Below are specific findings about news media attitudes and habits in Germany. The findings come from a Pew Research Center survey about news media and politics across eight Western European countries conducted from Oct. 30 to Dec. 20, 2017. The survey covered five countries in the north (Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands, Sweden and the United Kingdom) and three in the south (France, Italy and Spain).
CORRECTION: This fact sheet was updated on May 22, 2018, due to the possibility that the language used to identify the German news outlet Die Tageszeitung may have confused respondents. References to that outlet have been removed throughout. There were no substantive changes to the report’s conclusions.
Views of the news media in Germany
The sense of importance of and trust in the news media vary considerably by country. In general, adults in northern European countries – for example, Sweden and Germany – are more likely to say the news media are very important and that they trust the news media, while people in France and Italy are the least likely to say this.
A majority of German adults (61%) consider the news media very important to society. Similarly, around two-thirds (64%) say they trust the news media. This includes one-in-five who trust the news media a lot.

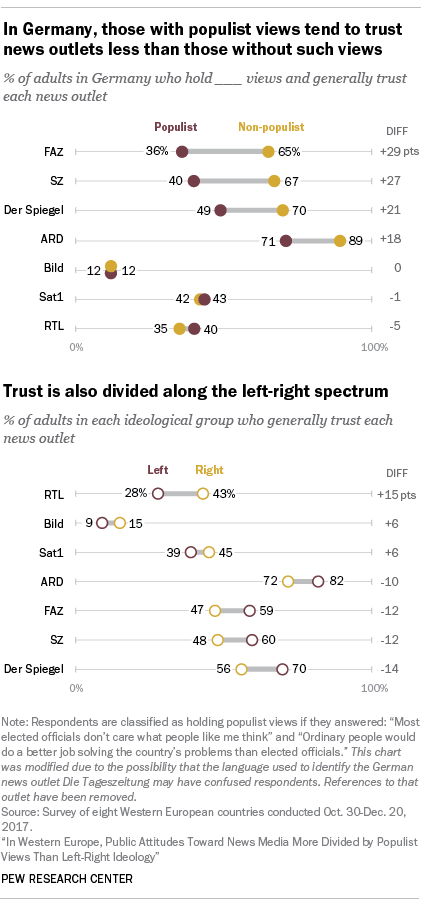
In most of the countries surveyed, people who hold populist views are less likely to say the news media are important and to trust the news media than people who don’t hold populist views. In general, the differences in these attitudes about the news media are small when comparing between people on the left and right of the ideological spectrum.
Populist divides in media attitudes are strong in Germany as well: 47% of people with populist views say they trust the news media, compared with 78% of those without populist views. On the question of importance, 51% of those with populist views say the news media are very important for society in Germany, compared with 75% of those with non-populist views.

Main sources used for news in Germany
When it comes to the news sources people say they turn to most frequently, the divides between adults with and without populist leanings are not as strong as those seen for attitudes about the news media more generally. And in the southern countries, there tend to be larger divides in main news source preference between people on the left and right of the ideological spectrum than between those with and without populist views.
In Germany, those on the left and the right do not differ in regard to the media source they turn to most for news. Both those on the ideological right and left cite ARD as their main news source.

Where users place outlets’ ideologies, on the right and on the left
For many of the news outlets across the eight countries, people who use an outlet to get news tend to think the outlet is closer to their own left-right ideological position. In Germany, this is true for one outlet asked about: the public broadcaster ARD. For this outlet, news users on the right tend to place it closer to their own ideology. For three news outlets – RTL, Sat1 and Der Spiegel – right-aligned and left-aligned news users generally agree on their placement. The tabloid newspaper Bild and the newspapers Süddeutsche Zeitung (SZ) and Frankfurter Allgemeine Zeitung (FAZ) are not included in this analysis, because they did not have a large enough sample of left or right users to analyze.1

In general, where the public places an outlet tends to differ from where the average audience actually sits ideologically. For each of the news outlets asked about in the survey, the average audience (based on self-reported usage) tends to fall near the ideological center. People who have heard of each outlet, however, tend to place the outlet either farther to the left or farther to the right than the actual ideological position of the outlet’s audience.
Germany is an exception. Not only are most German outlets’ news audiences near the center, but people who have heard of the outlets also tend to place them near the middle of the left-right spectrum.

Trust in news media outlets
In seven of the eight countries surveyed, the most trusted news outlet asked about is the public news organization in each country. In Germany, eight-in-ten say they trust the public news organization ARD.

As with trust in the news media generally, trust in specific outlets varies by populist leanings, with those who hold populist views expressing lower levels of trust than those who don’t.
In Germany, for example, those with populist leanings are 29 percentage points less likely than those with non-populist views to say they trust FAZ. Trust is also divided along the left-right ideological spectrum in Germany – those who place themselves on the left of the 0-to-6 ideological scale are 15 percentage points less likely than people on the right to trust RTL.
Social media usage and views
Many people in Western Europe get news through social media, with Facebook cited as the most widely used platform for news.
Among German adults, 41% get news on social media, including around a quarter (26%) who get news on social media daily. Facebook is the most common social network used for news. In Germany, young people (those 18 to 29 years old) are more likely to get news on social media daily than those 50 and older (50% vs. 11%).

About half or more social media news consumers in each of the eight countries surveyed say they are familiar with the sources they see on social media. Still, sizeable minorities say they typically do not pay attention to the source of the news they encounter there.
Social media news consumers in Germany are similar to other Western Europeans – 56% are familiar with the news sources they find on social media, but a quarter do not pay attention to the sources there.

Find out more
Read the methodology and full report for more on Germany and the other seven Western European countries included in the survey. For global data on media habits and attitudes see the report “Publics Globally Want Unbiased News Coverage, but Are Divided on Whether Their News Media Deliver.”