a decrease in arrests.
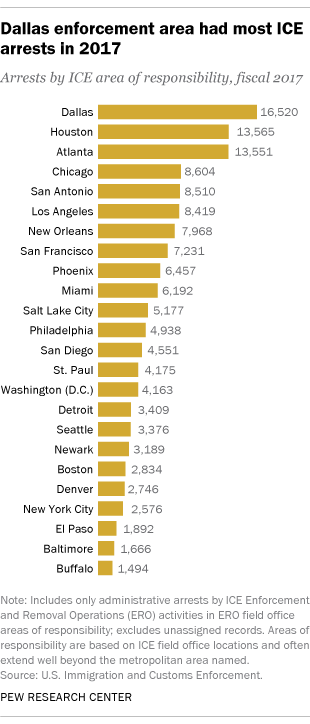 The overall number of immigration arrests made by ICE in 2017 varied around the U.S., and the most arrests did not always occur in areas close to the U.S.-Mexico border or in places with the largest unauthorized immigrant populations (such as the New York and Los Angeles metro areas).
The overall number of immigration arrests made by ICE in 2017 varied around the U.S., and the most arrests did not always occur in areas close to the U.S.-Mexico border or in places with the largest unauthorized immigrant populations (such as the New York and Los Angeles metro areas).
ICE arrests were highest in the agency’s Dallas area (16,520), which also saw the largest increase in absolute numbers between 2016 and 2017 (up 6,886). The Houston and Atlanta areas had the second- and third-highest totals in 2017 (each around 13,500), followed by the Chicago, San Antonio and Los Angeles areas (each with roughly 8,500 arrests).
The Dallas area led the nation in ICE arrests last year for the first time during the period analyzed (fiscal 2009-2017). In more recent years, areas closer to the Texas-Mexico border (including Houston and San Antonio) topped the list for arrests. However, the El Paso area, which is also located on the country’s southern border, had among the fewest ICE arrests in the nation in 2017, with fewer than 2,000 – just slightly more than in the Baltimore and Buffalo areas.
Despite a 39% increase in arrests, the New York area of responsibility had among the fewest total ICE arrests in 2017 (roughly 2,600), even though it includes the New York City metro area – home to one of the nation’s largest unauthorized immigrant populations, according to Pew Research Center estimates. The city itself has recently gained attention for its limited cooperation with federal immigration procedures and attempts to boost its “sanctuary city” status by expanding protections for unauthorized immigrants. New York was among several jurisdictions cited by ICE as having policies that restrict cooperation with federal immigration authorities. Jurisdictions within the Baltimore, Buffalo and El Paso areas also made the list. (Many of these policies were enacted long before Trump took office.)
Recent immigration arrest patterns demonstrate a growing emphasis by federal authorities on interior enforcement efforts. While ICE arrests went up significantly between 2016 and 2017, arrests made by U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP) – the federal agency responsible for enforcing U.S. immigration laws on the border – have declined. CBP agents made 310,531 apprehensions in 2017, down 25% from 2016 and the lowest total in over 45 years. Despite this decrease, CBP apprehensions still far outnumber arrests by ICE.
Note: This post and accompanying map have been updated to clarify that outlying U.S. territories are covered by areas of responsibility.



