h3>Overviewh3>Overview
The rise of smartphones has brought real-time location data into many aspects of Americans’ lives. Some mobile services use the smartphone’s location to offer directions, targeted recommendations, or other location-specific information to the user. Other services incorporate a location “layer” into other types of functions, while still others exist specifically to share the user’s location with friends or the general public.
To date, our surveys have tracked two types of location-based services: those that use people’s whereabouts to provide location-targeted information such as directions or recommendations, and geosocial services that let users “check in” to certain locations or share their location with friends. However, it is becoming increasingly difficult to delineate these two categories, as social media services incorporate location as an element of user activity and as location-centric services embrace varying degrees of social functionality.
Foursquare, a geosocial service that originally focused on location-sharing and points earned through “checking in” to locations, is now beginning to de-emphasize its system of points, badges, and social location-sharing.[5. numoffset="5" Vindu Goel, “With New App, Foursquare Strives to Be ‘Magic’ in Your Pocket.” New York Times, August 29, 2013.
http://bits.blogs.nytimes.com/2013/08/29/with-new-app-foursquare-strives-to-be-magic-in-your-pocket/] Instead, it is mining its previous check-in data to offer real-time location-triggered suggestions that incorporate friends’ and other users’ activities and recommendations.
On its blog, Foursquare offered examples of the new approach, such as sending a user a note about a “can’t miss dish on the menu” when she arrives at a new restaurant, or suggesting “a few places that your friends love” in a new neighborhood or city.[6. “A smarter Foursquare, so you don’t miss a thing.” Foursquare blog, August 29, 2013.
http://blog.foursquare.com/2013/08/29/a-smarter-foursquare-so-you-dont-miss-a-thing/]
Meanwhile, social media services like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter have added an optional location layer (in many cases built on Foursquare’s API) so that users can show where they are when they post material on the sites. And many information-focused services, from activity-tracking apps to rating sites such as Yelp, incorporate location-sharing and other social aspects as well.
As of May 2013:
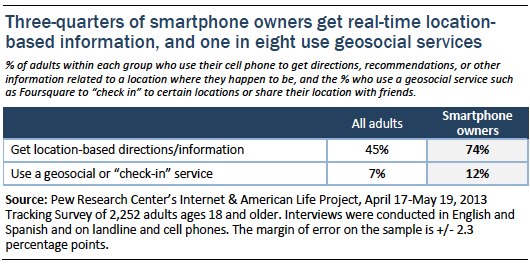
- Some 74% of adult smartphone owners get directions or other information based on their current location. This works out to 45% of all adults.
- Some 12% of smartphone owners use a geosocial service such as Foursquare to “check in” to certain locations or share their location with friends. This works out to 7% of all adults.

Location-based information servicesh3>Overview
The rise of smartphones has brought real-time location data into many aspects of Americans’ lives. Some mobile services use the smartphone’s location to offer directions, targeted recommendations, or other location-specific information to the user. Other services incorporate a location “layer” into other types of functions, while still others exist specifically to share the user’s location with friends or the general public.
To date, our surveys have tracked two types of location-based services: those that use people’s whereabouts to provide location-targeted information such as directions or recommendations, and geosocial services that let users “check in” to certain locations or share their location with friends. However, it is becoming increasingly difficult to delineate these two categories, as social media services incorporate location as an element of user activity and as location-centric services embrace varying degrees of social functionality.
Foursquare, a geosocial service that originally focused on location-sharing and points earned through “checking in” to locations, is now beginning to
de-emphasize its system of points, badges, and social location-sharing.[5. numoffset="5" Vindu Goel, “With New App, Foursquare Strives to Be ‘Magic’ in Your Pocket.” New York Times, August 29, 2013.
http://bits.blogs.nytimes.com/2013/08/29/with-new-app-foursquare-strives-to-be-magic-in-your-pocket/] Instead, it is mining its previous check-in data to offer real-time location-triggered suggestions that incorporate friends’ and other users’ activities and recommendations.
On its blog, Foursquare offered examples of the new approach, such as sending a user a note about a “can’t miss dish on the menu” when she arrives at a new restaurant, or suggesting “a few places that your friends love” in a new neighborhood or city.[6. “A smarter Foursquare, so you don’t miss a thing.” Foursquare blog, August 29, 2013.
http://blog.foursquare.com/2013/08/29/a-smarter-foursquare-so-you-dont-miss-a-thing/]
Meanwhile, social media services like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter have added an optional location layer (in many cases built on Foursquare’s API) so that users can show where they are when they post material on the sites. And many information-focused services, from activity-tracking apps to rating sites such as Yelp, incorporate location-sharing and other social aspects as well.
As of May 2013:
- Some 74% of adult smartphone owners get directions or other information based on their current location. This works out to 45% of all adults.
- Some 12% of smartphone owners use a geosocial service such as Foursquare to “check in” to certain locations or share their location with friends. This works out to 7% of all adults.


