CORRECTION (Jan. 12, 2024): Chapter 3 of a previous version of this report included an incorrect percentage because one survey question was asked only of women. Among Black adults, 55% say they have ever had at least one of six negative experiences with doctors or other health care providers.
Black Americans offer a mixed assessment of the progress that has been made improving health outcomes for Black people: 47% say health outcomes for Black people have gotten better over the past 20 years, while 31% say they’ve stayed about the same and 20% think they’ve gotten worse.
Less access to quality medical care is the top reason Black Americans see contributing to generally worse health outcomes for Black people in the U.S. Large shares also see other factors as playing a role, including environmental quality problems in Black communities, and hospitals and medical centers giving lower priority to the well-being of Black people.
Asked about their own health care experiences, most Black Americans have positive assessments of the quality of care they’ve received most recently. However, a majority (55%) say they’ve had at least one of six negative experiences, including having to speak up to get the proper care and being treated with less respect than other patients. (A seventh issue asked about applied only to women.)
By and large, Black Americans do not express a widespread preference to see a Black health care provider for routine care: 64% say this makes no difference to them, though 31% say they would prefer to see a Black health care provider for care.
The experiences of younger Black women in the medical system stand out in the survey. A large majority of Black women ages 18 to 49 report having had at least one of seven negative health care experiences included in the survey. They are also more likely than other Black adults to say they would prefer a Black health care provider for routine care and to say a Black doctor or other health care provider would do a better job than medical professionals of other races and ethnicities at providing them with quality medical care.
Beliefs about key factors in health disparities for Black Americans
There are long-standing differences in health outcomes for Black people. Disproportionate mortalities from COVID-19 have heightened disparities between Black and other racial and ethnic populations in the U.S. The most recent estimates from the U.S. Census bureau projects life expectancy at 71.8 years for non-Hispanic Black Americans, the lowest since 2000 and below that estimated for other racial and ethnic groups. The White, non-Hispanic population experienced a smaller decline and, as a result, the gap between expected lifespans for Black and White Americans has widened in the past few years.
Experts have pointed to a number of contributing factors to disparities in health outcomes for Black Americans. The Center survey asked Black Americans for their own views about the reasons behind these disparities and their sense of whether there has been progress over time.
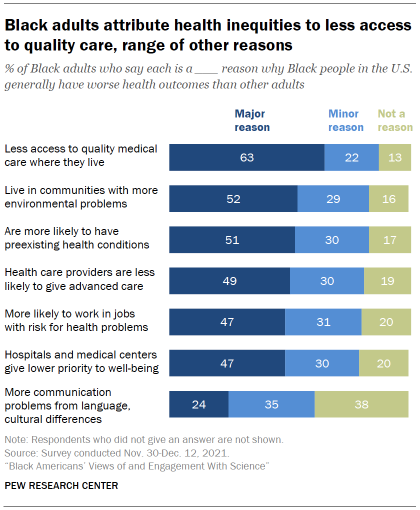
A majority of Black adults say less access to quality medical care where they live is a major reason why Black people in the U.S. generally have worse health outcomes than other adults. About two-in-ten (22%) say this is a minor reason, while just 13% say it is not a reason.
Black adults see a range of other factors – including environmental problems and less-advanced care from health care providers – as contributing to worse health outcomes for Black adults, though somewhat smaller shares cite these as major reasons than point to access issues.
About half (51%) say a major reason why Black people generally have worse health outcomes than others is because they are more likely to have preexisting health conditions. Issues with home and work environments also are seen as playing a role: 52% say a major reason why Black people have worse health outcomes than others is because they live in communities with more environmental problems that cause health issues; 47% say a major reason is that Black people are more likely to work in jobs that put them at risk for health problems.
The health care system is also seen as contributing to the problem: 49% say a major reason why Black people generally have worse health outcomes is because health care providers are less likely to give Black people the most advanced medical care. A roughly equal share (47%) says hospitals and medical centers giving lower priority to their well-being is a major reason for differing health outcomes.
