The analysis in this report is based on telephone interviews conducted March 20-25, 2019 among a national sample of 1,503 adults, 18 years of age or older, living in all 50 U.S. states and the District of Columbia (300 respondents were interviewed on a landline telephone, and 1,203 were interviewed on a cell phone, including 792 who had no landline telephone). The survey was conducted by interviewers under the direction of Abt Associates. A combination of landline and cell phone random-digit-dial samples were used; both samples were provided by Survey Sampling International, LLC. Interviews were conducted in English and Spanish. Respondents in the landline sample were selected by randomly asking for the youngest adult male or female who is now at home. Interviews in the cell sample were conducted with the person who answered the phone, if that person was an adult 18 years of age or older. The weighting procedure corrected for the different sampling rates. For detailed information about our survey methodology, see http://legacy.pewresearch.org/methodology/u-s-survey-research/.
The combined landline and cell phone sample is weighted using an iterative technique that matches gender, age, education, race, Hispanic origin and nativity, and region to parameters from the 2017 Census Bureau’s American Community Survey one-year estimates and population density to parameters from the decennial census. The sample also is weighted to match current patterns of telephone status (landline only, cell phone only, or both landline and cell phone), based on extrapolations from the 2018 National Health Interview Survey. The weighting procedure also accounts for the fact that respondents with both landline and cell phones have a greater probability of being included in the combined sample and adjusts for household size among respondents with a landline phone. The margins of error reported and statistical tests of significance are adjusted to account for the survey’s design effect, a measure of how much efficiency is lost from the weighting procedures.
The following table shows the unweighted sample sizes and the error attributable to sampling that would be expected at the 95% level of confidence for different groups in the survey:
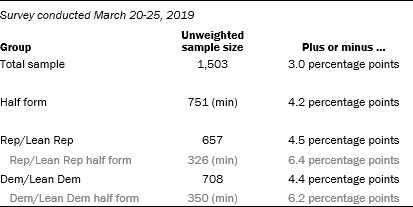
Sample sizes and sampling errors for other subgroups are available upon request.
In addition to sampling error, one should bear in mind that question wording and practical difficulties in conducting surveys can introduce error or bias into the findings of opinion polls.
Pew Research Center undertakes all polling activity, including calls to mobile telephone numbers, in compliance with the Telephone Consumer Protection Act and other applicable laws.
Pew Research Center is a nonprofit, tax-exempt 501(c)(3) organization and a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts, its primary funder.
© Pew Research Center, 2019