Location-based information services
Many web services and apps incorporate a user’s location in order to offer relevant information. For instance, driving directions may rely on the user’s location to offer detailed turn-by-turn directions to another location, or a to-do list app might offer “geo-fenced” alerts, such as reminding the user to buy milk when she is near a grocery store.
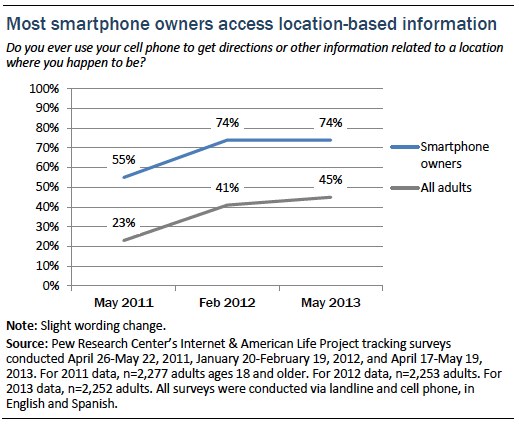
Almost three-quarters (74%) of smartphone owners say they use their phone to get directions or other information related to a location where they happen to be. This percentage has held steady in the past year, but the increasing popularity of smartphones means that among all adults, the proportion who say they access location-based information has risen from 41% in 2012 to 45% in May 2013.[7. Slight change in question wording over time. February 2012 and May 2013 question wording was “Get directions or other information related to a location where you happen to be.” May 2011 question wording was “Get directions, recommendations, or other information related to your present location.”]
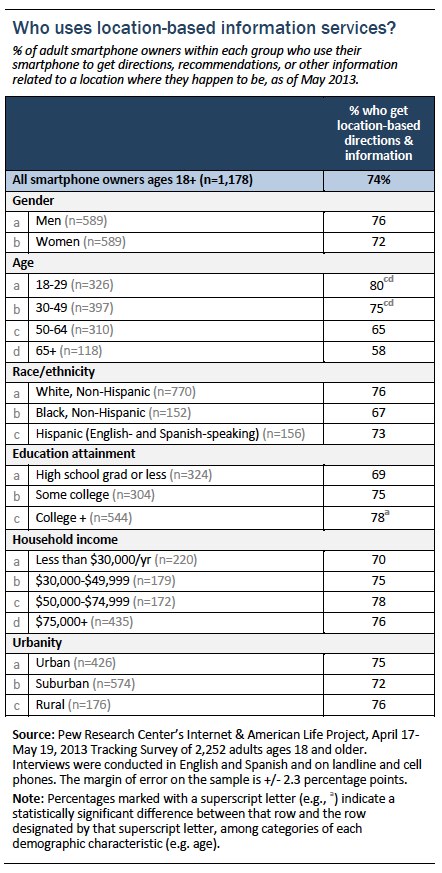
Smartphone users under age 50 are significantly more likely to say they get location-based directions and information than older smartphone users, and college graduates are more likely to do this than adults who only completed high school. There were no statistically significant differences among smartphone owners by gender, race or ethnicity, household income, or community type.
These adoption patterns are generally similar to those we found in early 2012, though
at that time whites were also more likely to use these services than African Americans, and adults in higher-income households were more likely to use these services than those in lower-income households.
The rise of smartphones has brought real-time location data into many aspects of Americans’ lives. Some mobile services use the smartphone’s location to offer directions, targeted recommendations, or other location-specific information to the user. Other services incorporate a location “layer” into other types of functions, while still others exist specifically to share the user’s location with friends or the general public.
To date, our surveys have tracked two types of location-based services: those that use people’s whereabouts to provide location-targeted information such as directions or recommendations, and geosocial services that let users “check in” to certain locations or share their location with friends. However, it is becoming increasingly difficult to delineate these two categories, as social media services incorporate location as an element of user activity and as location-centric services embrace varying degrees of social functionality.
Foursquare, a geosocial service that originally focused on location-sharing and points earned through “checking in” to locations, is now beginning to
de-emphasize its system of points, badges, and social location-sharing.[5. numoffset="5" Vindu Goel, “With New App, Foursquare Strives to Be ‘Magic’ in Your Pocket.” New York Times, August 29, 2013.
http://bits.blogs.nytimes.com/2013/08/29/with-new-app-foursquare-strives-to-be-magic-in-your-pocket/] Instead, it is mining its previous check-in data to offer real-time location-triggered suggestions that incorporate friends’ and other users’ activities and recommendations.
On its blog, Foursquare offered examples of the new approach, such as sending a user a note about a “can’t miss dish on the menu” when she arrives at a new restaurant, or suggesting “a few places that your friends love” in a new neighborhood or city.[6. “A smarter Foursquare, so you don’t miss a thing.” Foursquare blog, August 29, 2013.
http://blog.foursquare.com/2013/08/29/a-smarter-foursquare-so-you-dont-miss-a-thing/]
Meanwhile, social media services like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter have added an optional location layer (in many cases built on Foursquare’s API) so that users can show where they are when they post material on the sites. And many information-focused services, from activity-tracking apps to rating sites such as Yelp, incorporate location-sharing and other social aspects as well.
As of May 2013:
- Some 74% of adult smartphone owners get directions or other information based on their current location. This works out to 45% of all adults.
- Some 12% of smartphone owners use a geosocial service such as Foursquare to “check in” to certain locations or share their location with friends. This works out to 7% of all adults.