A smaller share (24%) views communication problems from language or cultural differences as a major reason why Black people generally have worse health outcomes than other adults in the U.S.
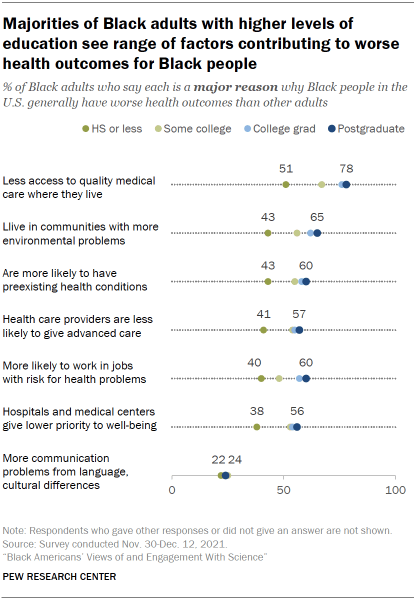
Black adults with higher levels of education are more likely than those with lower levels of education to point to a variety of factors as major reasons for worse health outcomes among Black people.
For instance, large majorities of Black postgraduates (78%) and college graduates (76%) say less access to quality medical care is a major reason Black people have worse health outcomes than other adults in the U.S., compared with 67% of those with some college experience and 51% of Black adults with a high school diploma or less education.
There are also differences in views by age. A majority of Black adults ages 50 and older (58%) say that being more likely to have preexisting health conditions is a major reason why Black people have worse health outcomes than others. Fewer of those under age 50 (46%) see this as a major reason.
Conversely, younger Black adults are more likely than older adults to cite actions from hospitals and medical centers: 50% of those under age 50 say hospitals and medical centers giving lower priority to their well-being is a major reason why Black people have worse health outcomes; 43% of Black adults 50 and older say the same.
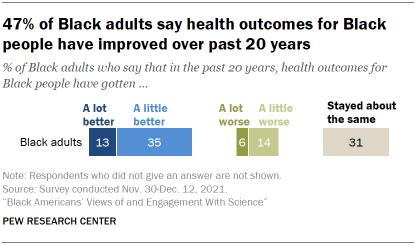
Overall, 47% think health outcomes for Black people have gotten a lot or a little better over the last 20 years. Still, 31% say they have stayed about the same and 20% think they have gotten a lot or a little worse.
For the most part, Black adults’ views on this question are fairly similar across characteristics such as age, gender and levels of educational attainment.
A majority of Black Americans give positive ratings of their recent health care, but can also point to negative experiences in the past
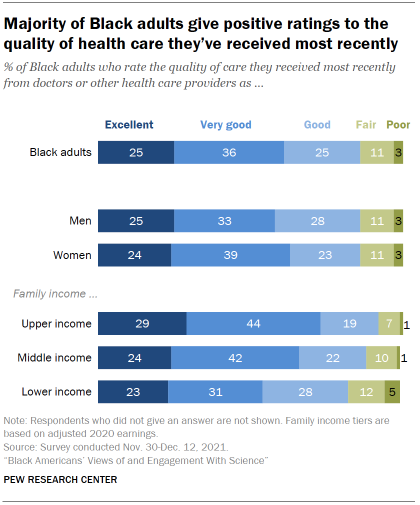
Black adults have generally positive impressions of their most recent experience with health care. A majority (61%) rate the quality of care they’ve received from doctors or other health care providers recently as excellent (25%) or very good (36%). A quarter describe the quality as good, while just 11% say it was fair and only 3% describe the quality of care they’ve received most recently as poor. These ratings are nearly identical to those of all U.S. adults.
Those with higher incomes report more positive recent experiences with doctors and other health care providers than do those with lower incomes.
When it comes to cost, 51% of Black adults describe the out-of-pocket cost of their most recent medical care as ‘about what is fair.’ About a quarter (27%) say they paid more than what’s fair, while 19% say they paid less than what’s fair. For more details, see the Appendix.
