Focus group findings from France, Germany and the United Kingdom
Pew Research Center has been conducting quantitative research on views of international cooperation, the United States and China over the past two decades. We held 12 focus groups from Nov. 8 to Nov. 18, 2022, in the capital cities of France (Paris), Germany (Berlin) and the United Kingdom (London), with four groups per country. Groups were organized by ideological affiliation – left or right – and views toward their own country’s involvement in world affairs – “internationally engaged” or “domestically focused”. See the Methodology for more information.
Focus groups were also held in the U.S. (Arlington, Virginia) in December 2022. For findings from discussions with young people in all four countries on international engagement and multilateralism, see “How Young Adults Want Their Country To Engage With the World.”
The conversations among group participants were video recorded, transcribed and translated. The final data sent to Pew Research Center was anonymized. The Center analyzed the transcripts (in English) for key themes. Our analysis is not a fact check of participants’ views.
While we do highlight sentiments expressed by individual participants in the report, they are meant to be representative of the themes discussed in the group more broadly. Nonetheless, quotations are not necessarily representative of the majority opinion in any particular group or country. Quotations may have been edited for grammar, spelling and clarity.
Young people ages 18 to 29 in British, French and German focus groups have few positive things to say about the United States or China as major players on the world stage. The U.S. is seen as the “world’s policeman” with a self-interested history of interventionism that is disappointing to Western allies, while China is labeled the “world’s factory,” respected for its economic dominance but strongly criticized for its expansionism and record of human rights violations.
“China is stronger in industry; the U.S. is stronger militarily.”
Man, France, 27
In November 2022, Pew Research Center conducted focus group sessions among four distinct ideological groups in the capital cities of France, Germany and the United Kingdom. The groups, which were convened to better understand how young people want their countries to engage with the world, revealed a series of nuanced and conflicting opinions about international engagement, the nature of that engagement, history and foreign policy priorities. But, when groups were asked to discuss the roles the U.S. and China play in global affairs and the international impact of their actions, the young participants expressed strong critiques of both major powers, regardless of country or ideological group.

China has received increasingly negative ratings in Pew Research Center surveys in Europe over the past few years, and the focus groups shed light on the deep concerns young people have about Beijing’s human rights record, China’s growing economic might and its policies in Taiwan, Hong Kong and elsewhere. Focus group participants are largely pessimistic about future relations with China. But there is also a strong sense of pragmatism among these young adults who have largely resigned themselves to China’s economic power and see few, if any, ways to disentangle relations with China without collapsing their own economies.
America’s image in Europe has, in contrast, improved markedly in recent years, following the election of President Joe Biden. He is much more popular than his predecessor, former President Donald Trump, and Biden’s more multilateralist approach to foreign policy is welcomed by most Europeans. And on a variety of survey questions we’ve asked in Europe over time – such as questions about human rights and which country should be the world’s leading power – the U.S. gets significantly higher marks than China.
Related: How Young Adults Want Their Country To Engage With the World
However, the focus groups reveal ongoing concerns about the way America has used its power in world affairs, often discussing U.S. actions abroad as a point of comparison with their own countries. Focus group participants echo a criticism of the U.S. we’ve regularly seen in our surveys: Most believe the U.S. does not take allies’ interests into account when making foreign policy decisions. And participants are especially critical of U.S. military interventions, such as Iraq and Afghanistan. Again, echoing themes from survey research, some participants also express concerns about the state of American politics and society. Many suggest the U.S. has been hypocritical in the past, arguing for human rights and democracy abroad without fixing its problems at home.
Regardless of these criticisms, however, young Europeans want to engage and cooperate with the U.S., and they remain cautiously optimistic about the future of trans-Atlantic relations because the U.S. and Europe share fundamental democratic values. And, in many ways, the criticisms they levy against the U.S. are similar to ones that people – especially those on the left – have of their own government, too.
Young Europeans do not approve of the United States’ role as the “world’s policeman”
Though surveys find that majorities in France, Germany and the UK have favorable views of the U.S., America’s role on the world stage is described in mostly negative terms by the focus group participants. Across all three countries and four ideological groupings, young Europeans are steadfast in the opinion that the U.S. acts as the world’s policeman to the detriment of the world community. One young Briton said clearly, “I think on balance, [they] probably hurt more than they help.”
One French man said, “They’ve started wars that were completely illegal, against the opinion of the UN even, without any mandate.” A German woman added that the U.S. generally “finds themselves too great” and “interferes wherever they want, just because of their military power.” For his part, one young man in Germany noted that “a lot is swept under the carpet. They’ve got their fingers everywhere in the world. It’s not so clean.”