Location-based information services
Many web services and apps incorporate a user’s location in order to offer relevant information. For instance, driving directions may rely on the user’s location to offer detailed turn-by-turn directions to another location, or a to-do list app might offer “geo-fenced” alerts, such as reminding the user to buy milk when she is near a grocery store.
Almost three-quarters (74%) of smartphone owners say they use their phone to get directions or other information related to a location where they happen to be. This percentage has held steady in the past year, but the increasing popularity of smartphones means that among all adults, the proportion who say they access location-based information has risen from 41% in 2012 to 45% in May 2013.[7. Slight change in question wording over time. February 2012 and May 2013 question wording was “Get directions or other information related to a location where you happen to be.” May 2011 question wording was “Get directions, recommendations, or other information related to your present location.”]

Smartphone users under age 50 are significantly more likely to say they get location-based directions and information than older smartphone users, and college graduates are more likely to do this than adults who only completed high school. There were no statistically significant differences among smartphone owners by gender, race or ethnicity, household income, or community type.
These adoption patterns are generally similar to those we found in early 2012, though
at that time whites were also more likely to use these services than African Americans, and adults in higher-income households were more likely to use these services than those in lower-income households.

Geosocial services
As of May 2013, 12% of smartphone owners use geosocial services such as Foursquare to “check in” to a certain location or share their location with friends. This is down from 18% of smartphone owners in February 2012. For all adults, this represents a change from 10% in 2012 to 7% in 2013.[8. Slight change in question wording over time. February 2012 and May 2013 question wording was: “Use a service such as Foursquare or Gowalla to 'check in' to certain locations or to share your location with your friends.” May 2011 question wording was: “Use a service such as Foursquare or Gowalla to “check in” to certain locations or share your location with friends.”]
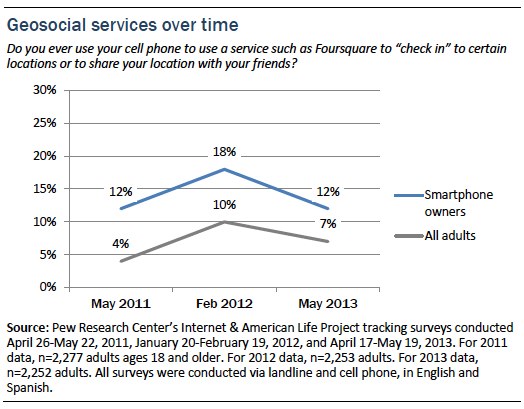
There are few clear differences in geosocial use between demographic groups, though Hispanic smartphone users are significantly more likely to use geosocial services than whites or blacks, and suburban adults are more likely to use these services than rural adults.
Finally, there were no statistically significant differences in geosocial service use among smartphone owners by gender or educational attainment.
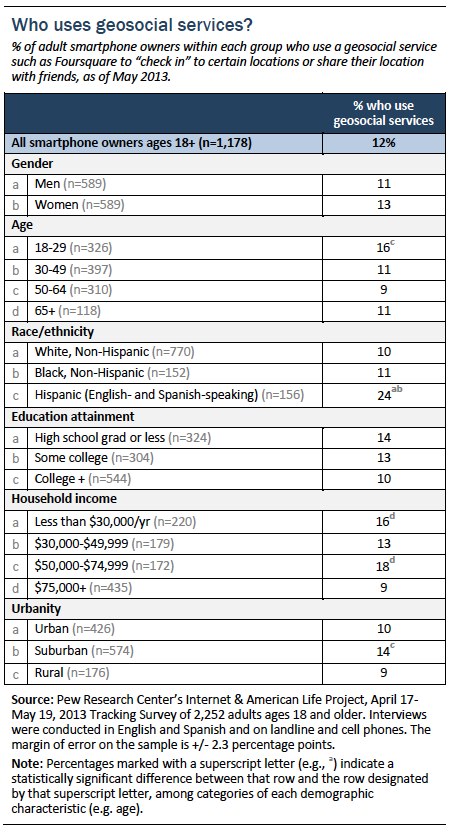
Which geosocial services people use