A majority of Black adults report at least one negative interaction with doctors and other health care providers at some point in the past
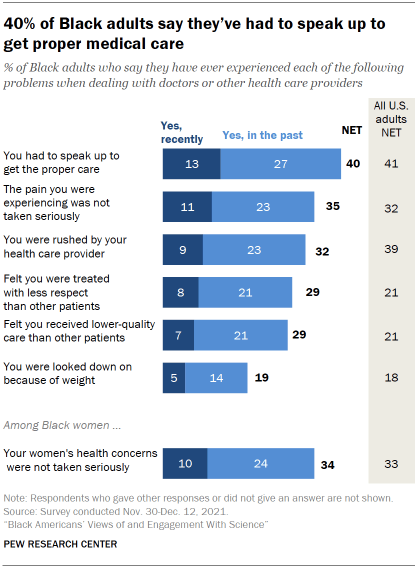
While Black adults generally offer positive ratings of the quality of care they’ve received most recently, a majority (55%) say they’ve had at least one of six negative experiences with doctors or other health care providers at some point in their lives. (A seventh issue asked about applied only to women.)
Overall, 40% of Black adults say they have had to speak up to get the proper care either recently (13%) or in the past (27%). This is the most frequently cited negative experience with medical care across the items included in the survey.
One focus group respondent described their experience this way:
“I had a situation where I had to go through about two different doctors until I was able to get the results that I was requesting, because they did not believe that the issues that I had were valid, or that they were as serious as I made them out to be. It’s kind of been an ongoing thing, so I’m always leery when I’m talking to physicians. I don’t trust them just because they are doctors. I know they have the Hippocratic Oath, but it feels like it’s a little different when they deal with African American patients. And I don’t care if it’s an African American physician or White physicians.” – Black woman, 25-39
When it comes to treatments for pain, 35% of Black adults say they’ve felt the pain they were experiencing was not taken seriously either recently (11%) or in past interactions (23%) with doctors and other health care providers.
About three-in-ten Black adults (32%) say they’ve felt rushed by their health care provider and 29% say they’ve felt they were treated with less respect than other patients, either recently or in past experiences with doctors and other health care providers. Similarly, 29% say they’ve felt they’ve received lower quality medical care at some point; 70% of Black adults say this has not happened to them.
Relatively fewer (19%) say they’ve been looked down on because of their weight or eating habits; 79% say this hasn’t happened to them.
Among Black women, 34% say their women’s health concerns or symptoms were not taken seriously in interactions with doctors and other health care providers.
Black adults at all family income levels are about equally likely to report having at least one of these experiences.
The frequency of negative experiences with the health care system are mostly similar between Black adults and all U.S. adults. However, greater shares of Black adults than all U.S. adults say they’ve felt they’ve received lower-quality care (29% vs. 21% of all U.S. adults) or been treated with less respect than other patients (29% vs. 21%). And fewer Black adults say they were rushed by a health care provider (32% vs. 39% of all U.S. adults).
Black women, especially younger Black women, stand out for the frequency with which they report having had negative health care experiences. Taken together, 63% of Black women say they’ve experienced at least one of the seven negative health care experiences measured in the survey. Among Black men, 46% say they’ve had at least one of six negative experiences with doctors or other health care providers. Black women were asked one more item than men, but the gap between men and women on the six experiences in common is almost identical (62% vs. 46%).
In their own words: Focus group participants on difficulties getting treatment for pain management
There are long-standing concerns about racial biases in pain management. A study in 2020 of emergency room patients experiencing acute appendicitis found wide racial disparities in pain management for both children and adults. The growing use of artificial intelligence algorithms to determine a patient’s need for pain management is raising new questions about how to address systematic bias in pain management treatments.
Here are a few of the comments from focus group participants about getting treatment for pain.