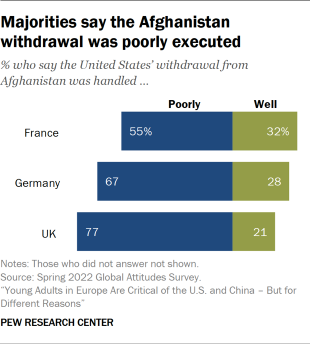
The United States’ actions in Iraq and Afghanistan, and its consequent withdrawal, were often pointed to as examples of this behavior. Majorities in each country considered the U.S. withdrawal poorly executed, according to Spring 2022 data from the Center, and the young people in the focus groups described both the withdrawal and the entire 20-year U.S. history in the country in forceful terms. One Briton framed it as “short-term help, long-term hurt.” Another French man said, “We saw with Iraq, they came in and left the country in ruins.” And a German man called the decision to withdraw from Afghanistan “a huge failure of a [20]-year long project. They just went away and the country was taken overnight.”
There was some reflection on the fact that each of these countries played their own role in Iraq and Afghanistan and have their own histories of military intervention. Still, the sense is that the charge was led by the U.S., as exemplified by a young Briton who said, in reference to his country’s presence in Iraq, “I think we can get influenced by larger countries, that we’re supposedly allies with, into conflicts that we shouldn’t really have involvement with.” Across the board, young people want to avoid military interventions, even among those eager for their countries to engage on the world stage. A young German woman questioned the extent to which intervening is beneficial, even “in countries where terrorism is high.”
Still, a few French individuals did highlight some of the potential benefits of American interventionism, focusing more on America as a strong power that can take forceful action. For example, noting U.S. support for Taiwan’s security, one French man said, “I think the only time the U.S. did well to intervene was regarding Taiwan … I think that if the U.S. hadn’t shown their support, Taiwan would have been part of China by now.” And one French woman shared respect for the idea of an “America first” policy,” suggesting it “is something France should do and be more strategic about.”

Disapproval of American interventionism among the focus group participants is tied clearly to their sense that U.S. actions abroad are self-interested. Center surveys have long found that people do not think the U.S. takes other countries’ interests into account when making foreign policy decisions; this theme was on full display in the focus groups. One German woman said she has “the impression that the U.S. doesn’t cooperate with anybody.” A French woman added that American interventions “aren’t in cooperation, it’s just themselves” and a Briton called it “just a power thing.”
Critiques of U.S. interventionism are particularly strong among internationally engaged Europeans who called out hypocrisy in the United States’ practice of addressing issues around the world while failing to tackle social inequities at home. In recent years, Center surveys have shown that people from these countries do not see the U.S. as a positive actor or example on climate, health care or civil rights. Take, for example, a French woman who called the U.S. a bad example for “human rights, in general.” When asked why, she said “they’ve gone back on abortion rights.” Others called out the United States’ lack of climate action, high rates of gun violence, inequitable health care system or even the fact that schools in poor areas get less funding.

The focus groups’ discussions led to a common conclusion: Young people are eager to see their countries maintain a strong, more independent presence on the world stage without relying on policy cues from the U.S. When describing his wishes for the UK, one Briton said, “I guess it’s not being like America and trying to save everyone, but offering help to people in need and communicating, sharing intelligence and collaborating on things that are world issues, whether that’s climate change or something else.” For her part, a young German woman called cooperation with the U.S. “sometimes useless, except for defining how we definitely don’t want to act.”
Still, most in these countries see the U.S. as at least a somewhat reliable and important partner to their country. And while there is a desire to disentangle their policies and reputations from the U.S., young people maintain the expectation of some trans-Atlantic partnership. One German suggested that “in foreign policy, we should keep a healthy closeness to them, because they have a lot of influence in the whole world.” Similarly, though few like the way the U.S. has utilized its military strength, there is a shared sense that it is “the most powerful” and is important to have as an ally. A young German internationalist called it “quite useful” to have “the biggest military force … within the Western community.”
One pain point in relations with the U.S. that came up in each country was leadership. Confidence in the U.S. president reached historic or near historic lows in Center surveys during Trump’s four-year term. In focus groups, one Briton said he thought it was a joke “when the U.S. elected Trump.” A French man cited Trump’s presidency as reasoning for France to have a strong presence on the world stage saying they “would suffer the consequences of the choices of other powers, such as the U.S., as we saw with Donald Trump, we had a lot of difficulty dealing with him, even though his decisions had a direct impact on Europe.”
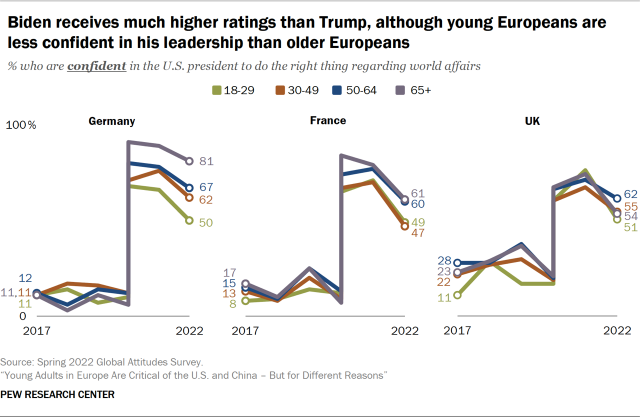
And, while confidence in the U.S. president jumped dramatically when Biden took office in 2021, it has since tempered, especially among young people. In Germany and France, those ages 18 to 29 are much less likely than those 50 or older to be confident in Biden’s leadership. While young adults are at least 30 percentage points more confident in Biden than they were in Trump in 2020, when the groups mentioned Biden, they often qualified their generally warm feelings with disappointment, with some suggesting he has done little to counteract Trump’s course. As one French respondent shared that, at this point, “I don’t even think U.S. policy changes that much when leaders change. It’s more the approach that changes but Biden won’t necessarily shift every policy.”
Young Europeans concerned by China’s power as the “world’s factory”