For the first time, we also asked users of geosocial or “check-in” services which location services they use. We found that a plurality of geosocial users (39%) say they use Facebook, while almost one in five (18%) say they use Foursquare, and 14% say they use Google Plus; several other services were mentioned as well, such as Instagram and Yelp.
Location Tagging Among Social Media Usersh3>Overview
The rise of smartphones has brought real-time location data into many aspects of Americans’ lives. Some mobile services use the smartphone’s location to offer directions, targeted recommendations, or other location-specific information to the user. Other services incorporate a location “layer” into other types of functions, while still others exist specifically to share the user’s location with friends or the general public.
To date, our surveys have tracked two types of location-based services: those that use people’s whereabouts to provide location-targeted information such as directions or recommendations, and geosocial services that let users “check in” to certain locations or share their location with friends. However, it is becoming increasingly difficult to delineate these two categories, as social media services incorporate location as an element of user activity and as location-centric services embrace varying degrees of social functionality.
Foursquare, a geosocial service that originally focused on location-sharing and points earned through “checking in” to locations, is now beginning to
de-emphasize its system of points, badges, and social location-sharing.[5. numoffset="5" Vindu Goel, “With New App, Foursquare Strives to Be ‘Magic’ in Your Pocket.” New York Times, August 29, 2013.
http://bits.blogs.nytimes.com/2013/08/29/with-new-app-foursquare-strives-to-be-magic-in-your-pocket/] Instead, it is mining its previous check-in data to offer real-time location-triggered suggestions that incorporate friends’ and other users’ activities and recommendations.
On its blog, Foursquare offered examples of the new approach, such as sending a user a note about a “can’t miss dish on the menu” when she arrives at a new restaurant, or suggesting “a few places that your friends love” in a new neighborhood or city.[6. “A smarter Foursquare, so you don’t miss a thing.” Foursquare blog, August 29, 2013.
http://blog.foursquare.com/2013/08/29/a-smarter-foursquare-so-you-dont-miss-a-thing/]
Meanwhile, social media services like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter have added an optional location layer (in many cases built on Foursquare’s API) so that users can show where they are when they post material on the sites. And many information-focused services, from activity-tracking apps to rating sites such as Yelp, incorporate location-sharing and other social aspects as well.
As of May 2013:
- Some 74% of adult smartphone owners get directions or other information based on their current location. This works out to 45% of all adults.
- Some 12% of smartphone owners use a geosocial service such as Foursquare to “check in” to certain locations or share their location with friends. This works out to 7% of all adults.