“Well, my husband’s condition (trigeminal neuralgia), it requires a narcotic. And before we got [to current health care provider] for so long, a lot of people just assumed that he was a junkie, like he was just coming in and trying to get pain medication and they wanted to put him on this rotation that just didn’t work, wanted him to take this Tylenol. And it was so frustrating.” – Black woman, age 25-39
“My mom, and I can’t think of it specifically, she has complained to me about being at the hospital and feeling as though they were treating her like she was a drug addict. When they would have to give her pain medication, or she would need something for pain – having her fill out forms, only allotting a certain amount, or cutting it, when her pain is … she goes through pain more times a day, they’ll cut it to less. Less than what she needs to get through the day and not be in pain.” – Black man, age 25-39
“At what point are you going to educate your nurses, your doctors, your ER team that, ‘Hey, this is the protocol when we have sickle cell’? Now, the ironic thing is, when she was going to the children’s hospital, they did have a sickle cell protocol and their treatment of their kids was a little bit different. Most of the time, … 85% of the time … because they were kids, they took their word for it. But when they transitioned over to the adult care, it’s terrible. It’s terrible with the pain, it’s terrible with pain management.” – Black woman, age 40-65
“I was in pain, like in my abdomen. Come to find out I had a fibroid. But I went to the emergency room. ‘Oh, no. You’re fine.’ Something like, ‘Your insurance won’t cover this emergency visit’ or something. ‘Just go to Walgreens and get some Tylenol.’ And I’m like, ’I’m in severe pain. Like I have abdominal pain.’ I ended up going to my doctor, the one I eventually found. He ended up getting me an ultrasound. We did blood work. It was just totally different.” – Black woman, age 25-39
A large majority of younger Black women ages 18 to 49 report negative interactions with health care providers: 71% say they’ve had at least one negative experience in the past. By comparison, a smaller share of Black women ages 50 and older say this (54%).
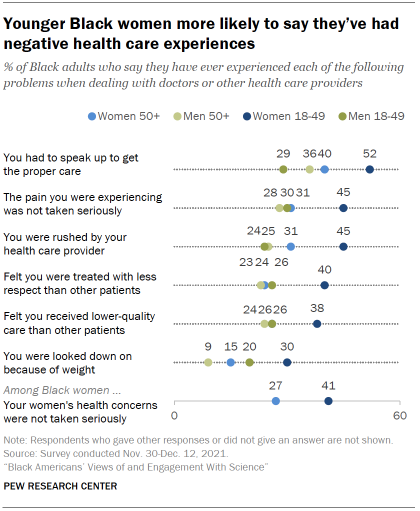
Among Black men, differences by age are more modest than among women, and the pattern runs in the opposite direction: 51% of men ages 50 and older report experiencing at least one of six negative experiences with health care providers, compared with a somewhat smaller share of men ages 18 to 49 (43%).
The experiences of younger Black women stand out across each individual item on health care interactions. For instance, 52% of younger Black women say they’ve had to speak up to get the proper care, compared with 40% of older women, 36% of older men and 29% of younger men.
Among U.S. adults, women ages 18 to 49 are also more likely than older women or than men to say they have had at least one of these negative experiences in a health care visit.
31% of Black adults say they would prefer to see a Black health care provider; a majority have no preference
The share of Black adults working in health-related jobs is roughly equal to their share in the overall workforce, although just 5% of physicians and surgeons are Black. The new survey asked people for their preferences and thoughts about what, if any, difference it makes to have a health care provider who shares their racial background.
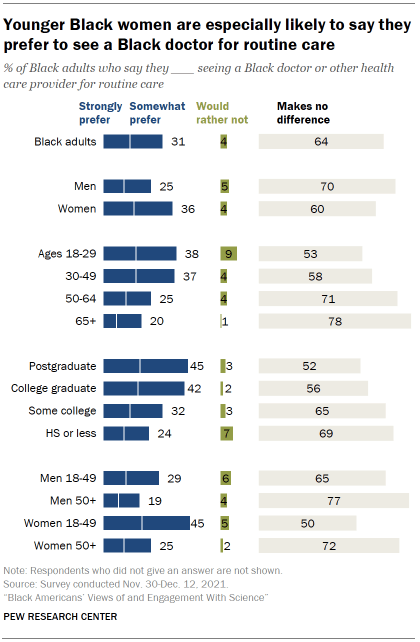
Overall, 31% of Black adults say they would strongly (14%) or somewhat prefer (17%) to see a Black doctor or other health care provider for routine medical care. About two-thirds (64%) say it makes no difference to them, and just 4% say they’d rather not do so for routine care.