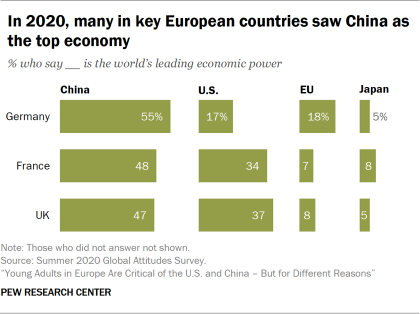
Whereas focus group participants heavily focused on the United States’ role as “the world’s policeman,” they discussed China more often as “the world’s factory.” This is driven by both its dominance in manufacturing and exporting goods as well as its investment and infrastructure building around the world. When surveyed, pluralities in Germany, France and the UK called China the world’s leading economic power over the U.S., European Union and Japan. Put simply, one French woman said, “Everything is Chinese.” Another Briton referenced China as “producers of technology and clothes” saying that “they have these giant industrial cities where they churn stuff out at a rate and price which other countries basically see as a deal that’s too good to refuse.” Technology emerged as a common thread in discussions about China’s production power, and multiple participants mentioned the role China plays in the manufacturing of technology products from American and European companies such as Apple and Nokia.
Young Europeans are also wary of China’s investment around the world. A German man said he “finds it extremely dangerous that they try to buy or build up infrastructure in every country. In Africa they are building roads, in Greece they have bought harbors and have agreed to assume Greece’s debts. And they have also tried to buy harbors in Germany.” This sort of lending was also an issue for a French woman who noted that “because they have money, they allow long loans in exchange for ports or infrastructure,” continuing that “there’s nothing fair and honorable in the way the government is managed.”
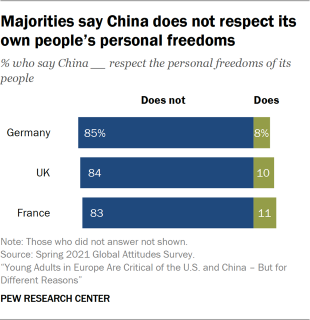
Underpinning the wariness of China’s economic dominance are severe critiques of the country on two fronts: domestic human rights abuses and military action in the South China Sea. In a 2021 survey, more than eight-in-ten Germans, Britons and French say China does not respect the personal freedoms of its people. This view was espoused by one young British woman who said, “What they do to Muslim people there, concentration camps and invading Hong Kong … I think they’re great in terms of commodities but crap in terms of human rights.” In a similar vein, a French man said he thinks of China as “a dictatorship, which carried out a genocide on its own soil.”
The same man noted that China “wants to invade Taiwan …, contests the statue of Hong Kong [and] Macau” and that “it doesn’t have any legitimacy to intervene.” Unlike the U.S., China’s military was rarely mentioned. When participants did bring up the Chinese military, it was often in reference to Taiwan. A British man shared his view, saying that in “situations sort of like China and Taiwan, everyone’s too afraid to get involved … and Taiwan is this tiny little piece of land where China is doing ballistic missile tests every week now just to show their strength.”
There is agreement that these actions are bad but many young participants, particularly those on the ideological left, are clear that their own countries and the U.S. are not above the same criticisms. A French man said “we blame them for things we do ourselves, we blame [them] for their aggression towards certain countries, which is true, but we are also very aggressive, we wage war to many countries in the West more generally.”

When asked to look toward the future and consider their countries’ ongoing relationships with China, the young focus group participants acknowledge the struggle of balancing China’s human rights track record with their economic power. In fact, when asked to choose between promoting human rights in China regardless of economic consequence and prioritizing economic relations over addressing human rights issues in a recent survey, majorities in each of these countries chose the former. Some are optimistic that their country could, to some degree, achieve this through multilateralism and strengthening economic ties with other major actors, like the U.S. A French man noted that “facing against China could be complicated,” suggesting that his country “could get closer to key institutions, the EU for example, to try to have more power, among others, to try and change the balance a bit, because France alone wouldn’t have much impact against … the force of the Chinese economy.”
More commonly, participants feel that some morally driven stand against China would be nice, but when asked to describe how that would happen, they acknowledge that untying their countries and themselves from China economically is not a pragmatic goal. Put simply by a young British man: “It’s quite easy to point fingers but once again, what would we actually do without them?” Another Briton called the price of material goods coming from China “a deal that’s too good to refuse.” A German man posited that “if [China] were to sanction, then the German economy would crash from one day to the next and also many other countries, because a lot comes from China.” In that vein, some level of cooperation with China seems to be just as inevitable as partnership with the U.S. to young Europeans.