Location-based information services
Many web services and apps incorporate a user’s location in order to offer relevant information. For instance, driving directions may rely on the user’s location to offer detailed turn-by-turn directions to another location, or a to-do list app might offer “geo-fenced” alerts, such as reminding the user to buy milk when she is near a grocery store.
Almost three-quarters (74%) of smartphone owners say they use their phone to get directions or other information related to a location where they happen to be. This percentage has held steady in the past year, but the increasing popularity of smartphones means that among all adults, the proportion who say they access location-based information has risen from 41% in 2012 to 45% in May 2013.[7. Slight change in question wording over time. February 2012 and May 2013 question wording was “Get directions or other information related to a location where you happen to be.” May 2011 question wording was “Get directions, recommendations, or other information related to your present location.”]

Smartphone users under age 50 are significantly more likely to say they get location-based directions and information than older smartphone users, and college graduates are more likely to do this than adults who only completed high school. There were no statistically significant differences among smartphone owners by gender, race or ethnicity, household income, or community type.
These adoption patterns are generally similar to those we found in early 2012, though
at that time whites were also more likely to use these services than African Americans, and adults in higher-income households were more likely to use these services than those in lower-income households.

Geosocial services
As of May 2013, 12% of smartphone owners use geosocial services such as Foursquare to “check in” to a certain location or share their location with friends. This is down from 18% of smartphone owners in February 2012. For all adults, this represents a change from 10% in 2012 to 7% in 2013.[8. Slight change in question wording over time. February 2012 and May 2013 question wording was: “Use a service such as Foursquare or Gowalla to 'check in' to certain locations or to share your location with your friends.” May 2011 question wording was: “Use a service such as Foursquare or Gowalla to “check in” to certain locations or share your location with friends.”]

There are few clear differences in geosocial use between demographic groups, though Hispanic smartphone users are significantly more likely to use geosocial services than whites or blacks, and suburban adults are more likely to use these services than rural adults.
Finally, there were no statistically significant differences in geosocial service use among smartphone owners by gender or educational attainment.

Which geosocial services people use
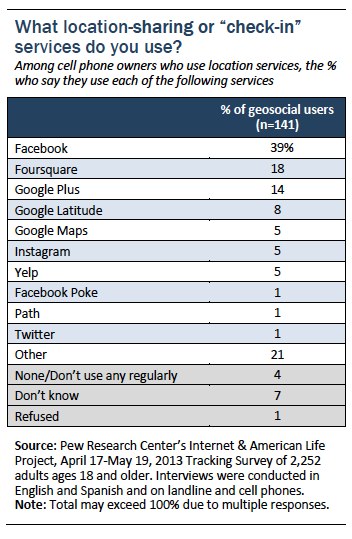
For the first time, we also asked users of geosocial or “check-in” services which location services they use. We found that a plurality of geosocial users (39%) say they use Facebook, while almost one in five (18%) say they use Foursquare, and 14% say they use Google Plus; several other services were mentioned as well, such as Instagram and Yelp.