Younger Black women stand out from their elders and from Black men in their preferences for seeing a Black health care provider.
Among Black women, a much greater share of those ages 18 to 49 than those 50 and older say they’d prefer to see a Black health care provider for routine care (45% vs. 25%). A majority of older Black women (72%) say it wouldn’t make a difference to them.
There’s a similar pattern in views among Black men, though the gap between younger and older Black men is not as large as among Black women: 29% of Black men ages 18 to 49 would prefer to see a Black health care provider for routine care, compared with 19% of Black men ages 50 and older.
There’s hardly any difference in views on this question between those who have seen a Black doctor or health care provider in the past and those who have not. Among the roughly two-thirds of Black adults who say they’ve seen a Black health care provider for routine care in the past, 32% say they would prefer to see a Black health care provider; among those who have not seen a Black health care provider previously, 30% express this view. See the Appendix for details.
Younger Black women are more likely to see benefits for the quality of medical care from health care treatment with same-race providers
When it comes to key aspects of medical care, majorities of Black adults view a Black doctor and other health care providers as about the same as providers who do not share their race or ethnicity at meeting their needs.

For instance, 72% of Black adults think a Black health care provider is about the same as other health professionals when it comes to the quality of medical care they provide; 21% think a Black health care provider is better than others at this, while just 4% say worse.
Roughly two-thirds view a Black health care provider as about the same as others when it comes to taking their symptoms and concerns seriously, treating them with respect, and looking out for their best interests. Roughly three-in-ten see a Black doctor or health care professional as better than other providers for each of these elements of care.
Among the 31% of Black Americans who say they would prefer to see a Black health care provider for routine matters, majorities think a Black health care provider is better than others at looking out for their best interests (64%), taking their symptoms seriously (64%), treating them with respect (60%) and providing the best quality medical care (53%).
It is unclear whether personal experience lies behind these beliefs. Black adults who have seen a Black health care provider in the past hold similar views on this as those who have not. See Appendix for more details.
Younger Black women are more inclined than older women and men to see an advantage from routine care with a Black health care provider. Still, the majority viewpoint across groups – including among younger Black women – is that a Black health care provider is about the same as others at providing key aspects of care.
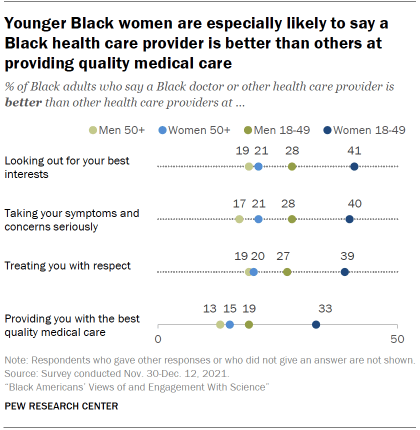
About four-in-ten Black women ages 18 to 49 (41%) say a Black health care provider is better than others at looking out for their best interests, compared with 53% who say they are about the same as other health care providers.
Smaller shares of Black women ages 50 and older (21%), Black men 18 to 49 (28%) and Black men ages 50 and older (19%) view a Black health care provider as better than others at looking out for their best interests. Majorities say they are about the same as others at this.
Age and gender patterns among Black adults are similar across the other aspects of care included in the survey.
When it comes to education, Black adults with higher levels of education tend to be more likely to view a Black doctor or health care provider as better than others when it comes to these key aspects of care. But as with patterns by age and gender, the majority view across levels of educational attainment remains that a Black health care provider is about the same as other healthcare professionals at providing routine health and medical care. See the Appendix for details.