Location Tagging Among Social Media Users
Adult social media users and location tagging
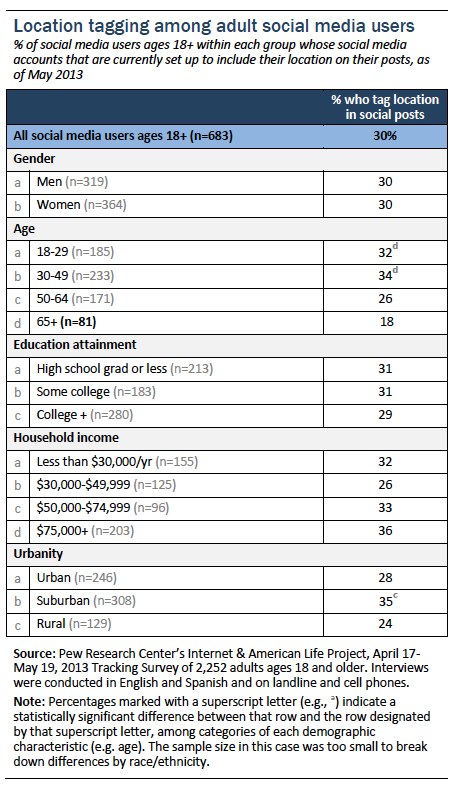
Many social media sites enable users to set up the service to automatically “tag” their updates on the site with the user’s current location. Our May 2013 survey found that 30% of adult social media users say that at least one of their accounts is currently set up to include their location in their posts,
up from 14% who had ever done this in 2011.[9. numoffset="9" Change in question wording over time. May 2013 question wording was: “Thinking about how you use social networking sites... are any of your social networking accounts currently set up so that they include your location on your posts?” February 2012 question wording was: “Thinking about the ways people might use social networking sites... Do you ever set up your account so that it automatically includes your location on your posts?” In May 2011, question was asked as an item in a list question with the following question wording: “Thinking about the ways people might use social networking sites... Do you ever... Set up your account so that it automatically includes your location on your posts?”]
Social media users under age 50 are the age group most likely to tag their location on social networking sites, and those living in suburban areas are more likely to say they do this than those living in rural areas. Among social media users, there were no significant differences by gender, education level, or household income.
The demographics of social media users with automatic location-tagging have changed since we last asked about this activity in May 2011.
At that time, we found that men, African Americans and Hispanics, adults in households earning less than $30,000 per year, and those who have not gone to college were significantly more likely than other social media users to use automatic location-tagging, and there were no significant differences between different age groups.[10. More: “28% of American adults use mobile and social location-based services” (2011):
https://legacy.pewresearch.org/internet/Reports/2011/Location.aspx]
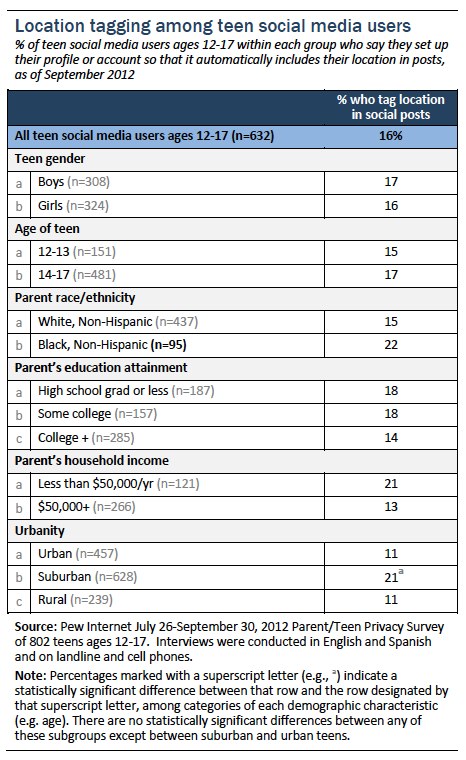
Teen social media users and location tagging
Previous surveys have also asked teens ages 12-17 about their social media practices, including location tagging. Our recent report on how teens share personal information and manage privacy settings on social media, “
Teens, Social Media, and Privacy,” found that 16% of teen social media users said they set up their profile or account so that it automatically includes their location in posts.[11. “Teens, Social Media, and Privacy” (2013):
https://legacy.pewresearch.org/internet/Reports/2013/Teens-Social-Media-And-Privacy.aspx]
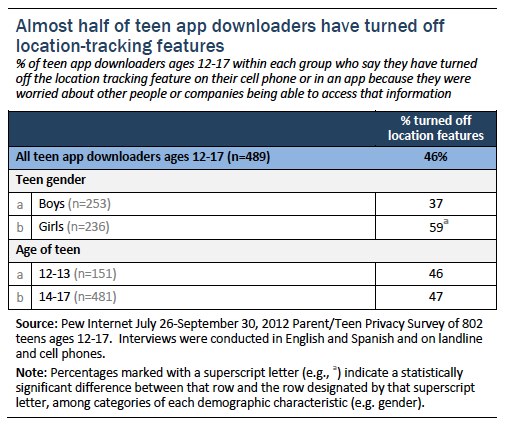
Boys and girls and teens of all ages and socioeconomic backgrounds are equally likely to say that they have set up their profile to include their location when they post. However, teen social media users living in suburban areas are significantly more likely to say they tag their location on social networking sites than teens living in rural or urban areas, as shown in the chart below.
Focus group data
suggests that many teens find sharing their location unnecessary and unsafe, while others appreciate the opportunity to signal their location to friends and parents.
Turning Off Location-Tracking Features